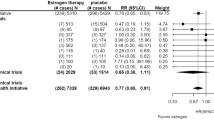
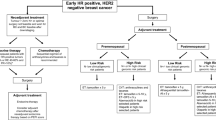
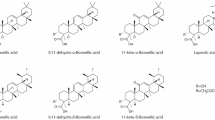
Abstract
The groundwork for making the concept of breast cancer chemoprevention a clinical reality began over a century ago. Although tamoxifen's first clinical use was for the treatment of breast cancer, the earliest animal studies with the drug provided the scientific basis for chemoprevention. The extensive clinical experience, safety and laboratory data have made tamoxifen the current standard-of-care for the prevention of breast cancer in women at elevated risk. The STAR trial will address the value of raloxifene as a chemopreventative in postmenopausal women. Results will be available by 2005. Newer compounds are under development which hold the promise of expanded efficacy and narrower side-effect profile. These compounds will function as multifunctional medicines and will hold the promise of preventing breast and endometrial cancer, while providing the beneficial effects of preventing osteoporosis and coronary heart disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beatson GT: On the treatment of inoperable cases of carcinoma of the mamma: Suggestions for a new method of treatment with illustrative cases. Lancet 2: 104–107, 1896
Boyd S: On oophorectomy in cancer of the breast. BMJ 2: 1161–1167, 1900
Lacassagne A: Hormonal pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma of the breast. Am J Cancer 27: 217–225, 1936
Allen E, Doisy EA: An ovarian hormone: Preliminary report on its localization, extraction and partial purification and action in test animals. JAMA 81: 819–821, 1923
Dodds EC, Lawson W, Noble RL: Biological effects of the synthetic oestrogenic substance 4:4´-dihydroxy-alpha:beta-diethylstilbene. Lancet 1: 1938
Robson JM, Schonberg A: Oestrous reactions including mating produced by triphenylethylene. Nature 140: 196, 1937
Jensen EV, Jacobson HI: Basic guides to the mechanism of estrogen action. Recent Prog Horm Res 18: 387–414, 1962
Gorski J, Toft D, Shyamala G, Smith D, Notides A: Hormone receptors: Studies on the interaction of estrogen with the uterus. Recent Prog Horm Res 24: 45–80, 1968
Jensen EV, Suzuki T, Kawashima T, Stumpf WE, Jungblut PW, DeSombre ER: A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 59: 632–638, 1968
Jensen EV, Block GE, Smith S, Kyser K, DeSombre ER: Estrogen receptors and breast cancer response to adrenalectomy. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 34: 55–70, 1971
McGuire WL, Carbone PP, Volmer EP: Estrogen Receptors in Human Breast Cancer. Raven Press, New York, 1975
Lerner LJ, Holthaus JF, Thompson CR: A non-steroidal estrogen antagonist 1-(p-2-diethylaminoethoxyphenyl)-1-phenyl-2-p-methoxyphenylethanol. Endocrinology 63: 295–318, 1958
Greenblatt RB, Barfield WE, Jungck EC, Ray AW: Induction of ovulation with MRL-41 – preliminary report. JAMA178: 101–104, 1961
Jordan VC, Prestwich G: Binding of [3H]tamoxifen in rat uterine cytosols: A comparison of swinging bucket and vertical tube rotor sucrose density gradient analysis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 8: 179–188, 1977
Jordan VC, Koerner S: Tamoxifen (ICI 46,474) and the human carcinoma 8S oestrogen receptor. Eur J Cancer 11: 205–206, 1975
Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID: A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI 46,474. Br J Cancer 25: 270–275, 1971
Ward HW: Anti-oestrogen therapy for breast cancer: A trial of tamoxifen at two dose levels. BMJ 2: 13–14, 1973
Jordan VC: Effect of tamoxifen (ICI 46,474) on initiation and growth of DMBA-induced rat mammary carcinomata. Eur J Cancer 12: 419–424, 1976
Jordan VC, Allen KE: Evaluation of the antitumour activity of the non-steroidal antioestrogen monohydroxytamoxifen in the DMBA-induced rat mammary carcinoma model. Eur J Cancer 16: 239–251, 1980
Gottardis MM, Jordan VC: The antitumor actions of keoxifene (raloxifene) and tamoxifen in the N-nitrosomethylurea-induced rat mammary carcinoma model. Cancer Res 47: 4020–4024, 1987
Jordan VC, Lababidi MK, Langan-Fahey S: Suppression of mouse mammary tumorigenesis by long-term tamoxifen therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 83: 492–496, 1991
Cuzick J, Baum M: Tamoxifen and contralateral breast cancer. Lancet 2: 282, 1985
Fisher B, Costantino J, Redmond C, Poisson R, Bowman D, Couture J, Dimitrov NV, Wolmark N, Wickerham DL, Fisher ER, et al.: A randomized clinical trial evaluating tamoxifen in the treatment of patients with node-negative breast cancer who have estrogen-receptor-positive tumors. N Engl J Med 320: 479–484, 1989
Sporn MB, Dunlop NM, Newton DL, Smith JM: Prevention of chemical carcinogenesis by vitamin A and its synthetic analogs (retinoids). Fed Proc 35: 1332–1338, 1976
Sporn MB: Approaches to prevention of epithelial cancer during the preneoplastic period. Cancer Res 36: 2699–2702, 1976
EBCTCG: Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 351: 1451–1467, 1998
Terenius L: Structure-activity relationships of antioestrogens with regard to interaction with 17-beta-oestradiol in the mouse uterus and vagina. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 66(Suppl): 431–447, 1971
Love RR, Mazess RB, Barden HS, Epstein S, Newcomb PA, Jordan VC, Carbone PP, DeMets DL: Effects of tamoxifen on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with breast cancer. N Engl J Med 326: 852–856, 1992
Love RR, Wiebe DA, Newcomb PA, Cameron L, Leventhal H, Jordan VC, Feyzi J, DeMets DL: Effects of tamoxifen on cardiovascular risk factors in postmenopausal women. Ann Intern Med 115: 860–864, 1991
Pappas SG, Jordan VC: Raloxifene for the treatment and prevention of breast cancer? Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy 1: 334–340, 2001
Levenson AS, Jordan VC: Selective oestrogen receptor modulation: Molecular pharmacology for the millennium. Eur J Cancer 35: 1628–1639, 1999
Wijayaratne AL, Nagel SC, Paige LA, Christensen DJ, Norris JD, Fowlkes DM, McDonnell DP: Comparative analyses of mechanistic differences among antiestrogens. Endocrinology 140: 5828–5840, 1999
Powles T, Eeles R, Ashley S, Easton D, Chang J, Dowsett M, Tidy A, Viggers J, Davey J: Interim analysis of the incidence of breast cancer in the Royal Marsden Hospital tamoxifen randomised chemoprevention trial. Lancet 352: 98–101, 1998
Veronesi U, Maisonneuve P, Costa A, Sacchini V, Maltoni C, Robertson C, Rotmensz N, Boyle P: Prevention of breast cancer with tamoxifen: Preliminary findings from the Italian randomised trial among hysterectomised women. Italian Tamoxifen Prevention Study. Lancet 362: 93–97, 1998
Decensi A, Bonanni B, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Torrisi R, Manetti L, Robertson C, De Palo G, Formelli F, Costa A, Veronesi U: Chemoprevention of breast cancer: The Italian experience. J Cell Biochem Suppl 34: 84–96, 2000
Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Kavanah M, Cronin WM, Vogel V, Robidoux A, Dimitrov N, Atkins J, Daly M, Wieand S, Tan-Chiu E, Ford L, Wolmark N: Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: Report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 90: 1371–1388, 1998
Narod SA, Brunet JS, Ghadirian P, Robson M, Heimdal K, Neuhausen SL, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Lerman C, Pasini B, de los Rios P, Weber B, Lynch H: Tamoxifen and risk of contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: A case-control study. Hereditary Breast Cancer Clinical Study Group. Lancet 356: 1876–1881, 2000
Bentrem DJ, Jordan VC: Tamoxifen, raloxifene and the prevention of breast cancer. Minerva Endocrinologica 26: 1–13, 2001
Gail MH, Brinton LA, Byar DP, Corle DK, Green SB, Schairer C, Mulvihill JJ: Projecting individualized probabilities of developing breast cancer for white females who are being examined annually [see comments]. J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 1879–1886, 1989
Costantino JP, Gail MH, Pee D, Anderson S, Redmond CK, Benichou J, Wieand HS: Validation studies for models projecting the risk of invasive and total breast cancer incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst 91: 1541–1548, 1999
Cathacart CKJS, Pumroy CS, et al.: Clinical recognition and management of depression in node-negative breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 27: 277–281, 1993
Love RR, Cameron L, Connell BL, Leventhal H: Symptoms associated with tamoxifen treatment in postmenopausal women. Arch Intern Med 151: 1842–1847, 1991
Shariff S, Cumming CE, Lees A, Handman M, Cumming DC: Mood disorder in women with early breast cancer taking tamoxifen, an estradiol receptor antagonist. An expected or unexpected effect? Ann N Y Acad Sci 761: 365–368, 1995
Day R, Ganz PA, Costantino JP, Cronin WM, Wickerham DL, Fisher B: Health-related quality of life and tamoxifen in breast cancer prevention: A report from the national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project P-1 study [In process citation]. J Clin Oncol 17: 2659, 1999
Fallowfield L, Fleissig A, Edwards R, West A, Powles TJ, Howell A, Cuzick J: Tamoxifen for the prevention of breast cancer: Psychosocial impact on women participating in two randomized controlled trials. J Clin Oncol 19: 1885–1892, 2001
Day R, Ganz PA, Costantino JP: Tamoxifen and depression: More evidence from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project's Breast Cancer Prevention (P-1) Randomized Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 93: 1615–1623, 2001
Assikis VJ, Neven P, Jordan VC, Vergote I: A realistic clinical perspective of tamoxifen and endometrial carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer 32A: 1464–1476, 1996
Jordan VC: Designer estrogens. Sci Am 279: 60–67, 1998
Black LJ, Jones CD, Falcone JF: Antagonism of estrogen action with a new benzothiophene derived antiestrogen. Life Sci 32: 1031–1036, 1983
Jones CD, Jevnikar MG, Pike AJ, Peters MK, Black LJ, Thompson AR, Falcone JF, Clemens JA: Antiestrogens. 2. Structure-activity studies in a series of 3-aroyl-2-arylbenzo[b]thiophene derivatives leading to [6-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzo[b]thien-3-yl] [4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy]-phenyl]methanone hydrochloride (LY156758), a remarkably effective estrogen antagonist with only minimal intrinsic estrogenicity. J Med Chem 27: 1057–1066, 1984
Black LJ, Sato M, Rowley ER, Magee DE, Bekele A, Williams DC, Cullinan GJ, Bendele R, Kauffman RF, Bensch WR, et al.: Raloxifene (LY139481 HCI) prevents bone loss and reduces serum cholesterol without causing uterine hypertrophy in ovariectomized rats. J Clin Invest 93: 63–69, 1994
Cohen FJ, Watts S, Shah A, Akers R, Plouffe L, Jr.: Uterine effects of 3-year raloxifene therapy in postmenopausal women younger than age 60. Obstet Gynecol 95: 104–110, 2000
Delmas PD, Bjarnason NH, Mitlak BH, Ravoux AC, Shah AS, Huster WJ, Draper M, Christiansen C: Effects of raloxifene on bone mineral density, serum cholesterol concentrations, and uterine endometrium in postmenopausal women [see comments]. N Engl J Med 337: 1641–1647, 1997
Boss SM, Huster WJ, Neild JA, Glant MD, Eisenhut CC, Draper MW: Effects of raloxifene hydrochloride on the endometrium of postmenopausal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177: 1458–1464, 1997
Jordan VC, Gapstur S, Morrow M: Selective estrogen receptor modulation and reduction in risk of breast cancer, osteoporosis, and coronary heart disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 93: 1449–1457, 2001
Buzdar AU, Marcus C, Holmes F, Hug V, Hortobagyi G: Phase II evaluation of Ly156758 in metastatic breast cancer. Oncology 45: 344–345, 1988
Gradishar W, Glusman J, Lu Y, Vogel C, Cohen FJ, Sledge GW, Jr.: Effects of high dose raloxifene in selected patients with advanced breast carcinoma. Cancer 88: 2047–2053, 2000
Lerner LJ, Jordan VC: Development of antiestrogens and their use in breast cancer: Eighth Cain memorial award lecture. Cancer Res 50: 4177–4189, 1990
Jordan VC, Phelps E, Lindgren JU: Effects of anti-estrogens on bone in castrated and intact female rats. Breast Cancer Res Treat 10: 31–35, 1987
Cummings SR, Eckert S, Krueger KA, Grady D, Powles TJ, Cauley JA, Norton L, Nickelsen T, Bjarnason NH, Morrow M, Lippman ME, Black D, Glusman JE, Costa A, Jordan VC: The effect of raloxifene on risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women: Results from the MORE randomized trial. Multiple outcomes of raloxifene evaluation [see comments]. JAMA 281: 2189–2197, 1999
Cauley JA, Norton L, Lippman ME, Eckert S, Krueger KA, Purdie DW, Farrerons J, Karasik A, Mellstrom D, Ng KW, Stepan JJ, Powles TJ, Morrow M, Costa A, Silfen SL, Walls EL, Schmitt H, Muchmore DB, Jordan VC: Continued breast cancer risk reduction in postmenopausal women treated with raloxifene: 4-year results from the MORE trial. Multiple outcomes of raloxifene evaluation. Breast Cancer Res Treat 65: 125–134, 2001
Jordan VC, Glusman JE, Powles TJ, Costa A, Morrow M, Norton L: Incident primary breast cancer are reduced by raloxifene: Integrated data from multicenter, double blind, randomized trials in 12,000 postmenopausal women Proc ASCO 122a (Abstract 466) 1998.
Jordan VC, Glusman JE, Eckert S, Lippman ME, Powles TJ, Costa A, Morrow M, Norton L: Raloxifene reduces incident primary breast cancers. Integrated data from multicenter double blind, placebo controlled, randomized trials in postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 50: 227, 1998
Jordan VC, Morrow M: Tamoxifen, raloxifene, and the prevention of breast cancer. Endocr Rev 20: 253–278, 1999
Barrett-Connor E, Grady D, Sashegyi A, Anderson PW, Cox DA, Hoszowski K, Rautaharju P, Harper KD: Raloxifene and cardiovascular events in osteoporotic postmenopausal women: Four-year results from the MORE (multiple outcomes of raloxifene evaluation) randomized trial. JAMA 287: 847–857, 2002
Walsh BW, Kuller LH, Wild RA, Paul S, Farmer M, Lawrence JB, Shah AS, Anderson PW: Effects of raloxifene on serum lipids and coagulation factors in healthy postmenopausal women [see comments]. JAMA 279: 1445–1451, 1998
Hulley S, Grady D, Bush T, Furberg C, Herrington D, Riggs B, Vittinghoff E: Randomized trial of estrogen plus progestin for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women. Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study (HERS) Research Group. JAMA 280: 605–613, 1998
Cummings SR, Duong T, Kenyon E, Cauley JA, Whitehead M, Krueger KA: Serum estradiol level and risk of breast cancer during treatment with raloxifene. JAMA 287: 216–220, 2002
Hayes DF, Van Zyl JA, Hacking A, Goedhals L, Bezwoda WR, Mailliard JA, Jones SE, Vogel CL, Berris RF, Shemano I, et al.: Randomized comparison of tamoxifen and two separate doses of toremifene in postmenopausal patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 13: 2556–2566, 1995
Maenpaa J, Holli K, Pasanen T: Toremifene. Where do we stand? Eur J Cancer 36(Suppl 4): S61–S62, 2000
Holli K, Valavaara R, Blanco G, Kataja V, Hietanen P, Flander M, Pukkala E, Joensuu H: Safety and efficacy results of a randomized trial comparing adjuvant toremifene and tamoxifen in postmenopausal patients with node-positive breast cancer. Finnish Breast Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 18: 3487–3494, 2000
Rosati RL, Da Silva Jardine P, Cameron KO, Thompson DD, Ke HZ, Toler SM, Brown TA, Pan LC, Ebbinghaus CF, Reinhold AR, Elliott NC, Newhouse BN, Tjoa CM, Sweetnam PM, Cole MJ, Arriola MW, Gauthier JW, Crawford DT, Nickerson DF, Pirie CM, Qi H, Simmons HA, Tkalcevic GT: Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a novel, potent, nonsteroidal estrogen receptor agonist/antagonist, CP-336156, a diaryltetrahydronaphthalene. J Med Chem 41: 2928–2931, 1998
Ke HZ, Paralkar VM, Grasser WA, Crawford DT, Qi H, Simmons HA, Pirie CM, Chidsey-Frink KL, Owen TA, Smock SL, Chen HK, Jee WS, Cameron KO, Rosati RL, Brown TA, Dasilva-Jardine P, Thompson DD: Effects of CP-336,156, a new, nonsteroidal estrogen agonist/antagonist, on bone, serum cholesterol, uterus and body composition in rat models. Endocrinology 139: 2068–2076, 1998
Willson TM, Henke BR, Momtahen TM, Charifson PS, Batchelor KW, Lubahn DB, Moore LB, Oliver BB, Sauls HR, Triantafillou JA, et al.: 3-[4-(1,2-Diphenylbut-1-enyl)phenyl]acrylic acid: A non-steroidal estrogen with functional selectivity for bone over uterus in rats. J Med Chem 37: 1550–1552, 1994
Bentrem D, Dardes R, Liu H, MacGregor-Schafer J, Zapf J, Jordan V: Molecular mechanism of action at estrogen receptor alpha of a new clinically relevant antiestrogen (GW7604) related to tamoxifen. Endocrinology 142: 838–846, 2001
Connor CE, Norris JD, Broadwater G, Willson TM, Gottardis MM, Dewhirst MW, McDonnell DP: Circumventing tamoxifen resistance in breast cancers using antiestrogens that induce unique conformational changes in the estrogen receptor. Cancer Res 61: 2917–2922, 2001
Gauthier S, Caron B, Cloutier J, Dory YL, Favre A, Larouche D, Mailhot J, Ouellet C, Schwerdtfeger A, Leblanc G, Martel C, Simard J, Merand Y, Belanger A, Labrie C, Labrie F: (S)-(+)-4-[7-(2,2-dimethyl-1-oxopropoxy)-4-methyl-2-[4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)-ethoxy]phenyl]-2H-1-benzopyran-3-yl]-phenyl2,2-dimethylpropanoate (EM-800): A highly potent, specific, and orally active nonsteroidal antiestrogen. J Med Chem 40: 2117–2122, 1997
Luo S, Labrie C, Belanger A, Candas B, Labrie F: Prevention of development of dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary tumors in the rat by the new nonsteroidal antiestrogen EM-800 (SCH57050). Breast Cancer Res Treat 49: 1–11, 1998
Martel C, Labrie C, Belanger A, Gauthier S, Merand Y, Li X, Provencher L, Candas B, Labrie F: Comparison of the effects of the neworally active antiestrogen EM-800 with ICI 182 780 and toremifene on estrogen-sensitive parameters in the ovariectomized mouse. Endocrinology 139: 2486–2492, 1998
Couillard S, Gutman M, Labrie C, Belanger A, Candas B, Labrie F: Comparison of the effects of the antiestrogens EM-800 and tamoxifen on the growth of human breast ZR-75-1 cancer xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res 58: 60–64, 1998
Martel C, Picard S, Richard V, Belanger A, Labrie C, Labrie F: Prevention of bone loss by EM-800 and raloxifene in the ovariectomized rat. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 74: 45–56, 2000
Schafer JI, Liu H, Tonetti DA, Jordan VC: The interaction of raloxifene and the active metabolite of the antiestrogen EM-800 (SC 5705) with the human estrogen receptor. Cancer Res 59: 4308–4313, 1999
Sato M, Turner CH, Wang T, Adrian MD, Rowley E, Bryant HU: LY353381.HCl: a novel raloxifene analog with improved SERM potency and efficacy in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287: 1–7, 1998
Suh N, Glasebrook AL, Palkowitz AD, Bryant HU, Burris LL, Starling JJ, Pearce HL, Williams C, Peer C, Wang Y, Sporn MB: Arzoxifene, a new selective estrogen receptor modulator for chemoprevention of experimental breast cancer. Cancer Res 61: 8412–8415, 2001
MacGregor-Schafer J, Lee E-S, Dardes R, Bentrem D, O'Regan RM, De los Reyes A, Jordan VC: Analysis of cross-resistance of the selective estrogen receptor modulators arzoxifene (LY 353381) and LY 117018 in tamoxifen-stimulated breast cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 7: 2505–2512, 2001
Munster PN, Buzdar A, Dhingra K, Enas N, Ni L, Major M, Melemed A, Seidman A, Booser D, Theriault R, Norton L, Hudis C: Phase I study of a third-generation selective estrogen receptor modulator, LY353381.HCL, in metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 19: 2002–2009, 2001
Peto R, Boreham J, Clarke M, Davies C, Beral V: UK and USA breast cancer deaths down 25% in year 2000 at ages 20–69 years. Lancet 355: 1822, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pappas, S.G., Craig Jordan, V. Chemoprevention of Breast Cancer: Current and Future Prospects. Cancer Metastasis Rev 21, 311–321 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021219212638
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021219212638