Abstract
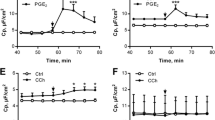
Several reports have confirmed that thecooperative interaction between cAMP- andCa2+-mediated transduction pathways maycontribute to the stimulatory or inhibitory regulationof Cl- secretion in intestinal epithelium.Saccharomyces boulardii has been shown to inhibitcholera toxin-induced secretion in rat jejunum. We haveidentified a 120-kDa protein in medium conditioned bySaccharomyces boulardii that reduces cholera toxin-inducedcAMP in intestinal cells. The present study evaluatedthe effect of medium conditioned by Saccharomycesboulardii on cAMP- and Ca2+-mediatedCl- secretion in T84 cells. Experiments performedwith cAMP agonists revealed that 1 hr of preincubationof cells with medium conditioned by Saccharomycesboulardii was necessary to elicit a 40-50% reduction in receptor (cholera toxin, prostaglandinE2, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide)and nonreceptor (forskolin) mediated cAMP synthesis and125I- efflux. Secretion induced by carbachol was inhibited when cells werepretreated for 1 hr with medium conditioned bySaccharomyces boulardii despite the absence ofinhibition of Ins (1,4,5)P3. From this studywe conclude that Saccharomyces boulardii exerts aninhibitory effect in vitro on Cl- secretionmediated through both cAMP- and Ca2+-mediatedsignaling pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
McFarland LV, Bernasconi P: Saccharom yces boulardii: A re-view of an innovative biotherapeutic agent. Microbiol Ecol Health Dis 6:157-177, 1993
Buts JP, Corthier G, Delmee M: Saccharom yces boulardii for Clostridium difficile-associated enteropathies in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 16:419-425, 1993
McFarland LV, Surawicz CM, Greenberg RN, et al: A randomized placebo-controlled trial of Saccharom yces boulardii in combination with standard antibiotics for Clostridium difficile disease. JAMA 271:1913-1918, 1994
Corthier G, Dubos F, Ducluzeau R: Prevention of Clostridium difficile mortality in gnotobiotic mice by Saccharom yces boulardii. Can J Microbiol 32:894-896, 1986
Toothaker RD, Elmer GW: Prevention of clindamycininduced mortality in hamster by Saccharomyces boulardii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 26:552-556, 1984
Castex F, Corthier G, Jouvert S, et al: Prevention of pseudomembranous cecitis by Saccharom yces boulardii: Topo-graphical histology of the mucosa, bacterial counts and analysis of toxin production. Microecol Ther 19:241-250, 1989
Castagliuolo I, LaMont JT, Nikulasson ST, Pothoulakis C: Saccharomyces boulardii protease inhibits Clostridium difficile toxin A effects in the rat ileum. Infect Immun 64:5225-5232,1996
Dias RS, Bambirra EA, Silva ME, Nicoli JR: Protective effect of Saccharomyces boulardii against cholera toxin in rats. Bras J Med Biol Res 28:323-325, 1995
Vidon N, Huchet B, Rambaud JC: Influencede S. boulardii sur la sécrétion jéjunale induite chezle rat par la toxine cholérique. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 10:13-16, 1986
Field M, Rao MC, Chang EB: Intestinal electrolyte transport and diarrheal disease. N Engl J Med 321:800-806, 879-883,1989
Czerucka D, Roux I, Rampal P: Saccharom yces boulardii inhibits se cre tagogue-mediated adenosine 39,59-cyclic monophosphate induction in intestinal cells. Gastroenterology 106:65-72, 1994
Barrett KE: Positive and negative regulation of chloride secretion. Am J Physiol 265:C859-C868, 1993
Dharmsathaphorn K, McRoberts JA, Mandel KG, et al: A human colonic tumor cell line that maintainsvectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol 246:G204-G208, 1984
Lencer WI, Constable C, Moe S, et al: Targeting of cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat labile toxin in polarized epithelia: Role of COOH-terminal KDEL. J Cell Biol 131:951-962, 1995
Lencer WI, Moe S, Rufo PA, Madara JL: Transcytosis of cholera toxin subunits across mode l human intestinal epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92:10094-10098, 1995
Beubler E, Kollar G, Saria A, Bufkhave K, Rask-Madsen J: Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine, prostaglandin E2, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in cholera toxin-induced fluid secretion in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gastroenterology 96:368-376, 1989
Cassuto J, Fahrenkrug J, Jodal M, Tuttle R, Lundgreen O: Release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide from the cat small intestine exposed to choleratoxin. Gut 22:958-963, 1981
Nilsson O, Casutto J, Larsson PA, et al: 5-Hydroxytryptamine and cholera secretion: A histochemical and physiological study in cats. Gut 24:542-548, 1983
Dharmsathaphorn K, Mandel KG, Masui H, McRoberts JA: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-induced chloride secretion by a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest 75:426-471, 1986
Weymer A, Huott P, Liu W, McRoberts JA, Dharmsathaphorn K: Chloride secretory me chanism induced by prostaglandin E1 in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest 76:1828-1836,1985
Berridge MJ: Inositol triphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361:315-325, 1993
Nishizuka Y: The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature 334:661-665, 1988
Dharmsathaphorn K, Pandol S: Mechanism of chloride secre-tion induced by carbachol in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest 77:348-354, 1986
Reinlib L, Mikkelsen R, Zahniser D, Dharmsathaphorn K, Donowitz M: Carbachol-induced cytosolic free Ca2+increases in T84 colonic cells seen by microfluorimetry. Am J Physiol 257:G950-G960, 1989
Kachintorn U, Vajanaphanich M, Barrett KE, Traynor-Kaplan AE: Elevation of inositiol tetrakisphosphate parallels inhibition of Ca2+-dependent Clflsecretion in T84 cells. Am J Physiol 269:C671-C676, 1993
Warhurst G, Higgs NB, Tonge A, Turnberg LA: Stimulatory and inhibitory actions of carbachol on chloride secretory responses in human colonic cell line T84. Am J Physiol 261:G220-G228, 1991
Warhurst G, Higgs NB, Lees M, Tonge A, Turnberg LA: Activation of protein kinase C attenuate s prostaglandin E2 response s in colonic cell line. Am J Physiol 255:G27-G32, 1988
Traynor-Kaplan AE, Buranawuti T, Vajanaphanich M, Barrett KE: Protein kinase C activity does not mediate the inhibitory effect of carbachol on chloride secretion by T84 cells. Am J Physiol 267:C1224-C1230, 1994
Vajanaphanich M, Schultz C, Rudolf MT, e t al: Long-term uncoupling of chloride secretion from intracellular calcium levels by Ins(3,4,5,6)P4. Nature 371:711-714, 1996
Krammer M, Karbach U: Antidiarrheal action of the ye ast Saccharom yces bou lardii in the rat small and large intestine by stimulating chloride absorption. Z Gastroenterol 31:73-77,1993
Venglarik CJ, Bridges RJ, Frizzell RA: A simple assay for agonist-regulated Cl and K conductances in salt-secreting epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 259:C358-C364, 1990
Kassis S, Hagmann J, Fishman PH, Chang PP, Moss J: Mechanism of action of cholera toxin on intact cells: Generation of a peptide and activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem 257:12148-12152, 1982
Warhurst G, Turnberg LA, Higgs NB, e t al: Multiple Gprotein-dependent pathways mediated the antisecretory effects of somatostatin and clonidine in the HT29-C119A colonic cell line. J Clin Invest 92:603-611, 1993
Ismalov II, Fuller CM, Berdiev BK, et al: A biologic function for an “orphan” messenger: D-myo-inositiol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate selectively blocks epithelial calcium-activated chloride channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10505-10509, 1996
Li M, McCann JD, Anderson MP, et al: Regulation of chloride channels by protein kinase C in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Science 244:1353-1356, 1989
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czerucka, D., Rampal, P. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii on cAMP- and Ca2+-dependent Cl- Secretion in T84 Cells. Dig Dis Sci 44, 2359–2368 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026689628136
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026689628136