Abstract
Purpose
The peptide transporter PEPT2 is expressed in alveolar type II epithelial cells. So far, however, no appropriate alveolar epithelial cell line for studying PEPT2 function has been known. In this study, we examined the functional expression of PEPT2 in the human distal lung epithelial cell line NCl-H441 (H441).
Methods
Expression of PEPT2 mRNA and protein was examined in H441 cells. Transport function of PEPT2 was studied using glycylsarcosine (Gly-Sar) as a substrate.
Results
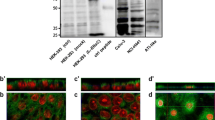
Lamellar bodies were well developed in H441 cells and mRNA expression of type II cell markers and PEPT2 increased during time in culture. PEPT2 protein expression was confirmed in H441 cells, but not in A549 cells, by immunostaining and Western blotting. The uptake of Gly-Sar in H441 cells was inhibited by cefadroxil, and the cefadroxil-sensitive uptake was pH-dependent and peaked at pH 6.5. Gly-Sar uptake in H441 cells showed saturation kinetics with a K m value of 112.5 μM. In addition, apical-to-basal, but not basal-to-apical, transport of cephalexin across H441 cell monolayers was sensitive to cefadroxil.
Conclusions
PEPT2 is functionally expressed in H441 cells, making the cell line a good in vitro model to study PEPT2 function and its regulation in human distal lung.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3OMG:
-
3-O-Methyl-D-glucose
- ABCA3:
-
ATP-binding cassette A3
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
- DEX:
-
Dexamethasone
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- Gly-Sar:
-
Glycylsarcosine
- H441:
-
NCl-H441
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- ITS:
-
Insulin-transferrin-sodium selenite
- LysoTracker Red:
-
Lyso-Tracker® Red DND-99
- NOD1:
-
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 1
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- rBBM:
-
Renal brush-border membrane
- SP-C:
-
Surfactant protein C
- TEER:
-
Transepithelial electrical resistance
- γ-iE-DAP:
-
γ-D-Glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid
References
Patton JS. Mechanisms of macromolecule absorption by the lungs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1996;19:3–36.
Takano M, Aoki A, Kawami M, Yumoto R. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of macromolecules and strategy to enhance their transport in alveolar epithelial cells. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12(5):813–25.
Patton JS, Brain JD, Davies LA, Fiegel J, Gumbleton M, Kim KJ, et al. The particle has landed--characterizing the fate of inhaled pharmaceuticals. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010;23 Suppl 2:S71–87.
Gumbleton M, Al-Jayyoussi G, Crandon-Lewis A, Francombe D, Kreitmeyr K, Morris CJ, et al. Spatial expression and functionality of drug transporters in the intact lung: objectives for further research. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(1–2):110–8.
Bur M, Huwer H, Lehr CM, Hagen N, Guldbrandt M, Kim KJ, et al. Assessment of transport rates of proteins and peptides across primary human alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;28(3):196–203.
Ikehata M, Yumoto R, Nakamura K, Nagai J, Takano M. Comparison of albumin uptake in rat alveolar type II and type I-like epithelial cells in primary culture. Pharm Res. 2008;25(4):913–22.
Daniel H, Kottra G. The proton oligopeptide cotransporter family SLC15 in physiology and pharmacology. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447(5):610–8.
Brandsch M, Knütter I, Bosse-Doenecke E. Pharmaceutical and pharmacological importance of peptide transporters. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2008;60(5):543–85.
Boll M, Herget M, Wagener M, Weber WM, Markovich D, Biber J, et al. Expression cloning and functional characterization of the kidney cortex high-affinity proton-coupled peptide transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(1):284–9.
Saito H, Terada T, Okuda M, Sasaki S, Inui K. Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of rat peptide transporter PEPT2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1280(2):173–7.
Newstead S. Towards a structural understanding of drug and peptide transport within the proton-dependent oligopeptide transporter (POT) family. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011;39(5):1353–8.
Terada T, Saito H, Mukai M, Inui K. Recognition of beta-lactam antibiotics by rat peptide transporters, PEPT1 and PEPT2, in LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(5 Pt 2):F706–11.
Biegel A, Knütter I, Hartrodt B, Gebauer S, Theis S, Luckner P, et al. The renal type H+/peptide symporter PEPT2: structure-affinity relationships. Amino Acids. 2006;31(2):137–56.
Groneberg DA, Nickolaus M, Springer J, Döring F, Daniel H, Fischer A. Localization of the peptide transporter PEPT2 in the lung: implications for pulmonary oligopeptide uptake. Am J Pathol. 2001;158(2):707–14.
Groneberg DA, Eynott PR, Döring F, Dinh QT, Oates T, Barnes PJ, et al. Distribution and function of the peptide transporter PEPT2 in normal and cystic fibrosis human lung. Thorax. 2002;57(1):55–60.
Takano M, Horiuchi T, Sasaki Y, Kato Y, Nagai J, Yumoto R. Expression and function of PEPT2 during transdifferentiation of alveolar epithelial cells. Life Sci. 2013;93(17):630–6.
Sakagami M. In vivo, in vitro and ex vivo models to assess pulmonary absorption and disposition of inhaled therapeutics for systemic delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58(9–10):1030–60.
Forbes B, Ehrhardt C. Human respiratory epithelial cell culture for drug delivery applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;60(2):193–205.
Hermanns MI, Unger RE, Kehe K, Peters K, Kirkpatrick CJ. Lung epithelial cell lines in coculture with human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells: development of an alveolo-capillary barrier in vitro. Lab Invest. 2004;84(6):736–52.
Shlyonsky V, Goolaerts A, Van Beneden R, Sariban-Sohraby S. Differentiation of epithelial Na+ channel function. An in vitro model. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(25):24181–7.
Salomon JJ, Muchitsch VE, Gausterer JC, Elena S, Huwer H, Daum N, et al. The cell line NCl-H441 is a useful in vitro model for transport studies of human distal lung epithelial barrier. Mol Pharm. 2014;11:995–1006.
Yumoto R, Suzuka S, Nishimoto S, Nagai J, Takano M. Enhancing effect of poly(amino acid)s on albumin uptake in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;28(6):497–503.
Kawami M, Miyamoto M, Yumoto R, Takanno M. Methotrexate influx via folate transporters into alveolar epithelial cell line A549. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.dmpk.2015.04.005.
Nagai J, Komeda T, Katagiri Y, Yumoto R, Takano M. Characterization of protamine uptake by opossum kidney epithelial cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(12):1942–9.
Fujii K, Nagai J, Sawada T, Yumoto R, Takano M. Effect of PEGylation of N-WASP181-200 on the inhibitory potency for renal aminoglycoside accumulation. Bioconjug Chem. 2009;20(8):1553–8.
Yamano G, Funahashi H, Kawanami O, Zhao LX, Ban N, Uchida Y, et al. ABCA3 is a lamellar body membrane protein in human lung alveolar type II cells. FEBS Lett. 2001;508(2):221–5.
Goodman BE, Crandall ED. Dome formation in primary cultured monolayers of alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1982;243(1):C96–C100.
Matthay MA, Folkesson HG, Clerici C. Lung epithelial fluid transport and the resolution of pulmonary edema. Physiol Rev. 2002;82(3):569–600.
Lieber M, Smith B, Szakal A, Nelson-Rees W, Todaro G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 1976;17(1):62–70.
Yumoto R, Nishikawa H, Okamoto M, Katayama H, Nagai J, Takano M. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of FITC-albumin in alveolar type II epithelial cell line RLE-6TN. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290(5):L946–55.
Takano M, Horiuchi T, Nagai J, Yumoto R. Effect of cigarette smoke extract on insulin transport in alveolar epithelial cell line A549. Lung. 2012;190(6):651–9.
Takano M, Yamamoto C, Sambuichi K, Oda K, Nagai J, Shimamoto A, et al. Introduction of a single transporter gene ABCA3 directs RLE-6TN to more type II-like alveolar epithelial cells. Membrane. 2013;38(5):246–53.
Gazdar AF, Linnoila RI, Kurita Y, Oie HK, Mulshine JL, Clark JC, et al. Peripheral airway cell differentiation in human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990;50(17):5481–7.
Hermanns MI, Fuchs S, Bock M, Wenzel K, Mayer E, Kehe K, et al. Primary human coculture model of alveolo-capillary unit to study mechanisms of injury to peripheral lung. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;336(1):91–105.
Neuhaus W, Samwer F, Kunzmann S, Muellenbach RM, Wirth M, Speer CP, et al. Lung endothelial cells strengthen, but brain endothelial cells weaken barrier properties of a human alveolar epithelium cell culture model. Differentiation. 2012;84(4):294–304.
Sala-Rabanal M, Loo D, Hirayama B, Wright E. Molecular mechanism of dipeptide and drug transport by the human renal H+/oligopeptide cotransporter hPEPT2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294(6):F1422–32.
Sakamoto A, Matsumaru T, Yamamura N, Suzuki S, Uchida Y, Tachikawa M, et al. Drug transporter protein quantification of immortalized human lung cell lines derived from tracheobronchial epithelial cells (Calu-3 and BEAS2-B), bronchiolar-alveolar cells (NCI-H292 and NCI-H441), and alveolar type II-like cells (A549) by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Sci. 2015. doi:10.1002/jps.24381.
Søndergaard HB, Brodin B, Nielsen CU. hPEPT1 is responsible for uptake and transport of Gly-Sar in the human bronchial airway epithelial cell-line Calu-3. Pflugers Arch. 2008;456(3):611–22.
Smith DE, Clémençon B, Hediger MA. Proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter family SLC15: physiological, pharmacological and pathological implications. Mol Asp Med. 2013;34(2–3):323–36.
Terada T, Sawada K, Saito H, Hashimoto Y, Inui K. Functional characteristics of basolateral peptide transporter in the human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Am J Physiol. 1999;276(6 Pt 1):G1435–41.
Terada T, Sawada K, Ito T, Saito H, Hashimoto Y, Inui K. Functional expression of novel peptide transporter in renal basolateral membranes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;279(5):F851–7.
Putnam WS, Pan L, Tsutsui K, Takahashi L, Benet LZ. Comparison of bidirectional cephalexin transport across MDCK and caco-2 cell monolayers: interactions with peptide transporters. Pharm Res. 2002;19(1):27–33.
Swaan PW, Bensman T, Bahadduri PM, Hall MW, Sarkar A, Bao S, et al. Bacterial peptide recognition and immune activation facilitated by human peptide transporter PEPT2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008;39(5):536–42.
Barton JL, Berg T, Didon L, Nord M. The pattern recognition receptor Nod1 activates CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta signalling in lung epithelial cells. Eur Respir J. 2007;30(2):214–22.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND DISCLOSURES
We thank the Analysis Center of Life Science, the Institute of Laboratory Animal Science, and the Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development, Hiroshima University for the use of their facilities. We also thank Ms. C. Yamamoto and Mr. J. Deguchi for their helpful assistance in working on this study. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takano, M., Sugimoto, N., Ehrhardt, C. et al. Functional Expression of PEPT2 in the Human Distal Lung Epithelial Cell Line NCl-H441. Pharm Res 32, 3916–3926 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-015-1751-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-015-1751-x