Abstract
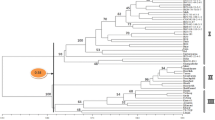
Downy mildew, caused by Sclerospora graminicola, is an economically important disease of pearl millet in the semiarid regions of Asia and Africa. Amplified restriction fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was used to detect the extent of genomic variation among 19 fungal isolates from different cultivars of pearl millet grown in various regions of India. Fourteen AFLP primer combinations produced 184 polymorphic bands. An unweighted pair-group method of averages cluster analysis represented by dendrogram and principal coordinate analysis separated the mildew collections into four distinct groups. Isolates having characteristic opposite mating abilities, geographic relatedness, virulence, common host cultivars, and changes through asexual generations reflected heterogeneity of the pathogen. The use of AFLP to detect genetic variation is particularly important in selecting mildew isolates to screen breeding material for identification of resistant millet and monitoring changes in S. graminicola in relation to changes in host for effective disease management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, D. J., King, S. B., Witcombe, J. R., Singh, S. D., Rai, K. N., Thakur, R. P., Talukdar, B. S., Chavan, S. B., & Singh, P. (1985). Breeding for disease resistance and yield in pearl millet. Field Crops Res. 11:241–258.
Baayen, R. P., van den Boogert, P. H. J. F., Bonats, P. J. M., Poll, J. T. K., Blok, W. J., & Waalwijk, C. (2000). Fusarium redolens f.sp asparagi, causal agent of asparagus root rot, crown rot and spear rot. Eur J Plant Pathol. 106(9):907–912.
Ball, L. S., & Pike, D. J. (1983). Pathogenic variability of downy mildew (Sclerospora graminicola) on pearl millet. II. Statistical techniques for analysis of data. Ann. Appl. Biol. 102:265–273.
Ball, S. L., Pike, D. J., & Burridge, C. Y. (1986). Characterization of populations of Sclerospora graminicola. Ann. Appl. Biol. 108:519–526.
Brunken, J. N. (1977). A systematic study of Pennisetum sect. Pennisetum (Graminae). Am. J. Bot. 64:161–176.
Day, P. R. (1974). Genetics of Host–Parasite Interactions, Freeman, San Francisco.
FAO (1992). Crop Production Yearbook, FAO, Rome.
Gonzalez, M., Rodriguez, R., Zavala, M. E., Jacobo, J. L., Hernandez, F., Acosta, J., Martinez, O., & Simpson, J. (1998). Characterization of Mexican isolates of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum by using differential culitvars and molecular markers. Phytopathology 88(4):292–299.
Govila, O. P. (1993). Pearl millet breeding strategies in India: Their relevance in molecular mapping. In Witcombe, J. R., & Duncan, R. R., (eds.), Proceedings of an ODA Plant Sciences Research Program Conference, 29 March–1 April, Norwich, UK, pp. 96–98.
Gower, J. C. (1966). Some properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 53:325–338.
Hash, C. T., Witcombe, J. R., Thakur, R. P., Bhatnagar, S. K., Singh, S. D., & Wilson, J. P. (1997). Breeding for Pearl millet disease resistance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Genetic Improvement of Sorghum and Pearl Millet, Sept. 22–27, 1996, pp. 337–372. INTSORMIL Publication No. 97–5.INTSORMIL and ICRISAT.
Idris, S. L., & Ball, M. O. (1984). Inter-and intra-continental sexual compatibility in Sclerospora graminicola. Plant Pathol. 33:219–223.
Janssen, P., Coopman, R., Huys, G., Sings, J., Bleeker, M., Vos, P., Zabeau, M., & Kersters, K. (1996). Evaluation of the DNA fingerprinting method AFLP as a new tool in bacterial taxonomy. Microbiology 142:1881–1893.
Jeger, M. J., Gilijamse, E., Bock, C. H., & Frinking, H. D. (1998). The epidemiology, variability and control of the downy mildews of pearl millet and sorghum, with particular reference to Africa. Plant Pathol. 47:544–569.
Jones, E. S., Liu, C. J., Gale, M. D., Hash, C. T., & Witcombe, J. R. (1995). Mapping quantitative trait loci for downy mildew resistance in pearl millet. Theor. Appl. Genet. 91(3):448–456.
Jones, E. S., Witcombe, J. R., Hash, C. T., Singh, S. D., Gale, M. D., Shaw, D. S., & Liu, C. J. (1993). Mapping QTLS controlling resistance to downy mildew in pearl millet and their application in plant breeding programs as part of Use of Molecular Markers in Sorghum and Pearl Millet Breeding for Developing countries. In Proceedings of an ODA Plant Sciences Research Program Conference, 29 March–1 April, Norwich, UK.
Julian, M. C., Acero, J., Salazar, O., Keijer, J., & Rubio, V. (1999). Mating type correlated molecular markers and demonstration of heterokaryosis in the phytopathogenic fungus Thanatephorus cucumeris (Rhizoctina solani) AG 1-IC by AFLP DNA fingerprinting analysis. J. Biotechnol. 67:49–56.
Kronstad, J. W., & Staben, C. (1997). Annu. Rev. Genet. 31:245–276.
Majer, D., Mithen, R., Lewis, B. G., Vos, P., & Oliver, R. P. (1996). The use of AFLP fingerprinting for the detection of genetic variability in fungi. Mycol. Res. 9:1107–1111.
Mehta, N., & Thakur, D. P. (1985). Role of cultivar blending in pearl millet downy mildew reduction. Indian J. Plant Pathol. 3(2):296–299.
Michelmore, R. W., Pawar, M. N., & Williams, R. J. (1982). Heterothallism in Sclerospora graminicola. Phytopathology 72:1368–1372.
Mueller, U. G., Lipari, S. E., & Milgroom, M. G. (1996). Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) fingerprinting of symbiotic fungi cultured by the fungus-growing ant Cyphomyrmex minutus. Mol. Ecol. 5(1):119–122.
Pei, M. H., Yuan, Z. W., Hunter, T., & Ruiz, C. (2000). Heterogeneous nature of a new pathotype of Melamospora Rust on Salix revealed by AFLP. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 106(8):771–779.
Reamon-Büttner, S. M., Schondelmaier, J., & Christian, J. (1998). AFLP markers tightly linked to the sex locus in Asparagus officinalis L. Mol. Breed. 4:91–98.
Rosendahl, S., & Taylor, J. W. (1997). Development of multiple genetic markers for studies of genetic variation in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi using AFLP. Mol. Ecol. 6:821–829.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Sastry, J. G., Ramakrishna, W., Sivaramakrishnan, S., Thakur, R. P., Gupta, V. S., & Ranjekar, P. K. (1995). DNA fingerprinting detects genetic variability in pearl millet downy mildew pathogen (Sclerospora graminicola). Theor. Appl. Genet. 91:856–861.
Sastry, J. G., Sivaramakrishnan, S., Rao, V. P., Thakur, R. P., Singru, R. S., Gupta, V. S., & Ranjekar, P. K. (2001). Genetic basis of host specificity in Sclerospora graminicola, the pearl millet downy mildew pathogen. Indian J. Phytopathol. 54(3):2001.
Sastry, J. G., Sivaramakrishnan, S., Thakur, R. P., Gupta, V. S., & Ranjekar P. K. (1997). Characterization of the genome of Sclerospora graminicola, the causal fungus of downy mildew of pearl millet. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13:693–697.
Singh, S. D., & Gopinath, R. (1985). A seedling inoculation technique for detecting downy mildew resistance in pearl millet. Plant Dis. 68:582–584.
Singh, S. D., & King, S. B. (1988). Recovery resistance to downy mildew in pearl millet. Plant Dis. 72:425–428.
Singh, S. D., King, S. B., & Weder, J. (1993). Downy Mildew Disease of Pearl Millet. Information bulletin no. 37, ICRISAT, Patancheru, India.
Singh, S. D., & Thakur, R. P. (1995). Variable pathogens of millets. In Leslie, J. F., & Frederickson, R. A. (eds.), Disease Analysis Through Genetics and Biotechnology: Interdisciplinary Bridges to Improved Sorghum and Millet Crops, ISBN 0–8138–2125–8, pp. 25–34.
Stappen Vander, J., Weltjens, I., Lopez Gama, S, & Volckaert, G. (2000). Genetic diversity in Mexican Styloanthes humilis as revealed by AFLP, compared to the variability of S. humilis accessions of South American origin. Euphytica 113(2):145–154.
Thakur, R. P. (1995). Status of international sorghum anthracnose and pearl millet downy mildew virulence nurseries. In Leslie, J. F., & Frederickson, R. A. (eds.), Disease Analysis Through Genetics and Biotechnology: Interdisciplinary Bridges to Improved Sorghum and Millet Crops. ISBN 0–8138–2125–8, pp. 75–92.
Thakur, R. P., Pushpavathi, B., & Rao, V. P. (1998). Virulence characterization of single zoospore isolates of S. graminicola. Plant Dis. 82(7):741–751.
Thakur, R. P., & Shetty, G. K. (1993). Variation in pathogenicity among single oospore isolates of Sclerospora graminicola, the causal agent of downy mildew of pearl millet. Plant Pathol. 42:715–721.
Thakur, R. P., Shetty, K. G., & King, S. B. (1992). Selection of host specific virulence in a sexual population of S. graminicola. Plant Pathol. 41:626–632.
Vos, P., Rene, H., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Hornes, M., Frijters Pot, A. J., Peleman, J., Kuiper, M., & Zabeau, M. (1995). AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 23:(21)4407–4414.
Williams, R. J. (1984). Downy mildew of tropical cereals. Adv. Plant Pathol. 3:1–103.
Williams, R. J., Singh, S. D., & Pawar, M. N. (1981). An improved field screening technique for downy mildew resistance in pearl millet. Plant Dis. 65:239–241.
Ziegler, R. S., Cuoc, L. X., Scott, R. P., Bernardo, M. A., Chen, D. H., Valent, B., & Nelson, R. J. (1995). The relationship between lineage and virulence in Pyricularia grisea in the Phillipines. Phytopathology 85:443–451.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singru, R., Sivaramakrishnan, S., Thakur, R.P. et al. Detection of Genetic Variability in Pearl Millet Downy Mildew (Sclerospora graminicola) by AFLP. Biochem Genet 41, 361–374 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIGI.0000007772.27724.0e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIGI.0000007772.27724.0e