Abstract
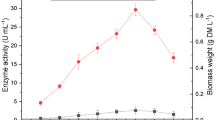
The white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor grown in submerged culture produced two laccase isoenzymes, LacI and LacII. Addition of insoluble lignocellulosic materials into the culture medium increased the total laccase activity. The proportion of laccase isoenzymes also changed depending on the lignocellulosic material employed, with ratios of activity LacII/LacI from 0.9 (barley straw) to 4.4 (grape stalks). Besides, this proportion played an important role in the dye decolourisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora DS, Gill PK (2000) Effects of various media and supplements on laccase production by some white rot fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 77: 89–91.
D'Souza TM, Merritt CS, Reddy CA (1999) Lignin-modifying enzymes of the white rot basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 5307–5313.
Klonowska A, Le Petit J, Tron T (2001) Enhancement of minor laccases production in the basidiomycete Marasmius quercophilus C30. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 200: 25–30.
Ko E-M, Leem Y-E, Choi HT (2001) Purification and characterization of laccase isozymes from the white-rot basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57: 98–102.
Moldes D, Gallego PP, Rodríguez Couto S, Sanromán A (2003) Grape seeds: the best lignocellulosic waste to produce laccase by solid state cultures of Trametes hirsuta. Biotechnol Lett. 25: 491–495.
Niku-Paavola ML, Raaska L, Itävaara M (1990) Detection of whiterot fungi by a non-toxic stain. Mycol. Res. 94: 27–31.
Palmieri G, Giardina P, Bianco C, Scaloni A, Capasso A, Sannia G (1997) A novel white laccase from Pleurotus ostreatus. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 31301–31307.
Salas C, Lobos S, Larrain J, Salas L, Cullen D, Vicuña R (1995) Properties of laccase isoenzymes produced by the basidiomycete Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 21: 323–333.
Schlosser D, Grey R, Fritsche W (1997) Patterns of ligninolytic enzymes in Trametes versicolor. Distribution of extra-and intracellular enzyme activities during cultivation on glucose, wheat straw and beech wood. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 47: 412–418.
Srinivasan C, D'Souza TM, Boominathan K, Reddy CA (1995) Demonstration of laccase in the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F-1767. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 4274–4277.
Yaver DS, Xu F, Golightly EJ, Brown KM, Brown SH, Rey MW, Schneider P, Halkier T, Mondorf K, Dalboge H (1996) Purification, characterization, molecular cloning and expression of two laccase genes from the white rot basidiomycete Trametes villosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 834–841.
Xu F (1999) Laccase. In: Flickinger MC, Drew SW, eds. Encyclopedia of Bioprocess Technology: Fermentation, Biocatalysis and Bioseparation, Vol. 3. New York: John Wiley & Sons, pp. 1545–1554.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moldes, D., Lorenzo, M. & Sanromán, M.A. Different proportions of laccase isoenzymes produced by submerged cultures of Trametes versicolor grown on lignocellulosic wastes. Biotechnology Letters 26, 327–330 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000015452.40213.bf
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000015452.40213.bf