Abstract
The presence of a low-level, capping inversion layer will affect the height and structure of the planetary boundary layer (PBL). Results from models of varying levels of sophistication, including analytical, turbulent kinetic energy (TKE), second-order closure (SOC), large-eddy simulation (LES) and direct numerical simulation (DNS) models, are used to investigate this influence for the neutral, barotropic PBL. Predicted and observed profiles of stress and geostrophic departure components, and integral measures, such as the parameters of Rossby-number similarity theory, are compared for the KONTUR, Marine Stratocumulus, JASIN, Leipzig, Pre-Wangara and Upavon field experiments.
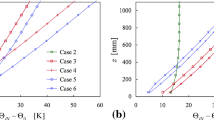
Analytical models of the equilibrium value of inversion height zi, which depend on the surface friction velocity u*, and both the Coriolis parameter f and the free-flow Brunt-Väisälä frequency N, are found to give reasonable estimates of the PBL height. They also indicate that only the KONTUR and Marine Stratocumulus experiments were strongly influenced by N. More quantitative comparisons would require larger, more comprehensive datasets. The effects of the presence of a capping inversion on the profile structure were found to be insignificant for h* = |f|zi/u* > 0.15.
The simple analytical model performed quite well over all values of h*; it predicted the profiles of the longitudinal stress component (in the direction of the surface stress) better than the lateral component. The more advanced models performed well for small values of h* (for flow over the sea), but systematically underestimated the cross-isobaric angle for flow over land. These models predicted the profiles of the lateral stress component better than the longitudinal component. The profiles of the analytical model agreed with those of the advanced models when the constant eddy viscosity of the outer layer was increased.Agreement with DNS was achieved by increasing the eddyviscosity of the analytical model by a factor of 5.
Zilitinkevich and Esau(2002, Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 104, 371–379)suggest that the neutral, barotropic values of A and B of Rossby-numbersimilarity theory are not universal constants, but depend on the ratio N/|f|. The dependence for A and B is calculated using the analytical model and TKE models. Over the sea (h* ≅ 0.1; N/|f| ∼ 100, where we have used the Zilitinkevich-Esau relation to convert between h* and N/|f|) there is agreement between the model predictions and observations; however over land where the equilibrium boundary-layer height is greater (h* ≅ 0.35; N/|f| ∼ 10) the inconsistency between the advanced model predictions (TKE, SOC, LES, and DNS) and observations, as noted previously by Hess and Garratt, still exists. We attribute this disagreement to violations of the strict assumptions of steady, horizontally homogeneous, neutral, barotropic conditions implicit in the observations. At small values of zi and a strongly stable background stratification (h* ≅ 0.04; N/|f| ∼ 1000) both the TKE and analytical models predict that A and B depend significantly on h*, however observations are unavailable to confirm these predictions. Zilitinkevich and Esau call this case the `long-lived near-neutral PBL', and state that it is found in cold weather at high latitudes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andren, A. and Moeng, C.-H.: 1993, 'Single-Point Closures in a Neutrally Stratified Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 50, 3366–3379.
Andren, A., Brown, A. R., Graf, J., Mason, P. J., Moeng, C.-H., Nieuwstadt, F. T. M., and Schumann, U.: 1994, 'Large-Eddy Simluation of a Neutrally Stratified Boundary Layer: A Comparison of Four Computer Codes', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 120, 1457–1484.
Arya, S. P. S.: 1974, 'Comments on “Similarity Theory for the Planetary Boundary Layer of Time-Dependent Height”', J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 839–840.
Arya, S. P. S.: 1978, 'Comparative Effects of Stability, Baroclinity and the Scale-Height Ratio on Drag Laws for the Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 40–46.
Arya, S. P.: 2001, Introduction to Micrometeorology, Second Edition, Academic Press, San Diego, 450 pp.
Blackadar, A. K.: 1965, 'A Simplified Two-Layer Model of the Baroclinic Neutral Atmospheric Boundary Layer', in Flux of Heat and Momentum in the Planetary Boundary Layer of the Atmosphere, AFCRL-65-531, Department of Meteorology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, pp. 49–65.
Blackadar, A. K.: 1974, 'Implications of a Simple Two-Layer Model of the Diabatic Planetary Boundary Layer', Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 10, 663–664.
Blackadar, A. K. and Tennekes, H.: 1968, 'Asymptotic Similarity in Neutral Barotropic Planetary Boundary Layers, J. Atmos. Sci. 25, 1015–1022.
Brost, R. A. and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1978, 'A Model Study of the Stably Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 1427–1440.
Brost, R. A., Lenschow, D. H., and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1982a, 'Marine Stratocumulus Layers. Part I: Mean Conditions', J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 800–817.
Brost, R. A., Wyngaard, J. C., and Lenschow, D. H.: 1982b, 'Marine Stratocumulus Layers. Part II: Turbulence Budgets', J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 818–836.
Caldwell, D. R., Van Atta, C. W., and Helland, K. N.: 1972, 'A Laboratory Study of the Turbulent Ekman Layer', Geophys. Fluid Dyn. 3, 125–160.
Clarke, R. H.: 1970, 'Observational Studies in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 96, 91–114.
Coleman, G. N.: 1999, 'Similarity Statistics from a Direct Numerical Simulation of the Neutrally Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 56, 891–900.
Counihan, J.: 1975, 'Adiabatic Atmospheric Boundary Layers: A Review and Analysis of Data from the Period 1880-1972, Atmos. Environ. 9, 871–905.
Csanady, G. T.: 1967, 'On the “Resistance Law” of a Turbulent Ekman Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 24, 467–471.
Csanady, G. T.: 1974, 'Equilibrium Theory of the Planetary Boundary Layer with an Inversion Lid', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 6, 63–79.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1972, 'Parameterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer for Use in General Circulation Models, Mon. Wea. Rev. 100, 93–106.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1973, 'An Explanation of Anomalously Large Reynolds Stresses within the Convective Planetary Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 30, 1070–1076.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1978, 'Observed Characteristics of the Outer Layer', Short Course on The Planetary Boundary Layer, Boulder, CO, 7-11 August 1978, American Meteorological Society (unpublished manuscript).
Dobson, G. M. B.: 1914, 'Pilot Balloon Ascents at the Central Flying School, Upavon, during the Year 1913', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 40, 123–135.
Garratt, J. R. and Hess, G. D.: 2002, 'The Idealised, Neutrally Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer', in J. R. Holton, J. Pyle, and J. Curry (eds.), Encyclopaedia of Atmospheric Sciences, Academic Press, Vol. 1, pp. 262–271.
Geisler, J. E. and Kraus, E. B.: 1969, 'The Well-Mixed Ekman Boundary Layer', Deep-Sea Res. 16, 73–84.
Gill, A. E.: 1967, 'The Turbulent Ekman Layer', Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, U.K. (unpublished manuscript).
Grant, A. L. M.: 1986, 'Observations of Boundary Layer Structure during the 1981 KONTUR Experiment', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 112, 825–841.
Grant, A. L. M.: 1992, 'The Structure of Turbulence in the Near-Neutral Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 49, 226–239.
Grant, A. L. M. and Whiteford, R.: 1987, 'Aircraft Estimates of the Geostrophic Drag Coefficient and the Rossby Similiarity Functions A and B over the Sea', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 39, 219–231.
Hess, G. D. and Garratt, J. R.: 2002a, 'Evaluating Models of the Neutral, Barotropic Planetary Boundary Layer Using Integral Measures. Part I. Overview', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 104, 333–358.
Hess, G. D. and Garratt, J. R.: 2002b, 'Evaluating Models of the Neutral, Barotropic Planetary Boundary Layer Using Integral Measures. Part II. Modelling Observed Conditions', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 104, 359–369.
Hinze, J. O.: 1959, Turbulence: An Introduction to its Mechanism and Theory, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 586 pp.
Kantha, L. H., Phillips, O. M., and Azad, R. S.: 1977, 'On Turbulent Entrainment at a Stable Density Interface', J. Fluid Mech. 79, 753–768.
Kato, H. and Phillips, O. M.: 1969, 'On the Penetration of a Turbulent Layer into Stratified Fluid', J. Fluid Mech. 37, 643–655.
Kazanski, A. B. and Monin, A. S.: 1961, 'On the Dynamic Interaction between the Atmosphere and Earth's Surface', Izv. ANSSR, Geophys. Ser. 5, 514–515.
Kitaigorodskii, S. A. and Joffre, S. M.: 1988, 'In Search of Simple Scaling for the Heights of the Stratified Atmospheric Boundary Layer', Tellus 40A, 419–433.
Klebanoff, P. S.: 1955, Characteristics of Turbulence in a Boundary Layer with Zero Pressure Gradient, NACA Report 1247. (Also published by Klebanoff in 1954 as NACA Technical Note 3178.)
Kraus, E. B.: 1968, 'What We Do Not Know about the Sea Surface Wind Stress', Bull. Am.Meteorol. Soc. 49, 247–253.
Krishna, K. and Arya, S. P. S.: 1981, Wind Structure in Neutral, Entraining PBL Capped by a Low-Level Inversion', in Preprints of the Fifth Symposium on Turbulence, Diffusion and Air Pollution, 9-13 March, Atlanta, GA, American Meteorological Society, Boston, pp. 65–66.
Lettau, H. H.: 1950, 'A Re-Examination of the “Leipzig Wind Profile” Considering some Relations between Wind and Turbulence in the Frictional Layer', Tellus 2, 125–129.
Mildner, P.: 1932, 'Ñber die Reibung in einer speziellen Luftmasse', Beitr. Phys. Atmos. 19, 151–158.
Miles, J.: 1994, 'Analytical Solutions for the Ekman Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 1–10.
Moeng, C.-H.: 1984, 'A Large-Eddy Simulation Model for the Study of Planetary Boundary-Layer Turbulence', J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 2052–2062.
Moeng, C.-H. and Sullivan, P. P.: 1994, 'A Comparison of Shear-and Buoyancy-Driven Planetary Boundary Layer Flows', J. Atmos. Sci. 51, 999–1022.
Moeng, C.-H. and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1988, 'Spectral Analysis of Large-Eddy Simulations of the Convective Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 45, 3575–3587.
Nicholls, S.: 1985, 'Aircraft Observations of the Ekman Layer during the Joint Air-Sea Interaction Experiment', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 111, 391–426.
Panofsky, H. A. and Dutton, J. A.: 1984, Atmospheric Turbulence: Models and Methods for Engineering Applications, John Wiley, New York, 397 pp.
Pendergrass, W. and Arya, S. P. S.: 1984, 'Dispersion in Neutral Boundary Layer over a Step Change in Surface Roughness-I.Mean Flow and Turbulence Structure', Atmos. Environ. 18, 1267–1279.
Phillips, O. M.: 1977, 'Entrainment', in E. B. Kraus (ed.), Modelling and Prediction of the Upper Layers of the Ocean, Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 92–101.
Pollard, R. T., Rhines, P. B., and Thompson, R. O. R. Y.: 1973, 'The Deepening of the Wind-Mixed Layer', Geophys. Dyn. 3, 381–404.
Rossby, C. G. and Montgomery, R. B.: 1935, 'The Layers of Frictional Influence in Wind and Ocean Currents', Papers Phys. Oceanogr. Meteorol. 3, No. 3, 101 pp.
So, R. M. C. and Mellor, G. L.: 1972, An Experimental Investigation of Turbulent Boundary Layers along Curved Surfaces, NASA CR 1940.
Swinbank, W. C.: 1970, 'Structure ofWind and the Shearing Stress in the Planetary Boundary Layer', Arch. Met. Geoph. Biokl. A19, 1–12.
Thompson, R. O. R. Y.: 1973, 'Stratified Ekman Boundary Layer Models', Geophys. Dyn. 5, 201–220.
Tjernström, M. and Smedman, A.-S.: 1993, 'The Vertical Turbulence Structure of the Coastal Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Geophys. Res. 98, C3, 4809–4826.
Townsend, A. A.: 1951, 'The Structure of the Turbulent Boundary Layer', Proc. Cambridge Phil. Soc. 47, 375–395.
Townsend, A. A.: 1976, The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flow, Second Edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 429 pp.
Walmsley, J. L.: 1992, 'Proposal for New PBL Resistance Laws for Neutrally-Stratified Flow', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 60, 271–306.
Walter, B. A. and Overland, J. L.: 1984, 'Observations of Longitudinal Rools in a Near Neutral Atmosphere. Mon. Wea. Rev. 112, 200–208.
Wippermann, F.: 1971, 'A Note on a Method for Solving the Planetary Boundary-Layer Equations', Beitr. Phys. Atmos. 44, 293–296.
Wyngaard, J. C.: 1975, 'Modeling the Planetary Boundary Layer-Extension to the Stable Case', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 9, 441–460.
Wyngaard, J. C., Coté, O. R., and Rao, K. S.: 1974, 'Modeling the Atmospheric Boundary Layer', Adv. Geophys. 18A, 193–211.
Zilitinkevich, S. S.: 1967, 'On Dynamic and Thermal Interaction between the Atmosphere and the Ocean', Izv. Atmos. Oceanic Phys. 3, 1067–1077.
Zilitinkevich, S. S. and Baklanov, A.: 2002, 'Calculation of the Height of Stable Boundary Layers in Practical Applications', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 105, 389–409.
Zilitinkevich, S. S. and Esau, I. N.: 2002, 'On Integral Measures of the Neutral, Barotropic Planetary Boundary Layers', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 104, 371–379.
Zilitinkevich, S. and Mironov, D. V.: 1996, 'A Multi-Limit Formulation for the Equilibrium Depth of a Stably Stratified Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 81, 325–351.
Zilitinkevich, S., Baklanov, A., Rost, J., Smedman, A.-S., Lykosov, V., and Calanca, P.: 2002, 'Diagnostic and Prognostic Equations for the Depth of the Stably Stratified Ekman Boundary Layer', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 128, 25–46.
Zilitinkevich, S. S., Laikhtman, D. L., and Monin, A. S.: 1967, 'Dynamics of the Boundary Layer in the Atmosphere', Izv. Atmos. Oceanic Phys. 3, 297–333.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hess, G.D. The Neutral, Barotropic Planetary Boundary Layer, Capped by a Low-Level Inversion. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 110, 319–355 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000007248.42321.d5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000007248.42321.d5