Abstract
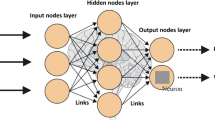
A neural network approach is presented for the estimation of shrinkage during a hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process of nickel-based superalloys for near net-shape manufacture. For the HIP process, the change in shape must be estimated accurately; otherwise, the finished piece will need excessive machining and expensive nickel-based alloy powder will be wasted (if shrinkage is overestimated) or the part will be scrapped (if shrinkage is underestimated). Estimating shape change has been a very difficult task in the powder metallurgy industry and approaches range from rules of thumb to sophisticated finite element models. However, the industry still lacks a reliable and general way to accurately estimate final shape. This paper demonstrates that the neural network approach is promising to estimate post-HIP dimensions from a combination of pre-HIP dimensions, powder characteristics and processing information. Compared to nonlinear regression models to estimate shrinkage, the neural network models perform very well. Furthermore, the models described in this paper can be used to find good HIP process settings, such as temperature and pressure, which can reduce operating costs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, H. V. and Davies, S. (2000) Fundamental aspects of hot isostatic pressing: an overview. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 31(12), 2981-3000.
Atkinson, H. V. and Rickinson, B. A. (1991) Hot Isostatic Processing, Galliard (Printers) Ltd., Norfolk, UK.
Cherian, R. P., Smith, L. N. and Midha, P. S. (2000) A neural network approach for selection of powder metallurgy materials and process parameters. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, 14, 39-44.
Coit, D. W., Jackson, B. T. and Smith, A. E. (1998) Static neural network process models: considerations and case studies. International Journal of Production Research, 36(11), 2953-2967.
Cook, D. F. and Chiu, C.-C. (1998) Using radial basis function neural networks to recognize shifts in correlated manufacturing process parameters. IIE Transactions, 30, 227-234.
Delo, D. P., Dutton, R. E., Semiatin, S. L. and Piehlier, H. R. (1999) Modeling of hot isostatic pressing and hot triaxial compaction of Ti-6A1-4V powder, Acta Mater., 47(11), 3159-3167.
Funahashi, K. (1989) On the approximate realization of continuous mappings by neural networks. Neural Networks, 2, 183-192.
Garibov, G. S., Samarov, V. N. and Feigin, V. I. (1979) Design of capsules for the hot hydrostatic pressing of disks from heat-resisting nickel alloy powders. Soviet Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 18(2), 136-140.
Geman, S., Bienenstock, E. and Doursat, R. (1992) Neural networks and the bias/variance dilemma, Neural Computation, 4, 1-58.
German, R. M. (1984) Powder Metallurgy Science, Metal Powder Industries Federation.
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M. and White, H. (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Networks, 2, 359-366.
Kalpakjian, S. (1995) Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc., Reading, MA.
Katz, Z. and Naude, J. (1999) A neural network/expert system approach for design improvement of products manufactured by EDM. Transactions of the ASME, Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 121, 733.
Khazami-Zadeh, M. and Petzoldt, F. (1995) Hot isostatic pressing of near net shape parts through finite element simulation. Advances in Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials Proceedings of the 1995 International Conference & Exhibition on Powder Metallurgy & Particulate Materials, 2, 5/125-5/138.
Kyeong, K. L., Brown, T., Dagnall, G., Bicknell-Tassius, R., Brown, A. and May, G. S. (2000) Using neural networks to construct models of the molecular beam epitaxy process. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 13(1), 34-45.
MPIF (2001) web site: http://www.mpif.org.
NCEMT (2001) web site: http://www.ncemt.ctc.com/modsim/hip.
Nissen, A., Jaktlund, L.-L., Tegman, R. and Garvare, T. (1989) Rapid computerized modeling of the final shape of HIPed axisymmetric containers. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Hot Isostatic Pressing: Theory and Applications, pp. 55-61.
Olevsky, E., Maximenko, A., Van Dyck, S, Froyen, L., Delaey, L. and Buekenhout, L. (1998) Container influence on shrinkage under HIP-I. shrinkage anisotropy of a cylindrical specimen. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 35(18), 2283-2303.
Raj, K. H., Sharma, R. S., Srivastava, S. and Patvardhan, C. (2000) Modeling of manufacturing processes with ANNs for intelligent manufacturing. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 40, 851-868.
Sathyanarayanan, G., Lin, I. J. and Chen, M.-K. (1992) Neural network modeling and multiobjective optimization of creep feed grinding of superalloys. International Journal of Production Research, 30, 2421-2438.
Schlang, M., Poppe, T. and Gramchow, O. (1996) Neural networks for steel manufacturing. IEEE Expert, August 1996, 8-9.
Smith, A. E. (1993) Predicting product quality with backpropagation: A thermoplastic injection molding case study. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 8, 252-257.
Smith, L. N. and Midha, P. S. (1999) A knowledge based system for optimum and concurrent design, and manufacture by powder metallurgy technology. International Journal of Production Research, 37(1), 125-137.
Twomey, J. M. and Smith A. E. (1998) Bias and variance of validation methods for function approximation neural networks under conditions of sparse data. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C, 28, 417-430.
Udo, G. J. (1992) Neural network applications in manufacturing processes. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 23, 97-100.
Wilson, R. K., Flower, H. L., Hack, G. A. J. and Isobe, S. (1996) Nickel-base alloys for severe environments. Advanced Materials & Processes, 3, 19-22.
Zhang, H.-C. and Huang, S. H. (1995) Applications of neural networks in manufacturing: A state-of-the-art survey. International Journal of Production Research, 33, 705-728.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konak, A., Kulturel-Konak, S., Smith, A.E. et al. Estimation of shrinkage for near net-shape using a neural network approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 14, 219–228 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022907615088
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022907615088