Abstract
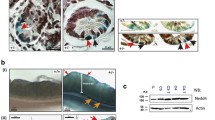
Cyclin D1 plays an important role in the multi-step process of gastrointestinal tumorigenesis. We hypothesize that normal enterocytes over-expressing Cyclin D1 will demonstrate a transformed phenotype. The nontumorigenic intestinal epithelial cell line, IEC-18, was transfected with the vector pMV7-CCND1, encoding Cyclin D1. Three clones, with cyclin D1 levels similar to those seen in colon cancer cell lines, were further evaluated in comparison to the vector control cells. They proliferated faster and demonstrated anchorage-independent growth in soft agar, higher saturation density, and higher plating efficiency. When injected into nude mice, tumors were generated after 6–8 weeks. On the other hand these cells were more sensitive to induction of apoptosis. There was no change in the level of β-catenin protein. In conclusion, Cyclin D1 can act as an oncogene in vitro and in vivo, when produced in immortalized normal intestinal epithelial cells. This model may be useful for understanding the role and interrelationships of Cyclin D1 in colorectal tumorigenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole P, Sateren W: The evolving picture of cancer in America. JNCI 87:59-160, 1995
Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J: Global cancer statistics: CA-Cancer J Clin. 49:33-64, 1999
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B: A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759-767, 1990
Morson B. President's address: The polyp-cancer sequence in the large bowel. Proc R Soc Mes. 67:451-457, 1974
Pines J. Cyclins: wheels within wheels. Cell Growth Differ 2:305-310, 1991
Reed SI: The role of p34 kinases in the G1 to S phase transition. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:529-561, 1992
Sherr CJ: Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell 73:1059-1065, 1993
Hunter T, Pines J: Cyclins and cancer II: cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell 79:573-582, 1994
Sherr CJ: G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell 79:551-555, 1994
Weinstein IB: Abnormalities in cell cycle regulation divided against itself. Helix 5:20-27, 1996
Motokura T, Bloom T, Kim HG, Juppner H, Ruderman JV, Kronenberg HM, Arnold A.: A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature 350:512-515, 2000
Xiong Y, Connolly T, Futcher B, Beach D: Human D-type cyclin. Cell 65:691-699, 1991
Lew DJ, Dulic V, Reed SI: Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin function in yeast. Cell 66:1197-1206, 1991
Matsushime H, Roussel MF, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ: Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell 65:701-713, 1991
Won KA, Xiong Y, Beach D, Gilman MZ: Growth regulated expression of D-type cyclin genes in human diploid fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9910-9914, 1992
Sewing A, Burger C, Brusselbach S, Schalk C, Lucibello FC, Muller R. Human cyclin D1 encodes a labile nuclear protein whose synthesis is directly induced by growth factor and suppressed by cyclic AMP. J Cell Sci 104:545-554, 1993
Quelle DE, Ashmun RA, Shurtleff SA, Kato JY, Bar-Sagi D, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ: Overexpression of mouse D type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev 7:1559-1571, 1993
Lukas J, Pagano M, Staskova Z, Draetta G, Bartek J: Cyclin D1 protein oscillates and is essential for cell cycle progression in human tumor cell lines. Oncogene 9:707-718, 1994
Resnitzky D, Gossen M, Bujard H, Reed SI: Acceleration of the G1/S transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol 14:1669-1679, 1994
Pardee AB: D types cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Science 246:603-608, 1989
Wang TC, Cardiff RD, Zukerberg L, Lees E, Arnold A, Schmidt EV: Mammary hyperplasia and carcinoma in MMTV-cyclin D1 transgenic mice. Nature 369:669-671, 1994
Hinds PW, Dowdy SF, NgEaton, E, et al: Function of a human cyclin gene as an oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:709-713, 1994
Lovec H, Sewing A, Lucibello FC, Muller R, Moroy T: Oncogenic activity of cyclin D1 revealed through cooperation with Ha-ras: link between cell cycle control and malignant transformation. Oncogene 9:323-326, 1994
Marx J: How cells cycle toward cancer. Science 263:319-321, 1994
Nakagawa H, Wang TC, Zukerberg L, Odze R, Togawa K, May GH, Wilson J, Rustgi AK: The targeting of the cyclin D1 oncogene by an Epstein-Barr virus promoter in transgenic mice causes dysplasia in the tongue, esophagus and forestomach. Oncogene 14:1185-1190, 1997
Imanishi Y, Hosokawa Y, Yoshimoto K, Schipani E, Mallya S, Papanikolaou A, Kifor O, Tokura T, Sablosky M, Ledgard F, Gronowicz G, Wang TC, Schmidt EV, Hall C, Brown EM, Bronson R, Arnold A: Primary hyperparathyroidism caused by parathyroid-targeted overexpression of cyclin D1 in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest 107:1079-1080, 2001
Bodrug SE, Warner BJ, Bath ML, Lindeman GJ, Harris AW, Adams JM: Cyclin D1 transgene impedes lymphocyte maturation and collaborates in lymphomagenesis with the myc gene. EMBO J. 13:2124-2130, 1994
Robles AI, Larcher F, Whalin RB, Murillas R, Richie E, Gimenez-Conti IB, Jorcano JL, Conti CJ: Expression of cyclin D1 in epithelial tissues of transgenic mice results in epidermal hyperproliferation and severe thymic hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93:7634-7638, 1996
Hunter T, Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. Cell 66:1071-1074, 1991
Lammie GA, Fantl V, Smith R, Schuuring E, Brookes S, Michalides R, Dickson C, Arnold A, Peters G: D11S287, a putative oncogene on chromosome 11q13, is amplified and expressed in squamous cell and mammary carcinomas and linked to BCL-1. Oncogene 6:439-444, 1991
Gaudray P, Szepetowski P, Escot C, Birnbaum D, Theillet C: DNA amplification at 11q13 in human cancer: from complexity to perplexity. Mutation Res. 276:317-328, 1992
Lammie GA, Peters G: Chromosome 11q13 abnormalities in human cancer. Cancer Cells 3:413-420, 1991
Motokura T, Arnold A: Cyclin D and oncogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 3:5-10, 1993
Arber N, Gammon MD, Hibshoosh H, Britton JA, Zhang Y, Schonberg JB, Roterdam H, Fabian I, Holt PR, Weinstein IB: Overexpression of cyclin D1 occurs in both saquamous carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and in adenocarcinomas of the stomach: Hum Pathol 30:1087-1092, 1999
Kornmann M, Arber N, Korc M: Inhibition of basal and mitogen-stimulated pancreatic cancer cell growth by cyclin D1 antisense is associated with loss of tumorigenicity and potentiation of cytotoxicity to cisplatinum. J Clin Invest 101:344-352, 1998
Kornmann M, Ishiwata T, Arber N, Beger HG, Korc M: Increased cyclin D1 expression in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 17:158-162, 1998
Arber N, Hibshoosh H, Yasui W, Neugut AI, Hibshoosh A, Yao Y, Sgambato A, Yamamoto H, Shapira I, Rosenman D, Fabian I, Weinstein IB, Tahara E, Holt PR: Abnormalities in the expression of cell cycle related proteins in tumors of the small bowel. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:1101-1105, 1999
Arber N, Hibshoosh H, Moss SF, Sutter T, Zhang Y, Begg M, Wang S, Weinstein IB, Holt PR: Increased expression of cyclin D1 is an early event in multistage colorectal carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 110:669-674, 1996
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M, Bartek J: The PRAD-1/cyclin D1 oncogene product accumulates aberrantly in a sub set of colorectal carcinomas. Int J Cancer 58:568-573, 1994
Sutter T, Doi S, Carnevale KA, Arber N, Weinstein IB: Expressions of cyclins D1 and E in human colon adenocarcinomas. J Med 28:285-309, 1997
Arber N, Lightdale C, Rotterdam H, Han KH, Sgambato A, Yap E, Ahsan H, Finegold J, Stevens PD, Green PH, Hibshoosh H, Neugut AI, Holt PR, Weinstein IB: Increased expression of the cyclin D1 gene in Barrett's esophagus. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 5:457-459, 1996
Zhou P, Jiang W, Zhang YJ, Kahn SM, Schieren I, Santella RM, Weinstein IB: Antisense of cyclin D1 inhibits growth and reverses the transformed phenotype of human esophageal cancer cells. Oncogene 11:571-580, 1995
Arber N, Doki Y, Han EK, Sgambato A, Zhou P, Kim NH, Delohery T, Klein MG, Holt PR, Weinstein IB: Antisense to cyclin D1 inhibits the growth and tumorigenesis of human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 57:1569-1574, 1997
Arber N, Strul H: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and selective apoptotic antineoplastic drugs in the prevention of colorectal cancer: the role of super aspirins. Isr Med Assoc J 2:695-702, 2000
DuBois RN, Giardiello FM: Smalley WE. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, eicosanoids, and colorectal cancer prevention. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 25:773-791, 1996.
Arber N: NSAIDs prevent colorectal cancer. Can J Gastroenterol 14:299-307, 2000
Thun MJ: NSAIDs use and decreased risk of gastrointestinal cancers. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 25:333-347, 1996
Quaroni A, Isselbacher KJ: Cytotoxic effects and metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene and 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene in duodenal and ileal epithelial cell cultures. J Natl Cancer Inst 67:1353-1362, 1981
Arber N, Sutter T, Miyake M, Kahn SM, Venkatraj VS, Sobrino A, Warburton D, Holt PR, Weinstein IB: Increased expression of cyclin D1 and the Rb tumor suppressor gene in c-K-ras transformed rat enterocytes. Oncogene 12:1903-1908, 1996
Kohno T, Yoshida S, Bessho M: Accelerated entry into S phase associated with up-regulation of cyclin D1 as a mechanisn for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-induced apoptosis of murine myeloid leukomia cells. Leuk Res 22:257-263, 1998
Muller H, Lukas J, Schneider A, Warthoe P, Bartek J, Eilers M, Strauss M: Cyclin D1 expression is regulated by the retinoblastoma protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2945-2949, 1994
Jiang W, Zhang YJ, Kahn SM, Hollstein MC, Santella RM, Lu SH, Harris CC, Montesano R, Weinstein IB: Altered expression of the cyclin D1 and retinoblastoma genes in human esophageal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9026-9030, 1993
Kitahara K, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Semba S, Hamamoto T, Hisatsugu T, Tahara E: Expression of cyclin D1, CDK4, and p27KIP1 is associated with the p16MTS1 gene status in human esophageal carcinoman cell lines. J Exp Ther Oncol. 1:7-12, 1996
Doki Y, Imoto M, Han EK, Sgambato A, Weinstein IB: Increased expression of the p27kip1 protein in human esophageal cancer cell lines that overexpress cyclin D1. Carcinogenesis 18:139-1148, 1997
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I, Albanese C, D'Amico M, Pestell R, Ben-Ze'ev A.: The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the β-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 6:5522-5527, 1999
Opitz OG, Suliman Y, Hahn WC, Harada H, Blum HE, Rustgi AK: Cyclin D1 overexpression and p53 inactivation immortalize primary oral keratinocytes by a telomerase-independent mechanism. J Clin Invest 108:665-667, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazanov, D., Shapira, I., Pick, M. et al. Oncogenic Transformation of Normal Enterocytes by Overexpression of Cyclin D1 . Dig Dis Sci 48, 1251–1261 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024138605802
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024138605802