Abstract
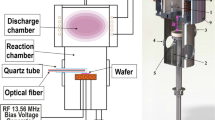
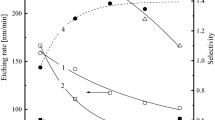
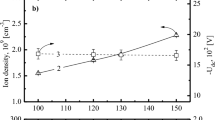
Silicon nitride is an important material layer in various types of microelectronic devices. Because of continuous integration of devices, patterning of this layer requires a highly selective and anisotropic etching process. Reactive ion etching is one of the most simple and popular plasma processes. The present work is an experimental analysis of primary etch characteristics in reactive ion etching of silicon nitride using chlorine- and/or fluorine-based organic and inorganic chemistries (CCl 2 F 2+O 2 , CHF 3+O 2 , SiF 4 +O2, SF6+O 2 , and SF 6+He) in order to obtain a simultaneous etch selectivity against polysilicon and silicon dioxide. A recipe, in CCl 2 F 2 /O 2 plasma chemistry, which provides acceptable etch characteristics, along with a reasonable simultaneous selectivity against polysilicon and silicon dioxide, has been formulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. K. Mazumder, K. Kobayashi, Tamotsu Ogata, J. Mitsuhashi, Y. Mashiko, and H. Koyama, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 368 (1996).
R. A. Colclaser, Microelectronic Processing and Device Design (Academic Press, NY, 1980), p. 47.
Yue Kuo, J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 186 (1995).
U. S. Tandon, B. D. Pant, and Ashok Kumar, Vacuum 42, 1219 (1991).
K. Nojiri, K. Tsunokuni, K. Horibe, K. Ito, and S. Kishino, Extended Abstr. 17th Conf. Solid State Devices Mater. p. 337 (1985).
K. Shiozawa, T. Oishi, H. Maeda, T. Murakami, K. Yasumura, Y. Abe, and Y. Tokuda, J. Electrochem Soc. 145, 1684 (1998).
V. K. Dwivedi, J. Electrochem Soc. 137, 2586 (1990).
S. Deleonibus, P. Molle, L. Tosti, and M. C. Taccusel, J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 3739 (1991).
D. C. Gray, J. W. Butterbaugh, C. F. Hiatt, A. S. Lawing, and H. H. Sawin, J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 3919 (1995).
S. S. Cooperman, A. I. Nasi, and G. J. Grula, J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 3180 (1995).
W. Grynkewich, T. H. Fednyshyn, and R. H. Dumas, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 8, 5 (1990).
Haselden, P. Peavy, B. Eliscon, and T. Ahmed, Proc. SPIE-Intern. Soc. Opt. Eng. 115, 1185 (1990).
A. Jacob, U. S. Patent 3,795,557 (1974).
H. M. Sanders, J. Dieleman, H. J. B. Peters, and J. A. M. Sanders, J. Electrochem. Soc. 129, 2559 (1983).
Field, D. F. Klenperer, and I. T. Wade, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 6, 551 (1988).
C. J. Mogab, A. C. Adams, and D. L. Flamm, J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 49, 3796 (1978).
G. Smolinsky and D. L. Flamm, J. Appl. Phys. 50, 982 (1979).
Y. Zhang, G. S. Oehrlein, G. M. W. Kroesen, M. Mittmer, and Stein, J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 1439 (1993).
B. E. E. Kastenmeir, P. J. Matsuo, and G. S. Oehrlein, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 14, 2802 (1996).
G. W. Grykewich, T. H. Fedynyshyn, and R. H. Dumas, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 8, 5 (1990).
L. M. Ephrath, J. Electrochem. Soc. 126, 1419 (1979).
Ho-Jun Lee, Joong Kyun Kim, Jung Hun Kim, and Ki-Woong Whang Jeong Jeong Ho Kim, and Jung Hoon Joo, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 16, 500 (1998).
Histaka Hayashi, Kazuaki Kurihara, and Makoto Sekine, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 2488 (1996).
Ying Zhang, G. S. Oehrlein, and F. H. Bell, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 14, 2127 (1996).
H. Toyoda, M. Tobinaga, and H. Komiya, Jpn. J Appl Phys. 20, 681 (1981).
D. H. G. Choe, C. Knapp, and A. Jacob, Solid State Technol. 27, 177 (1984).
T. K. S. Wong and S. G. Ingram, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 10, 2393 (1992).
A. M. Barklund and H. O. Blom, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 11, 1226 (1993).
Y. X. Li, M. Laros, P. M. Sarro, P. J. French, and R. F. Wolffenbuttel, Microelectr. Eng. 20, 321 (1993).
P. E. Riley, B. N. Defonseka, J. C. Sum, and D. Figueredo, IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 6, 290 (1993).
Ying Wang and L. Luo, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 16, 1582 (1998).
D. E. Ibbotson, J. A. Mucha, D. L. Flamm, and J. M. Cook, Appl. Phys. Lett 46, 794 (1985).
Barkanic, D. M. Reynolds, R. J. Jaccodine, H. G. Stenger, J. Parks, and M. Vedage, Solid State Technol. 32, 109 (1989).
H. Boyd and M. S. Tang, Solid State Technol. 22, 133 (1979).
E. P. G. T. van de Ven and P. A. Zijlstra, Proc. Electrochem. Soc. 81, 112 (1981).
J. W. Couburn, J. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2, 1 (1982).
B. Gorowitz and R. J. Saia, VLSI Electronics, Vol 8, Series Editor G. Norman, ed. (Academic Press, Orlando, Florida, 1984), p. 298.
P. E. Riley and D. A. Hanson, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 7, 1352 (1989).
P. H. Singer, Semicond Intern. 12, 68 (1988).
P. H. Singer, Semicond Intern. 10, 98 (1986).
H. W. Lehman and R. Widmer, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 15, 319 (1978).
M. J. Vacile and F. A. Stevie, J. Appl. Phys. 53, 3799 (1982).
D. W. Hess and R. C. Bruce, in Dry Etching for Microelectronics, R. A. Powell, ed. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1984), p. 8.
D. L. Flamm, Plasma Etching: An Introduction, D. M. Manos and D. L. Flamm, eds, (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1989), p. 165.
B. E. E. Kastenmeir, P. J. Matsuo, and G. S. Oehrlein, and J. G. Langan J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 16, 2047 (1998).
Hayasaka, H. Okana, and Y. Horiike, Solid State Technol. 31, 127 (1988).
J. Dulak, B. J. Howard, and C. Steinbruchel, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 9, 775 (1991).
B. E. Thompson and H. H. Sawin, J. Electrochem. Soc. 133, 1886 (1986).
K. M. Eisele, J. Electrochem. Soc. 128, 123 (1981).
R. Legtenberg, H. Janson, M. de Boerl and M. Elwenspoek, J. Electrochem. Soc. 142, 2020 (1995).
A. Burtsev, Y. X. Li, H. W. Ziezl, and C. I. M. Beenakker, Microelectr. Eng. 40, 85 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pant, B.D., Tandon, U.S. Etching of Silicon Nitride in CCl2F2, CHF3, SiF4, and SF6 Reactive Plasma: A Comparative Study. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing 19, 545–563 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021886511288
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021886511288