Abstract
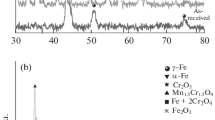
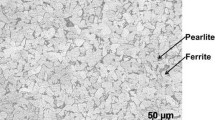
Cyclic voltammetric and potentiodynamic studies were carried out on 300W carbon steel in Bayer plant solution, at 100 °C, with different alumina concentrations. Alumina behaves as an anodic inhibitor, shifting the critical passivation potentials positively and decreasing the critical passivation current with increasing concentration. Increase in alumina concentration promotes the formation of a uniform and less porous film. The pore resistance model describes the properties of the oxide films. Aluminium was found in all oxides formed, supporting the formation of a mixed oxide Fe3−x Al x O4. Thermodynamic calculation of some equilibrium potentials was carried out using the Fe(OH)3 − ion rather than HFeO2 − ion. Moreover, the Al(OH)4 − ion was considered instead of AlO2 − ion in the oxidation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Sriram and D. Tromans, Corros. Sci. 25 (1985) 79.
S.-E. Liu, Z. Zhu and K. Wei, Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia 31 (1994) 427.
H.H. Le and E. Ghali, Corros. Sci. 30 (1990) 117.
D.D. Macdonald and B. Roberts, Electrochim. Acta 23 (1978) 781.
D.D. Macdonald and D. Owen, J. Electrochem. Soc. 120 (1973) 317.
A. Wieckowski, E. Ghali and H.H. Le, J. Electrochem. Soc. 131 (1984) 2024.
A. Wieckowski and E. Ghali, Electrochim. Acta 30 (1985) 1423.
R.S. Schrebler Guzman, J.R. Vilche and A.J. Arvia, Electrochim. Acta 24 (1979) 395.
R.D. Armstrong and I. Baurhoo, J. Electroanal. Chem. 40 (1972) 325.
D. Geana, A.A. El Miligy and W.J. Lorenz, J. Appl. Electrochem. 4 (1974) 337.
T. Zackroczmski, F. Chwei-Jer and Z. Szklarska-Smialowska, J. Electrochem. Soc. 132 (1985) 2862.
B. Kabanov, R. Burstein and A. Frumkin, Discuss. Faraday Soc. 111 (1947) 493.
L. Ojefors, J. Electrochem. Soc. 123 (1976) 1691.
R.D. Armstrong and I. Baurhoo, J. Electroanal. Chem. 34 (1972) 41.
H.H. Le, Thèse de doctorat, (Université Laval, Québec, 1990) p. 254.
C.F. Baes and R.E. Mesmer, ‘The Hydrolysis of Cations’ (J. Wiley & Sons, New York, 1976).
G.B. Naumov, B.N. Ryzhenko and I.L. Khodavsky, ‘Handbook of Thermodynamic Data’ (1974).
D.C. Silverman, Corrosion 10 (1982) 343.
S.P. Rosenberg and S.J. Healy, in Fourth International Alumina Quality Workshop, Darwin (1996).
W.J. Mu¨ ller, Trans. Faraday Soc. 27 (1931) 737.
A.J. Calandra, N.R. Tacconi, R. Pereiro and A.J. Arvia, Electrochim. Acta 19 (1974) 901.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavril, L., Breault, R. & Ghali, E. Aspects of electrochemical behaviour of carbon steel in different Bayer plant solutions. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 33, 311–317 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024128822241
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024128822241