Abstract
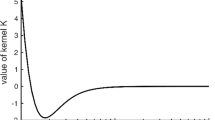
The physical meaning of the truncated geoid, which is defined by the convolution of gravity anomalies with the Stokes function on a spherical cap of specified radius, has been studied by the authors. They investigated its relation to the density distribution, generating the surface gravity, and its potential use in inversion. Some progress results for simulated studies on point mass anomalies are presented.
The behavior of the truncated geoid is controlled by the radius of the integration domain, hereinafter referred to as the truncation parameter, which is treated as a free parameter. The change of the truncated geoid in response to the change of the truncation parameter was studied in the context of the simulated mass distributions. By means of such computer simulations we have managed to demonstrate the clear sensitivity of the truncated geoid to the depths, in addition to the horizontal positions, of point mass anomalies generating the synthetic surface gravity. The objective of this paper is to illustrate, with the help of computer simulation as the method of our study, the contribution of the truncated geoid to the solution of the gravimetric inverse problem. Further work towards employing the truncated geoid in gravity exploration is being conducted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heiskanen W.A. and Moritz H., 1967: Physical Geodesy. Freeman and Company, San Francisco.
Vajda P., 1995: Truncated Geoid and the Gravimetric Inverse Problem. Ph.D. dissertation. Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, Canada
Vajda P. and Vaníček P., 1996: Truncated geoid and gravity inversion for one point mass anomaly. Submitted to Journal of Geodesy.
Vaníček P. and Krakiwsky E.J., 1986: Geodesy: The Concepts. 2nd rev.ed., North Holland Pub., Amsterdam
Vaníček P. and Kleusberg A., 1987: The Canadian geoid — Stokesian approach. Manuscripta Geodaetica, 12, 86-98.
Vaníček P., Wells D., Derenyi E., Kleusberg A., Yazdani R., Arsenault T., Christou N., Mntha J. and Pagiatakis S., 1987: Satellite Altimetry Applications for Marine Gravity. Technical report No. 128, Dept. of Surveying Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, N.B., Canada.
Vaníček P., Kleusberg A., Martinec Z., Sun W., Ong P., Najafi M., Vajda P., Harrie L., Tomášek P. and ter Horst B., 1995: Compilation of a Precise Regional Geoid. Technical Report No.184, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, N.B., Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vajda, P., Vaníček, P. On Gravity Inversion for Point Mass Anomalies by Means of the Truncated Geoid. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica 41, 329–344 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023307417037
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023307417037