Abstract
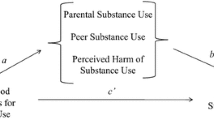
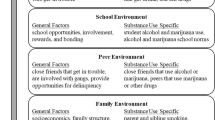
In considering the influences of microsystems on adolescent substance use, familial and peer contexts have received the most extensive attention in the research literature. School and neighborhood settings, however, are other developmental contexts that may exert specific influences on adolescent substance use. In many instances, school settings are organized to provide educational services to students who share similar educational abilities and behavioral repertoires. The resulting segregation of students into these settings may result in different school norms for substance use. Similarly, neighborhood resources, including models for substance use and drug sales involvement, may play an important role in adolescent substance use. We briefly review literature examining contextual influences on adolescent substance use, and present results from two preliminary studies examining the contribution of school and neighborhood context to adolescent substance use. In the first investigation, we examine the impact of familial, peer, and school contexts on adolescent substance use. Respondents were 283 students (ages 13 to 18) from regular and special education classrooms in six schools. Although peer and parental contexts were important predictors of substance use, school norms for drug use accounted for variance in adolescent use beyond that explained by peer and parental norms. Data from a second study of 114 adolescents (mean age = 15) examines neighborhood contributions to adolescent substance use. In this sample, neighborhood indices did not contribute to our understanding of adolescent substance use. Implications for prevention are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1983). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist. Burlington, VT: Author.
Allison, K. W., Burton, L., Marshall, S., Perez-Feblez, A., Yarrington, J., Kirsh, L. B., & Merriwether-DeVries, C. (in press). Life experiences among urban adolescents: Examining the role of context. Child Development.
Allison, K. W., & Richardson, K. A. (1989). Annotated bibliography of substance abuse among handicapped, disabled, and high risk individuals and treatment resources for the handicapped or disabled substance abuser. College Park: University of Maryland Department of Special Education.
Barnea, Z., Teichman, M., & Rahav, G. (1992). Personality, cognitive, and interpersonal factors in adolescent substance abuse: A longitudinal test of an integrative model. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 21, 187-201.
Barnes, G. M., Farrell, M. P., & Banerjee, S. (1994). Family influences on alcohol abuse and other problem behaviors among Black and White adolescents in a general population sample. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 4(2), 183-201.
Barnes, G. M., & Welte, J. H. (1986). Patterns and predictors of alcohol use among 7–12th grade students in New York State. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 47, 53-62.
Bauman, K. E., Botvin, G. J., Botvin, E. M., & Baker, E. (1992). Normative expectations and the behavior of significant others: An integration of traditions in research on adolescent cigarette smoking. Psychological Reports, 71, 568-570.
Blackwell, J. E. (1991). The Black community: Diversity and unity. New York: Harper Collins.
Blane, H. T. (1982–1983). Problem drinking in delinquent and nondelinquent adolescent males. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 9, 221-232.
Blount, W., & Dembo, R. (1984). Personal drug and attitudes toward prevention among youth living in a high risk environment. Journal of Drug Education, 14, 207-225.
Botvin, G. J., Botvin, E. M., Baker, E., Dusenbury, L., & Goldberg, C. J. (1992). The false consensus effect: Predicting adolescents' tobacco use from normative expectations. Psychological Reports, 70, 171-178.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1986). Ecology of the family as a context for human development: Research perspectives. Developmental Psychology, 22, 723-742.
Bronfenbrenner, U., Moen, P., & Garbarino, J. (1984). Child, Family, and Community. In R. Parke (Ed.), Review of Child Development Research (Vol 7, pp. 283-328). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Brook, J. S., Nomura, C., & Cohen, P. (1988). A network of influences on adolescent drug involvement: Neighborhood, school, peer, and family. Genetic, Social and General Psychology Monographs 115, 125-145.
Brooks, J. S., Lukoff, I. F., & Whiteman, M. (1977). Correlates of marijuana use as related to age, sex and ethnicity. Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine, 50, 383-390.
Burton, L. M. (1987). Intergenerational relationships and adolescent childbearing: Socioeconomic context and family transitions (Contract No. 5929MH46057-02). Washington, DC: National Institute of Mental Health.
Burton, L. M., Price-Spratlen, T., & Spencer, M. B. (1997). On ways of thinking about measuring neighborhoods: Implications for studying context and developmental outcomes for children. In J. Brooks-Gunn, G. J. Duncan, & J. L. Aber (Eds.), Neighborhood poverty: Context and consequences for children. New York: Russell Sage Foundation Press.
Calhoun, T., Parker, K. D., & Weaver, G. (1995). Attitudes of African American toward drugs in the community: A multivariate analysis. Western Journal of Black Studies, 19, 143-148.
Carroll, C. R. (1993). Drugs in modern society (3rd ed.). Dubuque, IA: Brown and Benchmark.
Chassin, L. (1984). Adolescent substance use and abuse. Advances in Child Behavioral Analysis & Therapy, 139, 9-152.
Clements, J. E., & Simpson, R. (1978). Environmental and behavioral aspects of glue sniffing in a population of emotionally disturbed adolescents. International Journal of the Addictions, 13, 129-134.
Compas, B., Davis, G. E., Forsythe, C. J., & Wagner, B. M. (1987). Assessment of major and daily life stressful events during adolescence: The Adolescent Perceived Events Scale. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55, 534-541.
Coombs, R. H. (Ed.). (1988). The family context of adolescent Drug use. New York: Haworth.
Coombs, R. H., & Landsverk, J. (1988). Parenting styles and substance use during childhood and adolescence. Journal of Marriage and Family, 50, 473-482.
Coombs, R. H., Paulson, M. J., & Richardson, M. A. (1991). Peer vs. parental influence in substance use among Hispanic and Anglo children and adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 20, 73-88.
Crane, J. (1991). The epidemic theory of ghettos and neighborhood effects on dropping out and teenage child bearing. American Journal of Sociology, 96, 1126-1260.
Dembo, R., Hughes, P., Jackson, L., & Mieczkkowski, T. (1993). Crack cocaine dealing by adolescents in two public housing projects: A pilot study. Human Organization, 52, 89-96.
Denton, R. E., & Kampfe, C. (1994). The relationship between family variables and adolescent substance abuse: A literature review. Adolescence, 29, 475-495.
De Obaldia, R., & Parsons, O. A. (1984). Relationship of neuropsychological performance to primary alcoholism and self-reported symptoms of childhood minimal brain dysfunction. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 45, 386-392.
Dishion, T., Capaldi, D., Sprackelen, K., & Li, F. (1995). Peer ecology of male adolescent drug use. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 803-824.
Dishion, T. J., Patterson, G. R. & Reid, J. R. (1988). Parent and peer factors associated with drug sampling in early adolescence: implications and treatment. Adolescent Drug Abuse: Analysis, Treatment, Research (NIDA Research Monograph). Washington DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Elliot, D. S., Huizinga, D., & Ageton, S. S. (1982). Explaining delinquency and drug use (Report No. 21). Boulder, CO: Behavioral Research Institute.
Elmquist, D. L., Morgan, D. P., & Bolds, P. K. (1992). Alcohol and other drug use among adolescents with disabilities. International Journal of the Addictions, 27, 1475-1483.
Ensminger, M. E., Lamkin, R. P., & Jacobson, N. (1996). School leaving: A longitudinal perspective including neighborhood effects. Child Development, 67, 2400-2416.
Entwistle, D. R., Alexander, K. L., & Olson, L. S. (1992). The gender gap in math: Its possible origins in neighborhood effects. American Sociological Review, 57, 822-838.
Fagan, J., & Chin, K. (1990). Violence as a regulation and social control in the distribution of crack. In M DeLaRosa, E. Y. Lambert, & B. Gropper (Eds.), Drugs and violence: Causes, correlates, and consequences (NIDA Research Monograph No. 103, pp. 8-43). Rockville, MD: NIDA.
Fawzy, I., Coombs, R. H., & Gerber, B. (1983). Generational continuity in the use of substances: The impact of parental substance use on adolescent substance use. Addictive Behaviors, 8, 109-114.
Feigelman, S., Stanton, B. F., & Ricardo, I. (1993) Perceptions of drug selling and drug use among urban youths. Journal of Early Adolescence, 13, 267-284.
Foxcroft, D., & Lowe, G. (1995). Adolescent drinking, smoking and other substance use involvement: links with perceived family life. Journal of Adolescence, 18, 159-177.
Fergusson, D. M., Horwood, L. J., & Lynskey, M. T. (1993). Prevalence and comorbidity of DSM-III-R diagnoses in a birth cohort of 15 years olds. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 32, 1127-1134.
Gorusch, R. L., & Butler, M. C. (1976). Initial drug abuse: A review of predisposing social-psychological factors. Psychological Bulletin, 83, 120-137.
Grilo, C. M., Becker, D. F., Fehon, D. C., & Edell, W. S. (1996). Conduct disorder, substance use disorders, and coexisting conduct and substance use disorders in adolescent inpatients. American Journal of Psychiatry, 153, 914-920.
Guba, E. G., & Lincoln, Y. S. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Hansen, W. B., & Graham, J. W. (1991). Preventing alcohol, marijuana, and cigarette use among adolescents: Peer pressure resistance training versus establishing conservative norms. Preventive Medicine, 20, 414-430.
Hirschi, T. (1969). Causes of delinquency. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Huang, A. M. (1981). The drinking behavior of the educable mentally retarded and nonretarded students. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education, 26, 41-50.
Huba, G. J., Wingard, J. A., & Bentler, P. M. (1979). Beginning adolescent drug use and peer and adult interaction patterns. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 47, 265-276.
Jessor, R., & Jessor, S. L. (1978). Theory testing in longitudinal research on marijuana use. In D. Kandel (Ed.), Longitudinal research on drug use: Empirical findings and methodological issues. Washington, DC: Hemisphere.
Kandel, D. (1978). Convergence in prospective longitudinal surveys of drug use in normal populations. In D. B. Kandel (Ed.), Longitudinal research on drug use: Empirical findings and methodological issues. New York: Halstead.
Kandel, D. B. (1980). Drug and drinking behavior among youth. Annual Review of Sociology, 6, 235-285.
Kandel, D. B., & Andrews, K. (1987). Processes of adolescent socialization by parents and peers. International Journal of the Addictions, 22, 319-342.
Kandel, D., Kessler, R., & Margulies, R. (1978). Adolescent initiation into stages of drug use: A developmental analysis. In D. Kandel (Ed.), Longitudinal research on drug use: Empirical findings and methodological issues (pp. 73-100). Washington, DC: Hemisphere-Wiley.
Kashani, J. H., Keller, M. B., Solomon, Reid, J. C., & Mazzola, D. (1985). Double depression in adolescent substance users. Journal of Affective Disorders, 8, 153-157.
Klein, R. G., & Mannuzza, S. (1991). Long-term outcome of hyperactive children: A review. Special Section: Longitudinal research. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 383-387.
Leone, P. E. (1991). Adolescent and other drugs: Use abuse and disabilities. Reston VA: Council for Exceptional Children.
Leone, P. E., Greenburg, J. M., Trickett, E. J., & Spero, E. (1989). A study of the use of cigarettes, alcohol, and marijuana by students identified as seriously emotionally disturbed. Counterpoint, 9, 6-7.
Leone, P., Moss-Greenburg, J., Trickett, E. J., Gould, J., & O'Neil, J. (1987). Substance abuse among handicapped adolescents. Unpublished manuscript.
Lie, G. Y. (1984). A longitudinal and multivariate study of adolescent alcohol involvement. Dissertation Abstracts International, 46, 264A.
Lund, C. A., & Landesman-Dwyer, S. (1979). Pre-delinquent and disturbed adolescents: the role of parental alcoholism. In M. Galanter (Ed.), Currents in alcoholism (Vol. 5, pp. 339-348). NY: Grune and Stratton.
Maddahain, E., Newcomb, M. D., & Bentler, P. M. (1985). Single and multiple patterns of adolescent substance use: Longitudinal comparisons of four ethnic groups. Journal of Drug Education, 15, 311-326.
Martin, M., & Pritchard, M. (1991). Factors associated with alcohol use in later adolescence. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 52, 5-9.
Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, Drug Abuse Administration. (1985). State of Maryland Adolescent Drug Survey.
Mayer, J. E. (1980). Adolescents alcohol misuse: A family systems perspective. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education, 26, 1-11.
Mayer, S. E., & Jencks, C. (1989). Growing up in poor neighborhood: How much does it matter? Science, 243, 1441-1445.
Morrison, J. R. (1979). Diagnosis of adult psychiatric patients with childhood hyperactivity. American Journal of Psychiatry, 136, 955-958.
Mounts, N., & Steinberg, L. (1995). An ecological analysis of peer influence on adolescent grade point average and drug use. Developmental Psychology, 31, 915-922.
Needle, R., McCubbin, H., Wilson, M., Reineck, R., Lazar, A., & Mederer, H. (1986). Interpersonal influences in adolescent drug use-the role of older siblings, parents, and peers. International Journal of the Addictions, 21, 739-766.
Nurco, D. N., Kinlock, T., O'Grady, K., Lerner, M., & Hanlon, T. E. (1996). Perceptions of social pathology in the neighborhood and the etiology of narcotic addiction: A retrospective study. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 184, 35-42.
O'Connell, D. L., Alexander, H. M., Dobson, A. J., Lloyd, D. M., Hardes, G. R., Springthorpe, H. S., & Leeder, S. R. (1981). Cigarette smoking and drug use in school children: 11 factors associated with smoking. International Journal of Epidemiology, 10, 223-244.
Paton, S., Kessler, R., & Kandel, D. (1977) Depressive mood and adolescent illicit drug use: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Genetic Psychology, 131, 267-289.
Pressons, C. C., Chassin, L., Sherman, S. J., Olshavsky, R., Bensenberg, M., & Corty, E. (1984). Predictors of adolescents' intentions to smoke: Age, sex, race and regional differences. International Journal of the Addictions, 19, 503-519.
Protinsky, H., & Shilts, L. (1990). Adolescent substance use and family cohesion. amily Therapy, 17, 173-175.
Raskin, R., Novacek, J., & Hogan, R. (1992). Drug culture expertise and substance abuse. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 21, 625-637.
Raudenbush, S., & Bryk, A. (1988). Methodological advances in studying effects of schools and classrooms on student learning. Review of Research in Education, Vol 15, pp. 423-475. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association.
Reichler, B. D., Clement, J. L., & Dunner, D. L. (1983). Chart review of alcohol problems in adolescent psychiatric patients in an emergency room. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 44, 338-339.
Scheier, L. M., & Newcomb, M. D. (1991). Differentiation of early adolescent predictors of drug use initiation and escalation: A developmental risk model. Journal of Substance Abuse, 3, 277-299.
Scott, J. W., & Black, A. (1989). Deep structures of African American family life: Female and male kin networks. Western Journal of Black Studies, 13, 17-24.
Segal, B., & Stewart, J. (1996). Substance use and abuse in adolescence: An overview. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 26(4), 193-210.
Shifts, L., (1991). The relationship of early adolescent substance use to extracurricular activities, peer influence, and personal attitudes. Adolescence, 26, 613-617.
Smart, R. G., Adlaf, E. M., & Walsh, G. W. (1994). Neighborhood socio-economic factors in relation to student drug use and programs. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse, 3, 37-46.
Spencer, M.B., McDermott, P. A., Burton, L. M., & Cole, S. P. (1997). An alternative approach to assessing neighborhood effects. In J. Brooks-Gunn, G. J. Duncan, & J. L. Aber (Eds.), Neighborhood poverty: Context and consequences for children. New York: Russell Sage Foundation Press.
Stephenson, A. L., Henry, C., & Robinson, L. (1996). Family characteristics and adolescent substance use. Adolescence, 31, 59-77.
Tarter, R. E., McBride, H., Buonpane, N., & Schneider, D. U. (1977). Differentiation of alcoholics. Archives of General Psychiatry, 34, 761-768.
Thompson, L. L., Riggs, P. D., Mikulich, S. K., & Crowley, T. J. (1996). Contribution of ADHD symptoms to substance problems and delinquency in conduct-disordered adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24, 325-347.
U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of the Census. (1993). Census of population and housing. 1990 (Summary Tape 3A computer file). Washington, DC: Author.
Van Kammen, W. B., Loeber, R., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1991). Substance use and its relationship to conduct problems and delinquency in young boys. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 20, 399-413.
Way, N., Stauber, H. Y., Nakkula, M. J., & London, P. (1994). Depression and substance use in two divergent high school cultures: A quantitative and qualitative analysis. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 23, 331-337.
Welte, J., & Barnes, G. M. (1987). Alcohol use among adolescent minority groups. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 48, 329-336.
Wills, T. (1986). Stress and coping in early adolescence: Relationships to substance use in urban school samples. Health Psychology, 5, 503-529.
Wills, T. A., & Vaughn, R. (1989). Social support and substance use in early adolescence. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 12, 321-339.
Windle, M. (1990). A longitudinal study of antisocial behaviors in early adolescence as predictors of late adolescent substance use: Gender and ethnic group differences. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 99, 86-91.
Zetlin, A. G. (1985). Mentally retarded teenagers: adolescent behavior disturbance and its relation to family environment. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 15, 243-254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allison, K.W., Crawford, I., Leone, P.E. et al. Adolescent Substance Use: Preliminary Examinations of School and Neighborhood Context. Am J Community Psychol 27, 111–141 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022879500217
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022879500217