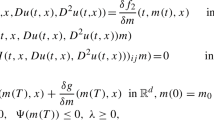Abstract
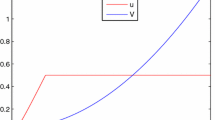
In this paper we propose a numerical approach for the solution of some optimalcontrol problems arising in the field of marketing decision models. Inparticular, we account for a specific innovation diffusion model. A numericalapproach may be useful to investigate some features of state variables andparameters of interest. The discrete problem is solved by the SimulatedAnnealing method and the resulting numerical scheme is applied to some testcases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass, F. (1969). A new product growth model for consumer durables. Management Science, 15, 215–227.
Capasso, V., Di Liddo, A. and Maddalena, L. (1994). Asymptotic behaviour of a nonlinear model for the geographical diffusion of innovation. Dynamic Systems and Appl., 3, 207–220.
Corana, A., Marchesi, M., Martini, C. and Ridella, S. (1987). Minimizing multimodal functions of continuous variables with the ‘simulated Annealing’ algorithm. ACM Trans. Math. Software, 13, 262–280.
De Cesare, L. and Di Liddo, A. (2000). A Bolza optimal control problem for innovation diffusion. Dynamic Systems and Appl., 9, 269–280.
De Cesare, L. and Di Liddo, A. (2001). A Stackelberg game of innovation diffusion: pricing, advertising and subsidy strategies. International Game Theory Review, 3, 325–339.
De Cesare, L., Di Liddo, A. and Ragni, S. (2002). On the shape of optimal price and advertising strategies arising in innovation diffusion. Rapporto Interno IAC CNR-Sez. Bari 21/02.
Di Liddo, A. and Maddalena, L. (1997). Nonlocal models for the spread of new products in spatially structured markets. Dynamic Systems and Appl., 6, 85–100.
Eliashberg, J. and Chatterjee, R. (1986). Stochastic issues in innovation diffusion models. In V. Mahajan and Y. Wind (eds.), Innovation Diffusion Models of New Product Acceptance, Ballinger, Cambridge, Mass., pp. 151–202.
Goffe, W.L., Ferrier, G.D. and Rogers, J. (1996). Global optimization of statistical functions with simulated annealing. Studies in Nonlinear Dynamics and Econometrics, 1(3), 169–176.
Jørgensen, S. and Zaccour G. (eds.) (1996). Dynamic Competitive Analysis in Marketing. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Kalish, S. (1985). A new product adoption model with price, advertising and uncertainty. Management Science, 31, 1569–1585.
Kendall, D.G. (1957). Discussion on ‘Bartlett, M.S., Measles, periodicity and communitysize’. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. A, 120, 48–70.
Lilien, G.L., Kotler, P. and Sridhar Moorthy, K. (1992). Marketing Models. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
Mahajan, V. and Peterson, R.A. (1978) Innovation diffusion in a dynamic potential adopter population. Management Science, 24, 1589–1597.
Mahajan, V. and Peterson, R.A. (1979) First-purchase diffusion models of new-product acceptance. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 15, 127–146.
Nocedal, J. and Wright, S.J. (1999). Numerical Optimization. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Norton, J.A. and Bass, F. (1987). A diffusion theory model of adoption and substitution for successive generations of high technology products. Management Science, 33, 1069–1086.
Rogers, E.M. (1995). Diffusion of Innovation. The Free Press, New York.
Smoller, J. (1983). Reaction-Diffusion Equations. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Cesare, L., Di Liddo, A. & Ragni, S. Numerical Solutions to Some Optimal Control Problems Arising from Innovation Diffusion. Computational Economics 22, 173–186 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026185814203
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026185814203