Abstract
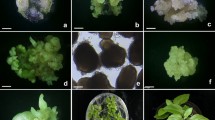
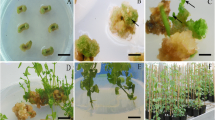
Culture conditions are described for high frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in petiole and leaf explant cultures and petiole-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Hylomecon vernalis Max. Petiole explants formed embryogenic calluses at a frequency of 53% when cultured on B5 medium supplemented with 13.6 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) alone. Leaf explants formed embryogenic calluses at a frequency of 21% when cultured at a combination of 4.52 μM 2,4-D and 2.22 μM 6-benzyladenine. Cell suspension cultures were established with petiole-derived embryogenic calluses using liquid B5 medium with 4.52 μM 2,4-D. Upon plating onto B5 basal medium, cell suspension cultures produced numerous somatic embryos, which then developed into plantlets. Regenerated plantlets were transplanted to potting soil and grown to maturity in a greenhouse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castillo B & Smith MAL (1997) Direct somatic embryogenesis from Begonia gracilis explants. Plant Cell Rep. 16: 385-388
Colombo ML & Bosisio E (1996) Pharmacological activities of Chelidonium majus L. (Papaveraceae). Pharmacol. Res. 33: 127-134
Colombo ML & Tome F (1991) Production of sanguinarine by Chelidonium majus callus culture. Planta Med. 57: 428-429
Gamborg OL, Miller RA & Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell Res. 50: 151-158
Kelkar SM & Krishnamurthy KV (1998) Adventitious shoot regeneration from root, internode, petiole and leaf explants of Piper colubrinum Link. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 721-725
Kim SW, Min BW & Liu JR (1999) High frequency plant regeneation from immature ovule-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Chelidonium majus var. asiaticum. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 56: 125-129
Marchant R, Davey MR, Lucas JA & Power JB (1996) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in floribunda rose (Rosa hybrida L.) cvs. Trumpeter and Glad Tidings. Plant Sci. 120: 95-105
Panzer A, Hamel E, Joubert AM, Bianchi PC & Seegers JC (2000) Ukrain TM, a semisynthetic Chelidonium majus alkaloid derivative, acts by inhibition of tubulin polymerization in normal and malignant cell lines. Cancer Lett. 160: 149-157
Rogelj B, Popovic T, Ritonja A, Strukelj B & Brzin J (1998) Chelidocystatin, a novel phytocystatin from Chelidonium majus. Phytochemistry 49: 1645-1649
Tome F & Colombo ML (1992) Characterization of a suspension culture of Chelidonium majus L. on growth and accumulation of sanguinarine. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 188: 116-120
Wakhlu AK & Sharma RK (1998) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Heracleum candicansWall. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 866-869
Wildi E, Schaffner W & Berger Buter K (1998) In vitro propagation of Petasites hybridus (Asteraceae) from leaf and petiole explants and from inflorescence buds. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 336-340
Woo JW, Huh GH, Ahn MY, Kim SW & Liu JR (1996) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in pedicel explant cultures of Chelidonium majus var. asiaticum. Kor. J. Plant Tiss. Cult. 23: 363-366
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., In, D., Kim, T. et al. High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in petiole and leaf explant cultures and petiole-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Hylomecon vernalis . Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 74, 163–167 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023997627578
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023997627578