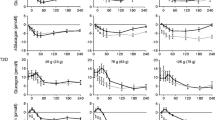
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of altering gastric emptying on postprandial plasma glucose concentration after a physiologic meal in patients with type II diabetes mellitus (T II DM). Nine T II DM patients underwent a double-blind, randomized, three-way crossover study, receiving erythromycin 200 mg, morphine 8 mg, or normal saline (placebo) intravenously prior to ingestion of a radiolabeled, dual-isotope, solid–liquid meal. Gastric emptying of solids and liquids and serial plasma glucose, glucagon, and serum insulin concentrations were measured at baseline and for 5 hr after meal ingestion. Erythromycin accelerated and morphine delayed solid- and liquid-phase gastric emptying compared to placebo (P < 0.05). During the first hour, the postprandial plasma glucose concentrations were higher after erythromycin (P < 0.05) and lower after morphine (P < 0.05) compared to placebo. The peak postprandial plasma glucose concentration was higher after erythromycin (P = 0.05) and lower after morphine (P < 0.05) compared to placebo. In conclusion, pharmacologic acceleration of gastric emptying resulted in higher postprandial glucose concentrations, while delaying gastric emptying resulted in lower postprandial glucose concentrations after a physiologic meal in T II DM. These results suggest that administration of opiate analgesics or prokinetic agents to diabetic patients may alter glucose control. Modifying gastric emptying may be helpful in achieving glucose control in T II DM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group: The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977-986, 1993
Dagogo-Jack S, Santiago JV: Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and modes of action of therapeutic interventions. Arch Intern Med 157:1802-1817, 1997
Dinneen S, Gerich J, Rizza R: Carbohydrate metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 327:707-713, 1992
Horowitz M, O'Donovan D, Jones KL, Feinle C, Rayner CK, Samsom M. Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment. Diabet Med 19:177-194, 2002
Kong MF, King P, Macdonald IA, Stubbs TA, Perkins AC, Blackshaw PE, Moyses C, Tattersall RB: Infusion of pramlintide, a human amylin analogue, delays gastric emptying in men with IDDM. Diabetologia 40:82-88, 1997
Phillips WT, Schwartz JG, McMahan CA: Reduced postprandial blood glucose levels in recently diagnosed non-insulin-dependent diabetics secondary to pharmacologically induced delayed gastric emptying. Dig Dis Sci 38:51-58, 1993
Phillips WT, Schwartz JG: Decelerating gastric emptying: therapeutic possibilities in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 13:S44-S48, 1996
Nauck M: Therapeutic potential of glucagon-like peptide 1 in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 13:S39-S43, 1996
Ray TK, Mansell KM, Knight LC, Malmud LS, Owen OE, Boden G: Long-term effects of dietary fiber on glucose tolerance and gastric emptying in noninsulin-dependent diabetic patients. Am J Clin Nutr 37:376-381, 1983
Torsdottir I, Alpsten M, Holm G, Sandberg AS, Tolli J: A small dose of soluble alginate-fiber affects postprandial glycemia and gastric emptying in humans with diabetes. J Nutr 121:795-799, 1991
Janssens J, Peeters TL, Vantrappen G, Tack J, Urbain JL, De Roo M, Muls E, Bouillon R: Improvement of gastric emptying in diabetic gastroparesis by erythromycin. N Engl J Med 322:1028-1031, 1990
Sullivan SN, Lee MG, Bloom SR, Lamki L, Dupre J: Reduction by morphine of human postprandial insulin release is secondary to inhibition of gastrointestinal motility. Diabetes 35:324-328, 1986
Maurer AH, Knight LC, Charkes ND, Vitti RA, Krevsky B, Fisher RS, Siegel JA: Comparison of left anterior oblique and geometric mean gastric emptying. J Nucl Med 32:2176-2180, 1991
Winer BJ, Brown DR, Michels KM: Statistical Principles in Experimental Design, 3rd ed. New York, McGraw-Hill, 1991, pp 158-166
Schwartz JG, Green GM, Guan D, McMahan CA, Phillips WT: Rapid gastric emptying of a solid pancake meal in type II diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 19:468-471, 1996
Frank JW, Saslow SB, Camilleri M, Thomforde GM, Dinneen S, Rizza RA: Mechanism of accelerated gastric emptying of liquids and hyperglycemia in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 109:755-765, 1995
Phillips WT, Schwartz JG, McMahan CA: Rapid gastric emptying of an oral glucose solution in type 2 diabetic patients. J Nucl Med 33:1496-1500, 1992
Kolterman OG, Gottlieb A, Moyses C, Colburn W: Reduction of postprandial hyperglycemia in subjects with IDDM by intravenous infusion of AC137, a human amylin analogue. Diabetes Care 18:1179-1182, 1995
Thompson RG, Peterson J, Gottlieb A, Mullane J: Effects of pramlintide, an analog of human amylin, on plasma glucose profiles in patients with IDDM: results of a multicenter trial. Diabetes 46:632-636, 1997
Thompson RG, Gottlieb A, Organ K, Koda J, Kisicki J, Kolterman OG: Pramlintide: a human amylin analogue reduced postprandial plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 14:547-555, 1997
Chandalia M, Garg A, Lutjohann D, von Bergmann K, Grundy SM, Brinkley LJ: Beneficial effects of high dietary fiber intake in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 342:1392-1398, 2000
Shiba Y, Mizumoto A, Satoh M, Inui A, Itoh Z, Omura S: Effect of nonpeptide motilin agonist EM523 on release of gut and pancreatic hormones in conscious dogs, Gastroenterology 110:241-250, 1996
Jones KL, Berry M, Kong M-F, Kwiater MA, Samsom M, Horowitz M: Hyperglycemia attenutates the gastrokinetic effect of erythromycin and affects the perception of postprandial hunger in normal subjects. Diabetes Care 22:339-344, 1999
Melga P, Mansi C, Ciuchi E, Giusti R, Sciaba L, Prando R: Chronic administration of levosulpiride and glycemic control in IDDM patients with gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 20:55-58, 1997
Ueno N, Inui A, Asakawa A, Takao F, Tani S, Komatsu Y, Itoh Z, Kasuga M: Erythromycin improves glycaemic control in patients with Type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 43:411-415, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonlachanvit, S., Hsu, CW., Boden, G.H. et al. Effect of Altering Gastric Emptying on Postprandial Plasma Glucose Concentrations Following a Physiologic Meal in Type-II Diabetic Patients. Dig Dis Sci 48, 488–497 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022528414264
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022528414264