Abstract
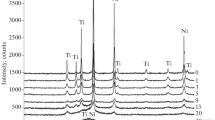
We used electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) to determine the dependence of the defect structure of zinc oxide powders on the physical characteristics of admixed particles during prolonged mechanical treatment (MT). Our results demonstrate a sequential two-stage thermal process contributing to the defect structure during MT. In the first stage of MT a collective break-up process of individual ZnO particles occurs and the defects are caused by hyper-rapid thermal defects annealing (HRTDA) of the particles. The second stage of defect formation is associated with annealing effects caused by heat accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowden, F. P. and Persson, P. A. (1961). Deformation heating and melting of solids in high-speed friction. Proceedings of the Royal Society A260, 433-451.
Broberg, K. B. (1999). Cracks and Fracture. Academic Press, San Diego-London-Boston-New York-Tokyo-Toronto.
Galland, D. and Herve, A. (1974). Temperature dependence of the ESR spectrum of the Zn vacancy in ZnO. Solid State Communications 14, 953-956.
Heinicke, G. (1984). Tribochemistry. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin.
Kakazey, N. G., Sreckovic, T. V. and Ristic, M. M. (1997). EPR-investigation of the evolution of defects in zinc oxide during tribophysical activation. Journal of Materials Science 32, 4619-4622.
Kakazey, M. G., Melnikova, V. A., Srechkovic, T., Tomila, T. V. and Ristic, M. M. (1999). Evolution of the microstructure of disperse Zinc-oxide during tribophysical activation. Journal of Materials Science 34, 1691-1697.
Nikitenko, V. A. (1992). Electronic paramagnetic resonance in ZnO. Applied Spectroscopy 57, 367-385.
Roitsin, A. B. and Mayevsky, V. M. (1992). Radiospectroscopy of Solid State Surfaces (in Russian), Naukova Dumka, Kiev. Samsonov G. V. (ed.). (1982). The oxide handbook. IFI/Plenum, New York-Washington-London.
Schallenberger, B. and Hausmann, A. (1976). Eigenstorstellen in elektronen bestrahlten zinkoxid. Zietschrift fur Physik B 23, 177-181.
Shone, R. (1969). Steigerung der Aktivitat von Kristalloberflachen durch Beschus mit Feststoffkomchen. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 41, 282-288.
Weichert, R. and Schonert, K. (1978). On the temperature rise at the tip of a fast running crack. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 26, 151-158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakazey, M., Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J., Leder, R. et al. Thermal Processes During Mechanical Treatment of ZnO and ZnO-TiO2 Powders and their Role in the Formation of Defect Structure. International Journal of Fracture 113, 13–18 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022652518917
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022652518917