Abstract
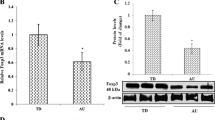
Although autism remains an enigmatic disease, there is mounting evidence that the immune system plays an important role in the pathogenesis. Immune system involvement is apparently widespread as numerous humoral and cellular abnormalities have been reported in both the innate and adaptive responses. Fas (CD95/APO-1) is a type I cell-surface protein from the TNF/NGF-R superfamily present on the surface of many immune related cells. Fas activation is instrumental in starting a complicated chain of events that results in programmed cell death (apoptosis) by DNA fragmentation. Preliminary data is presented, which indicate that subjects with austism have lower levels of Fas on their CD4+ helper T cells (p = .048) than have normal subjects. Data also indicates subjects with autism have significantly higher levels of soluble Fas (p = .01) than have normal subjects. A maturing individual must eliminate cells for proper morphogenesis to occur. Preliminary data suggest that faulty apoptosis may be involved in the pathogenesis of autism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becher, B., D'Souza, D., and Troutt, A. B. (1998). Fas expression on human fetal astrocytes without susceptibility to fas-mediated cytotoxicity. Neuroscience 84(2): 627-634.
Cohen, P. L., and Eisenberg, R. A. (1991). Lpr and gld: Single gene models of systemic autoimmunity and lymphoproliferative disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 9: 243.
Connolly, A. M., Chez, M. G., Pestronk, A., Arnold, S. T., Mehta, S., and Deuel, R. K. (1999). Serum autoantibodies to brain in Landau-Kleffner variant, autism, and other neurologic disorders. J. Pediatr. 134(5): 607-613.
Dorsam, G., Voice, J., Kong, Y., and Goetzl, E. J. (2000). Vasoactive intestinal peptide mediation of development and functions of T lymphocytes. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 921: 79-91.
Furlano, R. I., Anthony, A., Day, R., Brown, A., McGarvey, L., Thomson, M. A., Davies, S. E., Berelowitz, M., Forbes, A., Wakefield, A. J., Walker-Smith, J. A., and Murch, S. H. (2001). Colonic CD8 and gamma delta T cell infiltration with epithelial damage in children with autism. J. Pediatr. 138(3): 366-372.
Giordano, C., De Maria, R., Stassi, G., Todaro, M., Richiusa, P., Giordano, M., Testi, R., and Galluzzo, A. (1995). Defective expression of the apoptosis-inducing CD95 (FAS/APO-1) molecule on T and B cells in IDDM. Diabetologia 38: 449-1454.
Gupta, S. (2000). Immunological treatments for autism. J. Autism Dev. 30(5): 475-479.
Heard, R. (1994). HLA and autoimmune disease. In Lechler, R. (ed.), HLA and Disease, Chap. 7, Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Janeway, C. A., and Travers, P. (1997). ImmunoBiology: The Immune system in Health and Disease, 3rd edn, Garland Publishing, New York.
Jodo, S., Kobayashi, S., Kayagaki, N., Ogura, N., Feng, Y., Amasaki, Y., Fujisaku, A., Azuma, M., Yagita, H., Okumura, K., and Koike, T. (1997). Serum levels of soluble Fas/APO-1 (CD95) and its molecular structure in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and other autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 107(1): 89-95.
Messahel, S., Pheasant, A. E., Pall, H., Ahmed-Choudhury, J., Sungum-Paliwal, R. S., and Vostanis, P. (1998). Urinary levels of neopterin and biopterin in autism. Neurosci. Lett. 241: 17-20.
Musette, P. (1998). T Cells in Systemic Lupus erythematosus. Dermatology 196(3): 281-282.
Nawa, H., Takahashi, M., and Patterson, P. H. (2000). Cytokine and growth factor involvement in schizophrenia—Support for the developmental model. Mol. Psychiatry 5(6): 594-603.
Nelson, K. B., Grether, J. K., Croen, L. A., Dambrosia, J. M., Dickens, B. F., Jelliffe, L. L., Hansen, R. L., and Phillips, T. M. (2001). Neuropeptides and neurotrophins in neonatal blood of children with autism or mental retardation. Ann. Neurol. 49(5): 597-606.
Nozawa, K., Kayagaki, N., Tokano, Y., Yagita, H., Okumura, K., and Hasimoto, H. (1997). Soluble Fas (APO-1, CD95) and soluble Fas ligand in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 40(6): 1126-1129.
Plioplys, A. V., Greaves, A., Kazemi, K., and Silverman, E. (1994). Lymphocyte function in autism and Rett Syndrome. Neuropsychobiology 7: 12-16.
Potestio, M., Pawalec, G., Di Lorenzo, G., Candone, G., D'Anna, C., Gervasi, F., Lio, D., Tranchida, G., Caruso, C., and Romano, G. C. (1999). Age-related changes in the expression of CD95 (APO1/FAS) on blood lymphocytes. Exp. Gerentol. 34(5): 659-673.
Prodeus, A. P., Goerg, S., Shen, L.M., Pozdnyakova, O.O., Chu, L., Alicot, E. M, Goodnow, C. C., and Carroll, M. C. (1998). A critical role for complement in maintenance of self-tolerance. Immunity 9(5): 721-731.
Stassi, G., Todaro, M., De Maria, R., Candore, G., Cigna, D., Caruso, C., Galluzzo, A., and Giordano, C. (1997). Defective expression of CD95 (FAS/APO-1) molecule suggests impairment of T and B cells in HLA-B8, DR3-positive individuals. Hum. Immunol. 55: 39-45.
Tokano, Y., Miyake, S., Kayagaki, N., Nozawa, K., Morimoto, S., Azuma, M., Yagita, H., Takasaki, Y., Okumura, K., and Hashimoto, H. (1996). Soluble Fas molecule in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus J. Clin. Immunol. 16(5): 261-265.
Torres, A. R., Maciulis, A., and Odell, D. (2001). The association of MHC genes with autism. Front. Biosci. 6: d936-943.
Torres, A. R., Maciulis, A., Stubbs, E. G., Cutler, A., and Odell, D. (2002). The Transmission Disequilibrium Test Suggests That HLA-DR4 and DR13 are Linked to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Hum. Immunol. 63: 311-316.
Warren, R., Foster, A., and Margaretten, N. (1987). Reduced natural killer cell activity in autism. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psycho. 26: 333-335.
Warren, R. P., Odell, J. D., Warren, W. L., Burger, R. A., Maciulis, A., Daniels, W. W., and Torres, A. R. (1997). Brief Report: Immunoglobulin A deficiency in a subset of autistic participants. J. Autism Dev. Disor. 27(2): 187-192.
Warren, R., Singh, V., Cole, P., Odell, D., Pingree, C., Warren, L., DeWitt, C., and McCullough, M. (1992). Possible association of the extended MHC haplotype B44-SC30-DR4 with autism. Immunogenetics 36: 203-207.
Warren, R., Singh, V., Cole, P., Odell, D., Pingree, C., Warren, L., and White, E. (1991). Increased frequency of the null allele at the complement C4B locus in autism. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 83: 438-440.
Warren, R., Yonk, J., Burger, R., Odell, D., and Warren, L. (1995). DR-positive T cells in autism: Association with decreased plasma levels of the complement C4B protein. Neuropsychobiology 31: 53-57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engstrom, H.A., Ohlson, S., Stubbs, E.G. et al. Decreased Expression of CD95 (FAS/APO-1) on CD4+ T-lymphocytes from Participants with Autism. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities 15, 155–163 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022827417414
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022827417414