Abstract
Purpose. To study the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), lung resistance-related protein (LRP), and caveolin-1 (cav-1) in the human bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE14o-.
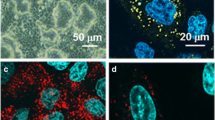
Methods. The presence of P-gp, LRP, and cav-1 in 16HBE14o- cell layers was evaluated using immunocytochemical staining and visuali- zation with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Functionality of P-gp was determined by bidirectional transport of rhodamine-123 with and without a P-gp inhibitor, verapamil. Caveolae were visualized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Flux of fluorescein-Na was also studied as a paracellular transport marker.
Results. Immunocytochemical staining showed expression of P-gp localized at the apical membrane of 16HBE14o- cell layers. The flux of rhodamine 123 across cell layers exhibited a greater P app value for the secretory (i.e., basolateral-to-apical) direction. This asymmetry disappeared in the presence of verapamil. CLSM provided evidence for the expression of LRP and cav-1. TEM further showed typically shaped caveolae at the apical and basolateral membranes.
Conclusion. Cell layers of 16HBE14o- express drug transport systems that are also present in the human bronchus in vivo, indicating that the 16HBE14o- cell line may be a suitable candidate for an in vitro model for mechanistic studies of drug transport processes involved in the smaller airways.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. S. Patton and R. M. Platz. Routes of delivery: case studies. (2) Pulmonary delivery of peptides and proteins for systemic action. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 8:179-196 (1992).
K. J. Elbert, U. F. Schaefer, H. J. Schaefers, K. J. Kim, V. H. L. Lee, and C. M. Lehr. Monolayers of human alveolar epithelial cells in primary culture for pulmonary absorption and transport studies. Pharm. Res. 16:601-608 (1999).
N. R. Mathias, F. Yamashita, and V. H. L. Lee. Respiratory epithelial cell culture models for evaluation of ion and drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Res. 22:215-249 (1996).
K. J. Kim, Z. Borok, and E. D. Crandall. A useful in vitro model for transport studies of alveolar epithelial barrier. Pharm. Res. 18:253-255 (2001).
K. A. Foster, M. L. Avery, M. Yazdanian, and K. L. Audus. Characterization of the Calu-3 cell line as a tool to screen pulmonary drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 208:1-11 (2000).
A. L. Cozens, M. J. Yezzi, K. Kunzelmann, T. Ohrui, L. Chin, K. Eng, W. E. Finkbeiner, J. H. Widdicombe, and D. C. Gruenert. CFTR expression and chloride secretion in polarized immortal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 10:38-47 (1994).
B. Forbes. Human airway epithelial cell lines for in vitro drug transport and metabolism studies. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 3:18-27 (2000).
B. Forbes, S. Lim, G. P. Martin, and M. B. Brown. An in vitro technique for evaluating inhaled nasal delivery systems. S.T.P. Pharm. 12:75-79 (2002).
C. Ehrhardt, C. Kneuer, J. Fiegel, J. Hanes, U. F. Schaefer, K. J. Kim, and C. M. Lehr. Influence of apical fluid volume on the development of functional cellular junctions in the human bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE14o-: implications for the use of this cell line as an in vitro model for bronchial drug absorption studies. Cell Tissue Res. 308:391-400 (2002).
V. J. Wacher, L. Salphati, and L. Z. Benet. Active secretion and enterocytic drug metabolism barriers to drug absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Res. 46:89-102 (2001).
Z. P. Pavelic, J. Reising, L. Pavelic, D. J. Kelley, P. J. Stambrook, and J. L. Gluckman. Detection of P-glycoprotein with four monoclonal antibodies in normal and tumor tissue. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 119:753-757 (1993).
E. Lechapt-Zalcman, I. Hurbain, R. Lacave, F. Commo, T. Urban, M. Antoine, B. Milleron, and J. F. Bernaudin. MDR 1-Pgp 170 expression in human bronchus. Eur. Respir. J. 10:1837-1843 (1997).
G. L. Scheffer, P. L. Wijngaard, M. J. Flens, M. A. Izquierdo, M. L. Slovak, H. M. Pinedo, C. J. Meijer, H. C. Clevers, and R. J. Scheper. The drug resistance-related protein LRP is the human major vault protein. Nat. Med. 1:578-582 (1995).
N. L. Kedersha, J. E. Heuser, D. C. Chugani, and L. H. Rome. Vaults. III. Vault ribonucleoprotein particles open into flower-like structures with octagonal symmetry. J. Cell Biol. 112:225-235 (1991).
G. L. Scheffer, A. B. Schroeijers, M. A. Izquierdo, E. A. C. Wiemer, and R. J. Scheper. Lung resistance-related protein/major vault protein and vaults in multidrug-resistant cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 12:550-556 (2000).
I. Sugawara, S. Akiyama, R. J. Scheper, and S. Itoyama. Lung resistance protein (LRP) expression in human normal tissue in comparison with that of MDR and MRP. Cancer Lett. 112:23-31 (1997).
S. Rybarova, M. Batekova, I. Hodorova, A. Mirossay, D. Kluchova, N. Bobrov, and M. Kocisova. Immunohistochemical detection of LRP protein in the normal human lung. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 102:66-72 (2001).
E. B. Inman. Visualization of vaults in living cells through fusion of rat major vault protein (MVP) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Aequoria victoria. Thesis, U.C.L.A., Los Angeles, California (1999).
S. Meschini, M. Marra, A. Calcabrini, E. Monti, M. Gariboldi, E. Dolfini, and G. Arancia. Role of the lung resistance-related protein (LRP) in the drug sensitivity of cultured tumor cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 16:389-398 (2002).
G. R. Newman, L. Campbell, C. von Ruhland, B. Jasani, and M. Gumbleton. Caveolin and its cellular and subcellular immunolocalisation in lung alveolar epithelium: Implications for alveolar epithelial type I cell function. Cell Tissue Res. 295:111-120 (1999).
C. Racine, M. Bélanger, H. Hirabayashi, M. Boucher, J. Chakir, and J. Couet. Reduction of caveolin 1 gene expression in lung carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 255:580-586 (1999).
W. Schubert, P. G. Frank, B. Razani, D. S. Park, C. W. Chow, and M. P. Lisanti. Caveolae-deficient endothelial cells show defects in the uptake and transport of albumin in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 276:48619-48622 (2001).
M. Gumbleton, A. G. Abulrob, and L. Campbell. Caveolae: An alternative membrane transport compartment. Pharm. Res. 17:1035-1048 (2000).
L. Pelkmans and A. Helenius. Endocytosis via caveolae. Traffic 3:311-320 (2002).
P. Thomsen, K. Roepstorff, M. Stahlhut, and B. van Deurs. Caveolae are highly immobile plasma membrane microdomains, which are not involved in constitutive endocytic trafficking. Mol. Biol. Cell 13:238-250 (2002).
M. Sargiacomo, P. E. Scherer, Z. L. Tang, E. Kübler, K. S. Song, M. C. Sanders, and M. P. Lisanti. Oligomeric structure of caveolin: Implications for caveolae membrane organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:9407-9411 (1995).
K. O. Hamilton, G. Backstrom, M. A. Yazdanian, and K. L. Audus. P-glycoprotein efflux pump expression and activity in Calu-3 cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 90:647-658 (2001).
R. J. Scheper, H. J. Broxterman, G. L. Scheffer, K. Kaaijk, W. S. Dalton, T. H. van Heijningen, C. K. van Kalken, M. L. Slovak, E. G. de Vries, and P. van der Valk. Overexpression of a M(r) 110,000 vesicular protein in non-P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 53:1475-1479 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrhardt, C., Kneuer, C., Laue, M. et al. 16HBE14o- Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Layers Express P-Glycoprotein, Lung Resistance-Related Protein, and Caveolin-1. Pharm Res 20, 545–551 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023230328687
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023230328687