Abstract
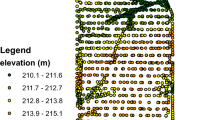
Crop yield, soil properties, and erosion are strongly related to terrain attributes. The objectives of our study were to examine the relationship between six years of corn (Zea mays L.) yield data and relative elevation, slope, and curvature, and to develop a linear regression model to describe the spatial patterns of corn yield for a 16 ha field in central Iowa, USA. Corn grain yield was measured in six crop years, and relative elevation was measured using a kinematic global positioning system. Slope and curvature were then determined using digital terrain analysis. Our data showed that in the four years with less than normal growing season precipitation, corn yield was negatively correlated with relative elevation, slope, and curvature. In the two years with greater than normal precipitation, yield was positively correlated with relative elevation and slope. A multiple linear regression model based on relative elevation, slope, and curvature was developed that predicted 78% of the spatial variability of the average yield of the transect plots for the four dry years. This model also adequately identified the spatial patterns within the entire field for yield monitor data from 1997, which was one of the dry years. The relationship between terrain attributes and corn yield spatial patterns may provide opportunities for implementing site-specific management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afyuni, M. M., Cassel, D. K. and Robarge, W. P. 1993. Effect of landscape position on soil water and corn silage yield. Soil Science Society of America Journal 57, 1573-1580.
Andrews, W. F. and Dideriksen, R. O. 1981. Soil Survey of Boone Country, Iowa (USDA—SCS U.S. Gov. Printing Office, Washington, D.C., USA), p. 152.
Arc/Info. 1998. Arc/Info Version 7.2.1. TOPOGRID Command Documentation (Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands, California USA).
Arslan, S. and Colvin, T. S. 1998. Laboratory test stand for combine grain yield monitors. Technical note. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 14, 369-371.
Arslan, S. and Colvin, T. S. 1999. Laboratory performance of a yield monitor. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 15, 189-195.
Belsley, D. A., Kuh, E. and Welsch, R. E. 1980. Regression diagnostic: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity (John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, USA), p. 292.
Ciha, A. J. 1984. Slope position and grain yield of soft white winter wheat. Agronomy Journal 76, 193-196.
Clark, R. L. and Lee, R. 1998. Development of topographic maps for precision farming with kinematic GPS. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 41, 909-916.
Colvin, T. S. 1990. Automated weighing and moisture sampling for a field plot combine. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 6, 713-714.
Colvin, T. S., Arslan, S. and Meek, D. W. 1999. Yield monitors combines and their interactions. Technical Paper 1999-01-2846 (Society of Automotive Engineers, Warrendale, Pennsylvania USA), p. 8.
Colvin, T. S., Jaynes, D. B., Karlen, D. L., Laird, D. A. and Ambuel, J. R. 1997. Yield variability within a central Iowa field. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 40, 883-889.
Daniels, R. B., Gilliam, J. W., Cassel, D. K. and Nelson, L. A. 1987. Quantifying the effects of past soil erosion on present soil productivity. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 42, 183-187.
Freund, R. J. and Littell, R. C. 2000. SAS Systems for Regression (Statistical Analysis System Institute Inc. Cary, North Carolina USA), p. 236.
Frye, W. W., Ebelhar, S. A., Murdock, L. W. and Blevins, R. L. 1982. Soil erosion effects on properties and productivity of two Kentucky soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 46, 1051-1055.
Halvorson, G. A. and Doll, E. C. 1991. Topographic effects on spring wheat yields and water use. Soil Science Society of America Journal 55, 1680-1685.
Hanna, A. Y., Harlan, P. W. and Lewis, D. T. 1982. Soil available water as influenced by landscape position and aspect. Agronomy Journal 74, 999-1004.
Jones, A. J., Mielke, L. N., Bartles, C. A. and Miller, C. A. 1989. Relationship of landscape position and properties to crop production. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 44, 328-332.
Karlen, D. L. and Colvin, T. S. 1992. Alternative farming system effects on profile nitrogen concentrations on two Iowa farms. Soil Science Society of America Journal 56, 1249-1256.
Khakural, B. R., Robert, P. C. and Huggins, D. R. 1998. Variability of corn/soybean yield and soil landscape properties across a southwestern Minnesota landscape. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Precision Agriculture edited by P. C. Robert, R. H. Rust and W. E. Larson (ASA, CSSA, and SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin USA), p. 573-579.
Khakural, B. R., Robert, P. C. and Mulla, D. J. 1996. Relating corn/soybean yield variability in soil and landscape characteristics. In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Precision Agriculture, edited by P. C. Robert, R. H. Rust and W. E. Larson (ASA, CSSA, and SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin USA), p. 117-128.
Kravchenko, A. N. and Bullock, D. G. 2000. Correlation of corn and soybean grain yield with topography and soil properties. Agronomy Journal 92, 75-83.
Langdale, G. W., Box, J. E., Leonard, R. A., Barnett, A. P. and Fleming, W. F. 1979. Corn yield reduction on eroded Southern Piedmont. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 34, 226-228.
Lark, R. M. and Stafford, J. V. 1998. Information on within-field variability from sequences of yield maps: multivariate classification as a first step of interpretation. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 50, 271-281.
Lark, R. M., Stafford, J. V. and Bolam, H. C. 1997. Limitations on the spatial resolution of yield mapping for combinable crops. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research 66, 183-193.
Larscheid, G., Blackmore, B. S. and Moore, M. 1997. Management decisions based on yield maps. In: Precision Agriculture '97: Proceedings of the 1st European Conference on Precision Agriculture, edited by J. V. Stafford (BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford, UK), p. 895-903.
Lindstrom, M. J., Nelson, W. W. and Schumacher, T. E. 1992. Quantifying tillage erosion rates due to moldboard plowing. Soil Tillage Research 24, 243-255.
Lyles, L. 1975. Possible effects of wind erosion on soil productivity. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 19, 279-283.
Malo, D. D., Worcester, B. K., Cassel, D. K. and Matzdorf, K. D. 1974. Soil-landscape relationships in a closed drainage system. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings 38, 813-818.
Montgomery, D. C. and Peck, E. A. 1982. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis (John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, USA), p. 504.
Moore, I. D., Gessler, P. E., Nielsen, G. A. and Peterson, G. A. 1993. Soil attribute prediction using terrain analysis. Soil Science Society of America Journal 57, 443-452.
Pennock, D. J. and de Jong, E. 1987. The influence of slope curvature on soil erosion and deposition in hummock terrain. Soil Science 144, 209-217.
Pierson, F. B. and Mulla, D. J. 1990. Aggregate stability in the Palouse region of Washington: effect of landscape position. Soil Science Society of America Journal 54, 1407-1412.
SAS, 1985. Statistical Analysis System. User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5 (Statistical Analysis System Institute Inc. Cary, North Carolina, USA), p. 956.
Schumacher, T. E., Lindstrom, M. J., Mokma, D. L. and Nelson, W. W. 1994. Corn yield: erosion relationships of representative losses and till soils in the north central United States. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 49, 77-81.
Spomer, R. G. and Piest, R. F. 1982. Soil productivity and erosion of Iowa loess soils. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 25, 1295-1299.
Steinwand, A. L. and Fenton, T. E. 1995. Landscape evolution and shallow groundwater hydrology of a till landscape in central Iowa. Soil Science Society of America Journal 59, 1370-1377.
Steinwand, A. L., Karlen, D. L. and Fenton, T. E. 1996. An evaluation of soil survey crop yield interpretations for two central Iowa farms. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 51, 66-71.
Stone, J. R., Gilliam, J. W., Cassel, D. K., Daniels, R. B., Nelson, L. A. and Kleiss, H. J. 1985. Effect of erosion and landscape position on the productivity of Piedmont soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 49, 987-991.
Sudduth, K. A., Drummond, S. T., Birrell, S. J. and Kitchen, N. R. 1997. Spatial modeling of crop yield using soil and topographic data. In: Precision Agriculture '97: Proceedings of the 1st European Conference on Precision Agriculture, edited by J. V. Stafford (BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford, UK), p. 439-447.
Swan, J. B., Shaffer, M. J., Paulson, W. H. and Peterson, A. E. 1987. Simulating the effects of soil depth and climate factors on corn yield. Soil Science Society of America Journal 51, 1025-1032.
Timlin, D. J., Pachepsky, Y., Snyder, V. A. and Bryant, R. B. 1998. Spatial and temporal variability of corn grain yield on a hillslope. Soil Science Society of America Journal 62, 764-733.
Walker, P. H., Hall, G. F. and Protz, R. 1968. Relation between landform parameters and soil properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal 32, 101-104.
Whelan, B. M. and McBratney, A. B. 1997. Sorghum grain flow convolution within a conventional combine harvester. In: Precision Agriculture '97: Proceedings of the 1st European Conference on Precision Agriculture, edited by J. V. Stafford (BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford, UK), p. 759-766.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaspar, T.C., Colvin, T.S., Jaynes, D.B. et al. Relationship Between Six Years of Corn Yields and Terrain Attributes. Precision Agriculture 4, 87–101 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021867123125
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021867123125