Abstract
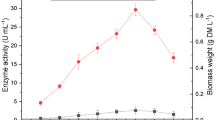
Grape seeds were used by Trametes hirsuta as a substrate for laccase production giving 23 kU l−1, which was 10-fold the value attained in the cultures with no lignocellulosic waste addition. The dyes, Indigo Carmine and Bromophenol Blue, were easily decolourised (100% in 24 h) by the extracellular liquid obtained in such cultures, whereas Methyl Orange (65% in 24 h) and Phenol Red (36% in 24 h) were more resistant to degradation. This shows the specificity of laccase towards different dye structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora DS, Gill PK (2000) Effect of various media and supplements on laccase production by some white-rot fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 77: 89–91.
Baldrian P, Gabriel J (2002) Copper and cadmium increase laccase activity in Pleurotus ostreatus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 206: 69–74.
Bollag JM, Leonowicz A (1984) Comparative studies of extracellular fungal laccases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48: 849–854.
Collins PJ, Dobson ADW (1997) Regulation of laccase gene transcription in Trametes versicolor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 3444–3450.
Dhawan S, Kuhad RC (2002) Effect of amino acids and vitamins on laccase production by the bird's nest fungus Cyathus bulleri. Bioresour. Technol. 84: 35–38.
Galhaup C, Wagner H, Hinterstoisser B, Haltrich D (2002) Incresed production of laccase by the wood-degrading basidiomycete Trametes pubescens. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 30: 529–536.
Lee IY, Jung KH, Lee CH, Park YH (1999) Enhanced production of laccase in Trametes versicolor by the addition of ethanol. Biotechnol. Lett. 21: 965–968.
Maier J (2002) Azo dye degradation in textile wastewaters by a newly isolated Bacillus sp. PhD Thesis, Graz, Austria, Institute of Microbiology and Environmental Biotechnology, Graz University of Technology.
Niku-Paavola ML, Raaska L, Itävaara M (1990) Detection of whiterot fungi by a non-toxic stain. Mycol. Res. 94: 27–31.
Novotný C, Rawal B, Bhatt M, Patel M, Sasek V, Molotoris HP (2001) Capacity of Irpex lacteus and Pleurotus ostreatus for decolorization of chemically different dyes. J. Biotechnol. 89: 113–122.
Nyanhongo GS, Gomes J, Gübitz GM, Zvauya R, Read J, Steiner W (2002) Decolorization of textile dyes by laccases from a newly isolated strain of Trametes modesta. Water Res. 36: 1449–1456.
Pandey A, Selvakumar P, Soccol CR, Nigam P (1999) Solid state fermentation for the production of industrial enzymes. Curr. Sci. 77: 149–162.
Rodríguez Couto S, Gundín M, Lorenzo M, Sanromám Á (2002) Screening of supports for laccase production by Trametes versicolor in semi-solid-state conditions. Proc. Biochem. 38: 249–255.
Srinivasan C, D'souza TM, Boominathan K, Reddy CA (1995) Demonstration of laccase in the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F-1767. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 4274–4277.
Wong Y, Yu J (1999) Laccase catalysed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Water Res. 33: 3512–3520.
Xu F (1999) Laccase. In: Flickinger MC, Drew SW, eds. Encyclopedia of Bioprocess Technology: Fermentation, Biocatalysis and Bioseparation, Vol. 3. New York: John Wiley &; Sons, pp. 1545–1554.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moldes, D., Gallego, P., Rodríguez Couto, S. et al. Grape seeds: the best lignocellulosic waste to produce laccase by solid state cultures of Trametes hirsuta . Biotechnology Letters 25, 491–495 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022660230653
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022660230653