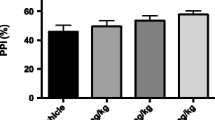
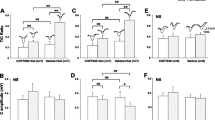
Abstract
Rats were pretreated with 0.9% NaCl, or 0.1 or 1.0 mg/kg MK-801, an anticonvulsant and a psychotomimetic drug, and 60 minutes later given ECS or sham ECS. After six sessions the animals were sacrificed and neuropeptide Y (NPY-), neurokinin A (NKA-), and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP-) like immunoreactivity (-LI) measured with radioimmunoassays. ECS increased NPY-LI in frontal cortex, striatum, occipital cortex and hippocampus, and NKA-LI in occipital cortex and hippocampus. MK-801 increased CGRP in a dose-response manner in frontal cortex, and NKA-LI in occipital cortex. Although the higher MK-801 dose reduced seizure duration by 50%, the ECS induced NPY-LI increase in striatum, occipital cortex and hippocampus, and NKA-LI in occipital cortex was not diminished. In contrast, there was a parallel decrease in seizures and NPY-LI and NKA-LI changes in frontal cortex and hippocampus, respectively. Investigation of neuropeptides in brain may contribute to understanding of the mechanisms of action of antide-pressive and antipsychotic treatments and of psychotomimetic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Stenfors, C., Theodorsson, E., and Mathé, A. A. 1989. Effect of repeated electroconvulsive treatment on regional concentrations of tachykinins, neurotensin, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, neuropeptide Y, and galanin in rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 24:445–450.
Stenfors, C., Mathé, A. A., and Theodorsson, E. 1994. Repeated electroconvulsive stimuli: Changes in neuropeptide Y, neurotensin and tachykinin concentrations in time. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psych. 18:201–209.
Stenfors, C., Bjellerup, P., and Mathé, A. A. Theodorsson, E. 1995. Concurrent analysis of neuropeptides and biogenic amines in brain tissue of rats treated with electroconvulsive stimuli. Brain Res. 698:39–45.
Stenfors, C., Mathé, A. A., and Theodorsson, E. 1995. Chromatographic and immunochemical characterization of rat brain neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity (NPY-LI) following repeated electroconvulsive stimuli. J. Neurosci. Res. 41:206–212.
Theodorsson, E., Mathé, A. A., and Stenfors, C. 1990. Brain neuropeptides: Tachykinins, neuropeptide Y, neurotensin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat brain: modifications by ECT and indomethacin. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psych. 14:387–407.
Stenfors, C., Theodorsson, E., and Mathé, A. A. 1992. Brain neuropeptides: Changes by treatment with the convulsants pentylenetetrazole and bicuculline. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psych. 16:747–753.
Zachrisson, O., Mathé, A. A., Stenfors, C., and Lindefors, N. 1995. Limbic effects of repeated electroconvulsive stimulation on neuropeptide Y and somatostatin mRNA expression in the rat brain. Molec. Brain Res. 31:71–85.
Zachrisson, O., Mathé, A. A., and Lindefors, N. 1997. Decreased levels of preprotachykinin-A and tachykinin NK1 receptor mRNA in specific regions of the rat striatum after electroconvulsive stimuli. Eur. J. Pharmac. 319:191–195.
Zachrisson, O., Mathé, A. A., and Lindefors, N. 1997. Effects of chronic lithium and electroconvulsive stimuli on cholecystokinin mRNA expression in the rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 43:347–350.
Zachrisson, O., Mathé, A. A., Stenfors, C., and Lindefors, N. 1995. Region-specific effects of chronic lithium administration on neuropeptide Y and somatostatin mRNA expression in the rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 194:87–92.
Mathé, A. A., Nomikos, G. G., and Svensson, T. H. 1995. Effects of acute and chronic electroconvulsive treatment on interstitial concentrations of somatostatin in the rat hippocampus and striatum. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psych. 19:323–332.
Mathé, A. A., Hertel, P., Nomikos, G., Mathé, J. M., and Svensson, T. H. 1994. Microdialysis of extracellular neurotensin and calcitonin gene-related peptide from the rat brain: Effects of d-amphetamine and phencyclidine. In Monitoring Molecules in Neuroscience. Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on in vivo Methods. (Eds. A. Louilot, T. Durkin, U. Spampinato, M. Cador) pp 361–362.
Mathé, A. A., Hertel, P., Nomikos, G. G., Gruber, S., Mathé, J. M., and Svensson, T. H. 1996. The psychotomimetic drugs d-ampethamine and phencyclidine release calcitonin gene-related peptide in the limbic forebrain of the rat. J. Neurosci. Res., 46:316–323.
Mathé, A. A., Rudorfer, M. V., Stenfors, C., Manji, H. K., Potter, W. C., and Theodorsson, E. 1996. Effects of electroconvulsive treatment on somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, endothelin and neurokinin A concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients. Depression, 3:250–256.
Langer, G., Karazman, R., Neumark, J., Saletu, B., Schönbeck, G., Grünberger, J., Dittrich, R., Petricek, W., Hoffmann, P., Linzmayer, L., Anderer, P., and Steinberger, K. 1995. Isoflurane narcotherapy in depressive patients refractory to conventional antidepressant drug treatment. Neuropsychology 31:182–194.
Hoffmann, O., Johnson, L., Mebius, C., Stenfors, C., Vinnars, E., and Mathé, A. A. 1991. Isoflurane and electroconvulsive treatment in depression: A pilot study. In Pharmacotherapies, Psychotherapies, Other Therapies. (Eds. C.N. Stefanis, G. R. Soldatos, A. D. Rabavilas), Excerpta Medica, pp 480–486.
Stenfors, C., Srinivasan, G. R., Theodorsson, E., and Mathé, A. A. 1992. Electroconvulsive stimuli and brain peptides: Effect of modification of seizure duration on neuropeptide Y, neurokinin A, substance P and neurotensin. Brain Res. 596:251–258.
Clineschmidt, B. V., Martin, E., and Bunting, P. R. 1982. Anticonvulsant activity of (+)-5-methyl-10, 11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo(a,d)cyclohepten-5, 10-imine (MK-801), a substance with potent anticonvulsant, central sympathomimetic, and apparent anxiolytic properties. Drug Develop. Res. 2:123–134.
Löscher, Q., Annies, R., and Hönack, D. 1991. The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801 induces increases in dopamine and serotonin metabolism in several brain regions or rats. Neurosci. Lett. 128:191–194.
McNamara, J. O., Russell, R. D., Rigsbee, L., and Bonhaus, D. W. 1988. Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic actions of MK-801 in the kindling and electroshock models. Neuropharmacology 27:563–568.
Nomikos, G. G., Mathé, A. A., Mathé, J. M., and Svensson, T. H. 1992. MK-801 prevents the enhanced behavioural response to apomorphine elicited by repeated electroconvulsive treatments in mice. Psychopharmacology 108:367–370.
Theodorsson, E., Stenfors, C., and Mathé, A. A. 1990. Microwave irradiation increases recovery of neuropeptides from brain tissues. Peptides 11:1191–1197.
Mathé, A. A., Stenfors, C., Brodin, E., and Theodorsson, E. 1990. Neuropeptides in brain: Effects of microwave irradiation and decapitation. Life Sci. 46:287–293.
Mathé, A. A., Norstedt Wikner, B., Stenfors, C., and Theodorsson, E. 1994. Effects of lithium on neuropeptide Y, neurokinin A and substance P in brain and peripheral tissues of rat. Litium 5:241–247.
Mathé, A. A., Ågren, H., Lindström, L., and Theodorsson, E. 1994. Increased concentration of calcitonin gene-related peptide in cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients. A possible trait marker of major depressive disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 182:138–142.
Heilig, M., and Widerlöv, E. 1995. Neurobiology and clinical aspects of neuropeptide Y. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 9:115–136.
Wahlestedt, C., Heilig, M. 1995. Neuropeptide Y and related peptides. Pages 543–551, in Psychopharmacology. The Fourth Generation of Progress. F. E. Bloom, D. J. Kupfer (eds). Raven Press Ltd, New York.
Otsuka, M., and Yoshioka, K. 1993. Neurotransmitter functions of mammalian tachykinins. Physiol. Rev. 73:329–308.
Taché, Y., Holzer, P., and Rosenfeld, M. G. 1992. Calcitonin gene-related peptide. The first decade of a novel pleiotropic neuropeptide. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 657:1–561.
Mathé, A. A., Stenfors, C., and Theodorsson, E. 1994. Effects of NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 on electroconvulsive treatment induced seizures and brain neuropeptides. Psychopharmacology 113:89.
Glowinski, J., and Iversen, L. L. 1965. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain: The disposition of (3H) norepinerphine, (3H) dopamine and (3H) dopa in various regions of the brain. J. Neurochem. 13:655–669.
Mathé, A. A., Jousisto-Hanson, J., Stenfors, C., and Theodorsson, E. 1990. Effect of lithium on tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and neuropeptide Y in rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 26:233–237.
Berrettini, W. H., Doran, A. R., Kelsoe, J., Roy, A., and Pickar, D. 1987. Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptide Y in depression and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 1:81–83.
Widerlöv, E., Lindström, L. H., Wahlestedt, C., and Ekman, R. 1988. Neuropeptide Y and peptide YY as possible cerebrospinal markers for major depression and schizophrenia, respectively. J. Psychiat. Res. 22:69–79.
Widdowson, P. S., Ordway, G. A., and Halaris, A. E. 1992. Reduced neuropeptide Y in suicide brain. J. Neurochem. 59:73–80.
Ordway, G. A., Stockmeier, C. A., Meltzer, H. Y., Ocerholser, J. C., Jaconetta, S., and Widdowson, P. S. 1995. Neuropeptide Y in frontal cortex is not altered in major depression. J. Neurochem. 65:1646–1650.
Heilig, M., Wahlestedt, C., Ekman, R., and Widerlöv, E. 1988. Antidepressant drugs increase the concentration of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 147:465–467.
Widdowson, P. S., and Halaris, A. E. 1989. Increased levels of neuropeptide-Y immunoreactivity in rat brain limbic structures following antidepressant treatment. J. Neurochem. 52(Suppl):577.
Smilowska, M., and Legutko, B. 1991. Influence of imipramine on neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Neurosci. 41:767–771.
Bellmann, R., and Sperk, G. 1993. Effects of antidepressant drug treatment on levels of NPY or prepro-NPY-mRNA in the rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 22:183–187.
Wahlestedt, C., Karoum, F., Jaskiw, G., Wyatt, J. R., Larhammar, D., Ekman, R., and Reis, D. J. 1991. Cocaine-induced reduction of brain neuropeptide Y synthesis dependent on medial prefrontal cortex. Prog. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 88:2078–2082.
Gruber, S., and Mathé, A. A. 1996. Both antipsychotic drugs and psychotomimetic compounds affect peptides in brain. Nordic J. Psychiatry 50:106.
Gruber, S., Nomikos, G. G., Svensson, T. H., and Mathé, A. A. 1996. Effects of D-amphetamine and dopamine receptor antagonists on calcitonin gene-related peptide levels in ventral striatum. Pages 205–206, in Monitoring Molecules in Neuroscience. Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on in vivo Methods. J. L. Gonzáles-Mora, R. Borges, M. Mas (eds).
Whitton, P. S., Biggs, C. S., Pearce, B. R., and Fowler, L. J. 1992. Regional effects of MK-801 on dopamine and its metabolites studied by in vivo microdialysis. Neurosci. Lett. 142:5–8.
Kashiwa, A., Nishikawa, T., Nishijima, K., Umino, A., and Kiyohisa, T. 1995. Dizocilpine (MK-801) elicits a tetrodotoxin-sensitive increase in extracellular release of dopamine in rat medial frontal cortex. Neurochem. Int. 26:269–279.
Dai, H., Gebhardt, K., and Carey, R. J. 1995. Time course effects of MK-801: The relationship between brain neurochemistry and behavior. Brain Res. Bull. 36:175–180.
Jones, P. M., Ghatei, M. A., Steel, J., O'Halloran, D., Gon, G., Legon, S., Burrin, J. M., Leonhardt, U., Polak, J. M., and Bloom, S. R. 1989. Evidence for neuropeptide Y synthesis in the rat anterior pituitary and the influence of thyroid hormone status: comparison with vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P, and neurotensin. Endocrinology 125:334–341.
Bowker, R. M., Wetlund, K., Sullivan, M. C., Wilber, J. F., and Coulter, J. D. 1983. Descending serotonergic, peptidergic and cholinergic pathways from the raphe nuclei: a multiple transmitter complex. Brain Res. 288:33–48.
Chiba, T., and Masuko, S. 1989. Coexistence of varying combinations of neuropeptides with 5-hydroxytryptamine in neurons of the raphe pallidus et obscurus projecting to the spinal cord. Neurosci. Res. 7:13–23.
Lindefors, N., Brodin, E., and Ungerstedt, U. 1989. Amphetamine facilitates the in vivo release of neurokinin A in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 160:417–420.
Sharp, T., Zetterström, T., Ljungberg, T., and Ungerstedt, U. 1987. A direct comparison of amphetamine-induced behaviours and regional brain dopamine release in the rat using intracerebral dialysis. Brain Res. 401:322–330.
Haring, C., Humpel, C., Skofitsch, G., Krobath, J., Javorsky, F., and Saria A. 1991. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the amygdaloid complex of the rat: immunohistochemical and quantitative distribution, and drug effects on calcium dependent, potassium-evoked in vitro release. Synapse 8:261–269.
Kresse, A., Jacobowitz, M., and Skofitsch, G. 1995. Detailed mapping of CGRP mRNA expression in rat central nervous system: Comparison with previous immunocytochemical findings. Brain Res. Bull. 36:261–274.
Saria, A., Bernatzky, G., Humpel, C., Haring, C., Skofitsch, G., and Panksepp, J. 1992. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the brain. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 657:164–169.
Sexton, P. M. 1991. Central nervous system binding sites for calcitonin and calcitonin gene-related peptide. Mol. Neurobiol. 5:251–273.
Yasui, Y., Saper, C. B., and Cechetto, D. F. 1991. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactive projections from the thalamus to the striatum and amygdala in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 308:293–310.
Deutch, A. Y., and Roth, R. 1987. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the ventral tegmental area: selective modulation of prefrontal cortical dopamine metabolism. Neurosci. Lett. 74:169–174.
Drumheller, A., Menard, D., Fournier, A., and Jolicoeur, F. B. 1992. Neurochemical effects of CGRPa. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 657:546–548.
Kovács, A., Papp, E., and Telegdy, G. 1994. In vivo microdialysis study of effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) on rat striatal dopamine release. Pages 137–138, in Monitoring Molecules in Neuroscience. Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on in vivo Methods. A. Louilot, T. Durkin, U. Spampinato, M. Cador (eds.).
Jolicoeur, F. B., Menard, D., Fournier, A., and St-Pierre, S. 1992. Structure activity analysis of CGRP's neurobehavioral effects. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 657:154–163.
Clementi, G., Grassi, M., Valerio, C., Prato, A., Fiore, C. E., and Drago, F. 1992. Effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on extrapyramidal motor system Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 42:545–548.
Kovács, A. M., and Telegdy, G. 1992. Effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on passive avoidance behavior in rats. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 657:543–545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathé, A.A., Gruber, S., Jiménez, P.A. et al. Effects of Electroconvulsive Stimuli and MK-801 on Neuropeptide Y, Neurokinin A, and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in Rat Brain. Neurochem Res 22, 629–636 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022482322329
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022482322329