Abstract
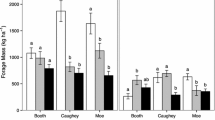
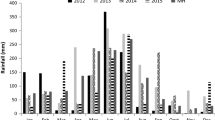
Silvopastoral systems offer an alternative to the conventional cow-calf segment of the beef industry in the Midwestern region of the United States. Little information exists for transitioning from a conventional pasture-based beef operation to a silvopastoral system utilizing multiple deciduous tree species. Nine pastures approximately 1 ha in size were established with a mixture of cool-season grasses and legumes to investigate tree protection methods and cattle performance. Four tree species (Juglans nigra, Gleditsia triacanthos, Quercus rubra, & Carya illinoensis) were planted within six of these pastures. Three methods of protection were tested, and included a no protection control (Con), foliar application of 0.20% denatonium benzoate (TreeGuard™), or a single strand of electrified poly-wire (EF) in each of the two grazing years. Cattle damage to young trees was prominent during the two years for Con and TreeGuard™. EF offered acceptable protection. Red oak trees suffered the highest degree of damage from livestock. Establishing trees within grazed pastures did not hinder performance of beef cattle. Transitioning from conventional pastures to silvopastures can be accelerated utilizing an electrified fencing system to prevent cattle damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benfeldt E.S., Feldhake C.M. and Burger J.A. 2001. Establishing trees in Appalachian silvopasture: response to shelters, grass control, mulch, and fertilization. Agrofor. Syst. 53: 291-295
Clason T.R. 1995. Economic implications of silvipastures on southern pine plantations. Agrofor. Syst. 29: 227-238
Eason W.R., Gill E.K. and Roberts J.E. 1996. Evaluation of anti-sheep tree-stem-protection products in silvopastoral argroforestry. Agrofor. Syst. 34: 259-264
Haines P.J., Bell A.B. and Thatcher L.P. 1994. Evaluation of some factors involved in reducing browsing damage to eucalypt trees by sheep. Australian J. Expt. Agri.
Kingery J.L. and Graham R.T. 1991. The effect of cattle grazing on Ponderosa pine regeneration. J. For. 67: 245-248
Lehmkuhler J.W., Kerley M.S., Garrett H.E., Cutter B.E. and McGraw R.L. 1998-1999. Comparison of continuous and rotational silvopastoral systems for established walnut plantations in southwest. Missouri, USA. Agrofor. Syst. 44: 267-279
Lemieux N.C., Maynard B.K. and Johnson W.A. 2000. Evaluation of commercial deer repellents on ornamentals in nurseries. J. Environ. Hort. 18: 5-8
Mitchell R.L. and Wright J.C. 1991. Experiences in pecan orchard floor vegetation management: Two years of stocker steer performances and evaluation of grazing management. Annu.-Rep.-North-Nut.-Grow.-Assoc. 82: 72-79
Nolte D.L. 1998. Efficacy of selected repellents to deter deer browsing on conifer seedlings. Inter. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 42: 101-107
NRC 1996. Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle (7th Ed.). National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Pearson H.A., Baldwin V.C. and Barnett J.P. 1990a. Cattle grazing and pine survival and growth in subterranean clover pasture. Agrofor. Syst. 10: 161-168
Pearson H.A., Prince T.E. and Todd Jr. C.M. 1990b. Virginia pines and cattle grazing-an agroforestry opportunity. South J. Appl. For. 14: 55-59
Pearson H.A. and Whitaker L.B. 1974. Forage and cattle responses to different grazing intensities on southern pine ridge. J. Range Manage 27: 444-446.
Sharrow S.H. 2001. Effects of shelter tubes on hardwood tree establishment in western Oregon silvopastures. Agrofor. Syst. 53: 283-290
Sharrow S.H., Carlson D.H., Emmingham W.H. and Lavender D. 1996. Productivity of two Douglas fir/subclover/sheep agroforests compared to pasture and forest monocultures. Agrofor. Syst. 34: 305-313
Stace C. 1993. Stock protectors for tree seedlings: a review of Conservation Plants research. New Zealand Tree Grower. 14: 16-19
Wright I.A. and Milne J.A. 1996. Aversion of Red deer and Roe deer to denatonium benzoate in the diet. Forest. 69: 1-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehmkuhler, J., Felton, E., Schmidt, D. et al. methods during the silvopastoral-system establishment in midwestern USA: Cattle performance and tree damage. Agroforestry Systems 59, 35–42 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026184902984
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026184902984