Abstract
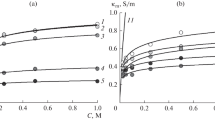
Main transport properties were studied for selective membranes with low dielectric constants based on liquid ion exchangers involving nitrogen-containing organic base cations. Permeabilities and ion flows through a membrane were calculated for major and interfering ions. Dependences of the transport properties of membranes on the concentrations of the ion exchanger and near-membrane solution and their potentiometric characteristics are presented. It was demonstrated that the transport properties of liquid membranes are determined by two main factors: the transfer of counterions through the phase boundary by the extraction–exchange mechanism and the leaching of the ion exchanger from the membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Spichiger, U.E., Chemical Sensors and Biosensors for Medical and Biological Applications, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 1998.
Cosofret, V.V. and Buck, R.P., Pharmaceutical Applications of Membrane Sensors, Boca Raton, Florida: CRC, 1992.
Chen, Z.Z. and Qui, Z.F., Applications of Ion-Selective Electrodes in Pharmaceutical Analysis, Beijing: Renmin Weisheng Publ. House, 1985.
Cosofret, V.V., Membrane Electrodes in Drug Substances Analysis, Oxford: Pergamon, 1982.
Ma, T.S. and Hassan, S.S.M., Organic Analysis Using Ion-Selective Electrodes, London: Academic, 1982.
Baiulescu, G.E. and Cosofret, V.V., Applications of Ion-Selective Membrane Electrodes in Organic Analysis, New York: Wiley. Translated under the title Primenenie ion-selektivnykh membrannykh elektrodov v organicheskom analize, Moscow: Mir, 1980.
Solsky, R.L., CRC Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 1983, vol. 14, p. 1.
Cosofret, V.V. and Buck, R.P., Ion-Sel. Electrode Rev., 1984, vol. 6, p. 59.
Patriarche, G.J., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 1986, vol. 4, p. 789.
Yao, S. and Nie, L., Anal. Proc., 1987, vol. 24, p. 338.
Zarechenskii, M.A., Gaidukevich, A.N., and Kizim, E.G., Farmatsiya, 1988, vol. 37, p. 88.
Byrne, T.P., Ion-Sel. Electrode Rev., 1988, vol. 10, p.107.
Vytras, K., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 1989, vol. 7, p. 789.
Zhang, Z. and Cosofret, V.V., Ion-Sel. Electrode Rev., 1990, vol. 12, p. 35.
Cosofret, V.A. and Buck, R.P., CRC Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 1993, vol. 24, p. 1.
Granzhan, A.V. and Charykov, A.K., Khim.—Farm. Zh., 1993, vol. 28, p. 51.
Kulapina, E.G. and Barinova, O.V., Khim.—Farm. Zh., 1997, vol. 32, p. 40.
Morf, W., The Principles of Ion-Selective Electrodes and of Membrane Transport, Budapest: Akad. Kiado, 1981. Translated under the title Printsipy raboty ionoselektivnykh elektrodov i membrannyi transport, Moscow: Mir, 1985.
Vigassy, T., Ceresa, A., Badertscher, M., Morf, W.E., de Rooij, N.F., and Pretsch, E., Sens. Actuators, B, 2001, vol. 76, p. 476.
Ceresa, A., Sokalski, T., and Pretsch, E., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2001, vol. 501, p. 70.
Ceresa, A., Bakker, E., Hattendorf, B., Günther, D., and Pretsch, E., Anal. Chem., 2001, vol. 73, p. 343.
Morf, W.E., Badertscher, M., Zwickl, T., Reichmuth, P., De Rooij N.F., and Pretsch, E., J. Phys. Chem., 2000, vol. 104, p. 8201.
Bakker, E. and Meyerhoff, M.E., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2000, vol. 416, p. 121.
Morf, W.E., Badrtscher, M., Zwickl, T., De Rooij N.F., and Pretsch, E., J. Phys. Chem., 1999, vol. 103, p. 11346.
Zwickl, T., Sokalski, T., and Pretsch, E., Electroanalysis (N. Y.), 1999, vol. 11, p. 673.
Sokalski, T., Ceresa, A., Fibbioli, M., Zwickl, T., Bakker, E., and Pretsch, E., Anal. Chem., 1999, vol. 71, p.1210.
Sokalski, T., Zwickl, T., Bakker, E., and Pretsch, E., Anal. Chem., 1999, vol. 71, p. 1204.
Mi, Y., Mathison, S., Goines, R., Logue, A., and Bakker, E., Anal. Chim. Acta, 1999, vol. 397, p. 103.
Mathison, S. and Bakker, E., Anal. Chem., 1998, vol. 70, p. 303.
Sokalski, T., Ceresa, A., Zwickl, T., and Pretsch, E., J.Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, vol. 119, p. 11347.
Mathison, S., Goines, R., and Bakker, E., in Chemical and Biological Sensors and Analytical Electrochemical Methods, Ricco, A.J., Butler, M.A., Vanysek, P., Horvai, G., and Silva, A.F., Eds., Sensor and Physical Electrochemistry Divisions, The Electrochem. Soc. Proc. Series, Pennington, 1997, vol. 97-19, p. 646.
Schaller, U., Bakker, E., and Pretsch, E., Anal. Chem., 1995, vol. 67, p. 3123.
Samec, Z., Langmaier, J., Trojánek, A., Samcová, E., and Málek, J., Anal. Sci., 1998, vol. 14, p. 35.
Kulapina, E.G. and Apukhtina, L.V., Elektrokhimiya, 1998, vol. 34, p. 177.
Kulapina, E.G. and Barinova, O.V., Elektrokhimiya, 2001, vol. 37, p. 935.
Jee, J.-G., Kwun, O.C., Jhon, M.S., and Ree, T., Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 1982, vol. 3, p. 23.
Thoma, A.P., Viviani-Nauer, A., Aravantis, S., Morf, W.E., and Simon, W., Anal. Chem., 1977, vol. 49, p. 1567.
Morf, W.E. and Simon, W., Helv. Chim. Acta, 1986, vol.69, p. 1120.
Horvai, G., Graf, E., Toth, K., Pungor, E., and Buck, R.P., Anal. Chem., 1986, vol. 58, p. 2735.
Van den Berg, A., Van der Wal, P.D., Skowronska-Ptasinska, M., Sundholter, E.J.R., Reingoudt, D.N., and Bergveld, P., Anal. Chem., 1987, vol. 59, p. 2827.
Lindner, E., Graf, E., Niegreisz, Z., Toth, K., Pungor, E., and Buck, R.P., Anal. Chem., 1988, vol. 60, p. 295.
Buhlmann, P., Yajima, S., Tohda, K., and Umezawa, Y., Electrochim. Acta, 1995, vol. 40, p. 3021.
Yajima, S., Tohda, K., Buhlmann, P., and Umezawa, Y., Anal. Chem., 1997, vol. 69, p. 1919.
Markin, V.S. and Sokolov, V.S., Elektrokhimiya, 1988, vol. 26, p. 781.
Koryta, J., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1986, vol. 213, p. 323.
Koryta, J. and Scalicky, M., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1987, vol. 229, p. 265.
Sandblom, J., Eisenman, G., and Walker, J.L., J. Phys. Chem., 1967, vol. 71, p. 3862.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharitonov, S.V. Transport Properties of Selective Membranes Reversible to Nitrogen-Containing Organic Base Cations: Permeability and Ion Flow. Journal of Analytical Chemistry 58, 176–183 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022318424085
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022318424085