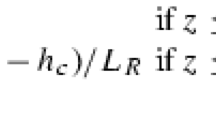Abstract
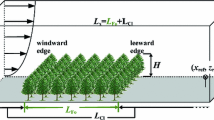
This study proposes a two-dimensional Lagrangian stochastic dispersion model forestimating spatial and temporal variation of scalar sources, sinks, and fluxes withina forest canopy. Carbon dioxide and heat dispersion experiments were conducted forfield testing the model. These experiments also provided data for field testing a newlydeveloped one-dimensional Lagrangian analytical dispersion model. It was found that these two models produce similar scalar source-sinkand flux distribution patterns. Comparing with CO2 flux measurements, the one-dimensional model performed as well as the two-dimensional model even whenthe fetch is short (≈100 m). To drive these Lagrangian models, velocitystatistics through the canopy volume must be specified a priori. The sensitivity of thecomputed sources, sinks, and fluxes to the description of the flow statistics was furtherexamined. All in all, we found good agreement between model predicted andeddy-correlation measured CO2 and sensible heat fluxes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayotte, K. W., Finnigan, J. J., and Raupach, M. R.: 1999, 'A Second-Order Closure for Neutrally Stratified Vegetative Canopy Flows', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 90, 189-216.
Borgas, M. S., Flesch, T. K., and Sawford, B. L.: 1997, 'Turbulent Dispersion with Broken Reflexional Symmetry', J. Fluid Mech. 332, 141-156.
Coppin, P. A., Raupach, M. R., and Legg, B. J.: 1986, 'Experiments on Scalar Dispersion within a Model Plant Canopy. Part II: An Elevated Plane Source', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 35, 167-191.
Denmead, O. T., 1995, 'Novel Meteorological Methods for Measuring Trace Gas Fluxes', Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 351, 383-396.
Ellsworth, D. S., Oren, R., Huang, C., Phillips, N., and Hendrey, G. R.: 1995, 'Leaf and Canopy Responses to Elevated CO2 in a Pine Forest under Free-Air CO2 Enrichment', Oecologia 104, 139-146.
Falge, E., Baldocchi, D., Olson, R., Anthoni, P., Aubinet, M., Bernhofer, C., Burba, G., Ceulemans, R., Clement, R., Dolman, H., Granier, A., Gross, P., Grünwald, T., Hollinger, D., Jenson, N-O., Katul, G., Keronen, P., Kowalski, A., Lai, C. T., Law, B. E., Meyers, T., Moncrief, J., Moors, E., Munger, J.W., Pilegaard, K., Rannik, U., Rebmann, C., Sukyer, A., Tenhunen, J., Tu, K., Verma, S., Vesala, T., Wilson, K., and Wofsy, S.: 2001a, 'Gap Filling Strategies for Long Term Energy Flux Data Sets, A Short Communication', Agric. For. Meteorol. 107, 71-77.
Falge, E., Baldocchi, D., Olson, R., Anthoni, P., Aubinet, M., Bernhofer, C., Burba, G., Ceulemans, R., Clement, R., Dolman, H., Granier, A., Gross, P., Grünwald, T., Hollinger, D., Jenson, N-O., Katul, G., Keronen, P., Kowalski, A., Lai, C. T., Law, B. E., Meyers, T., Moncrief, J., Moors, E., Munger, J.W., Pilegaard, K., Rannik, U., Rebmann, C., Sukyer, A., Tenhunen, J., Tu, K., Verma, S., Vesala, T., Wilson, K., and Wofsy, S.: 2001b, 'Gap Filling Strategies for Defensible Annual Sums of Net Ecosystem Exchange', Agric. For. Meteorol. 107, 43-69.
Gifford, F. A.: 1982, 'Horizontal Diffusion in the Atmosphere: A Lagrangian Dynamical Theory', Atmos. Environ. 16, 505-512.
Kaiser, J.: 1998, 'Climate Change-New Network Aims to Take the Worlds CO2 Pulse Source', Science 281, 506-507.
Katul, G. G. and Albertson, J. D.: 1998, 'An Investigation of Higher-Order Closure Models for a Forested Canopy', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 89, 47-74.
Katul, G. G. and Albertson, J. D.: 1999, 'Modeling CO2 Sources, Sinks, and Fluxes within a Forest Canopy', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 6081-6091.
Katul, G. G. and Chang, W. H.: 1999, 'Principal Length Scales in Second-Order Closure Models for Canopy Turbulence', J. Appl. Meteorol. 38, 1631-1643.
Katul, G. G., Hsieh, C. I., Bowling, D., Clark, K., Shurpali, N., Turnipseed, A., Albertson, J., Tu, K., Hollinger, D., Evans, B., Offerle, B., Anderson, D., Ellsworth, D., Vogel, C., and Oren, R.: 1999, 'Spatial Variability of Turbulent Fluxes in the Roughness Sublayer of an Even-Aged Pine Forest', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 93, 1-28.
Katul, G. G., Leuning, R., Kim, J., Denmead, O. T., Miyata, A., and Harazono, Y.: 2001, 'Estimating CO2 Source/Sink Distributions within a Rice Canopy Using Higher-Order Closure Models', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 98, 103-125.
Katul, G. G., Oren, R., Ellsworth, D., Hsieh, C. I., Philips, N., and Lewin, K.: 1997, 'A Lagrangian Dispersion Model for Predicting CO2 Sources, Sinks, and Fluxes in a Uniform Loblolly Pine (Pinus Taeda L.) Stand', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 9309-9321.
Kurbanmuradov, O. and Sabelfeld, K.: 2000, 'Lagrangian Stochastic Models for Turbulent Dispersion in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 97, 191-218.
Lai, C. T., Katul, G. G., Oren, R., Ellsworth, D., and Schäfer, K.: 2000, 'Modeling CO2 and Water Vapor Turbulent Flux Distributions within a Forest Canopy', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 26333-26351.
Lee, J. T. and Stone, G. L.: 1983, 'The Use of Eulerian Initial Conditions in a Lagrangian Model of Turbulent Diffusion', Atmos. Environ. 17, 2477-2481.
Leuning, R.: 2000, 'Estimation of Scalar Source/Sink Distributions in Plant Canopies Using Lagrangian Dispersion Analysis: Corrections for Atmospheric Stability and Comparison with a Multilayer Canopy Model', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 96, 293-314.
Leuning, R., Denmead, O. T., Miyata, A., and Kim, J.: 2000, Source/Sink Distributions of Heat, Water Vapor, Carbon Dioxide, and Methane in a Rice Canopy Estimated Using Lagrangian Dispersion Analysis', Agric. For. Meteorol. 103, 233-249.
Massman, W. J. and Weil, J. C.: 1999, 'An Analytical One-Dimensional Second-Order Closure Model of Turbulence Statistics and the Lagrangian Time Scale within and above Plant Canopies of Arbitrary Structure', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 91, 81-107.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971, Statistical Fluid Mechanics, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp. 215-249, 769 pp.
Novikov, E. A.: 1963, 'Random ForceMethod in Turbulence Theory', Sov. Phys. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 17, 1449-1454.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vettering, W. T., and Flannery, B. P.: 1992, Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN, 2nd edn., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 963 pp.
Rannik, U., Aubinet, M., Kurbanmuradov, O., K. Sabelfeld, K. K., Markkanen, T., and Vesala, T.: 2000, 'Footprint Analysis Measurements over a Heterogeneous Forest', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 97, 137-166.
Raupach, M. R.: 1989a, 'A Practical Lagrangian Method for Relating Scalar Concentrations to Source Distributions in Vegetation Canopy', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 115, 609-632.
Raupach, M. R.: 1989b, 'Applying Lagrangian Fluid Mechanics to Infer Scalar Source Distributions from Concentration Profiles in Plant Canopies', Agric. For. Meteorol. 47, 85-108.
Raupach, M. R., Finnigan, J. J., and Brunet, Y.: 1996, 'Coherent Eddies and Turbulence in Vegetation Canopies: The Mixing-Layer Analogy', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 351-382.
Reynolds, A. M.: 1998a, 'On the Formation of Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Scalar Dispersion within Plant Canopies', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 86, 333-344.
Reynolds, A. M.: 1998b, 'On Trajectory Curvature as a Selection Criterion for Valid Lagrangian Stochastic Dispersion Models', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 77-86.
Reynolds, A.M.: 1998c, 'A Lagrangian Stochastic Model for the Trajectories of Particle Pairs and Its Application to the Prediction of Concentration Variance within Plant Canopies', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 467-478.
Rodean, H.: 1996, Stochastic Lagrangian Models of Turbulent Diffusion, Meteorological Monographs, Vol. 26, No. 48, American Meteorological Society, 84 pp.
Sawford, B. L.: 1999, 'Rotation of Trajectories in Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Turbulent Dispersion', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 93, 411-424.
Siqueira, M. and Katul, G. G.: 2002, 'Estimating Heat Sources and Fluxes in Thermally Stratified Canopy Flows Using Higher-Order Closure Models', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 103, 125-142.
Siqueira, M., Lai, C. T., and Katul, G.: 2000, 'Estimating Scalar Sources, Sinks, and Fluxes in a Forest Canopy Using Lagrangian, Eulerian, and Hybrid Inverse Models', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 29475-29488.
Taylor, G. I.: 1921, 'Diffusion by Continuous Movements', Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. Ser. 2, 20, 196-221.
Thomson, D. J.: 1987, 'Criteria for the Selection of Stochastic Models of Particle Trajectories in Turbulent Flows', J. Fluid Mech. 180, 529-556.
Warland, J. S. and Thurtell G. W.: 2000, 'A Lagrangian Solution to the Relationship between a Distributed Source and Concentration Profile', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 96, 453-471.
Wilson, J. D. and Flesch, T. K.: 1997, 'Trajectory Curvature as a Selection Criterion for Valid Lagrangian Stochastic Models', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 84, 411-426.
Wilson, J. D. and Sawford, B. L.: 1996, 'Review of Lagrangian Stochastic Models for Trajectories in the Turbulent Atmosphere', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 191-210.
Wilson N. R. and Shaw, R. H.: 1977, 'A Higher Order Closure Model for Canopy Flow', J. Appl. Meteorol. 16, 1198-1205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, CI., Siqueira, M., Katul, G. et al. Predicting Scalar Source-Sink and Flux Distributions Within a Forest Canopy Using a 2-D Lagrangian Stochastic Dispersion Model. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 109, 113–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025461906331
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025461906331