Abstract
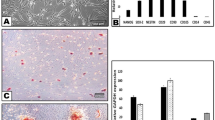
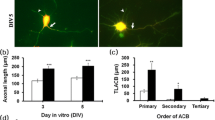
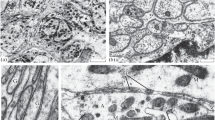
The effects of components from medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis) salivary gland secretions and the therapeutic agent Piyavit on the growth of chick embryo neurites in organotypic culture were studied. Native destabilase and bdellin A at concentrations of 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, and 0.1 ng/ml, bdellin B at a concentration of 0.05 ng/ml, and eglin at a concentration of 0.1 ng/ml had neurite-stimulating activity, evident on the third day of organotypic culture of spinal ganglia. The stimulatory activity of destabilase was lost after revere-phase chromatography. The neurite-stimulating activity of the extract of the therapeutic agent Piyavit (200 ng/ml) in organotypic ganglion culture appeared to result from the neurite-stimulating salivary gland components within this agent, suggesting that Piyavit could be used for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
I. P. Baskova and G. I. Nikonov, “Destabilase - an enzyme from medicinal leech salivary gland secretion which hydrolyzes isopeptide bonds in stabilized fibrin,” Biokhimiya, 50, No. 4, 424–431 (1985).
V. P. Goncharova, N. I. Chalisova, A. V. Romanyuk, G. N. Akoev, and E. N. Chumasov, “The neurite-stimulating activity of brain tissue serine proteases in tissue culture,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 285, No. 2, 1238–1241 (1985).
G. S. Isakhanyan, Hirudotherapy in Clinical Practice in Internal Diseases [in Russian], Aiastan, Erevan (1991).
A. I. Krashenyuk, S. V. Krashenyuk, and N. I. Chalisova, “A neurotrophic factor from Hirudo medicinalis (the medicinal leech),” in: Proceedings of the Fifth Scientific and Applied Conference of the Association of Leech Therapists [in Russian], St. Petersburg, Russia (1997).
A. A. Muslyakovskaya, E. L. Khodorov, and T. M. Pozdnyakova, “Extraction of a dimer of fragment D from stabilized fibrin and studies of its antipolymerization effect,” Ukr. Biokhim. Zh., 48, No. 2, 139–143 (1976).
N. I. Chalisova, V. F. Mel'kishev, G. N. Akoev, M. I. Lyudyno, and T. Yu. Kurenkova, “The neurite-stimulating action of prolactin in organotypic neuron cultures,” Tsitologiya, 33, No. 2, 29–31 (1991).
V. Kh. Khavinson, V. G. Morozov, N. I. Chalisova, and V. V. Okulov, “The effects of brain peptides on nerve tissue cells in vitro,” Tsitologiya, 39, No. 7, (1997).
P. Ascenzi, G. Amiconi, W. Bode, M. Bolognese, M. Coletta, and E. Menegatti, “Protease inhibitors from European medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis: structural, functional and biomedical aspects,” Mol. Aspects Med., 16, 215–313 (1995).
Y. Bardem D, Edgar, and H. Thoenen, “Sensory neurons in culture: changing requirements for survival factors during embryonic development,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 77, 1199–1203 (1980).
I. P. Bascova, A. N. Korostelev, L. D. Chirkova, L. L. Zavalova, A. V. Basanova, and Ch. Doutremepuich, “Piyavit from the medicinal leech is a new orally active anticoagulating and antithrombotic drug,” Clin, Appl. Thrombosis/Hemostasis, 31, 40–45 (1996).
R. Levi-Montalcini, “Developmental neurobiology and the natural history of nerve growth factor,” Ann. Rev. Neurosci., 5, 341–362 (1982).
M. Manthorpe, S. Scaper, Y. Barde, and S. Varon, “Cholinergic neurotrophic factors (CNTF's): concurrent activities on certain nerve growth factor-responsive neurons,” J. Neurochem., 38, 415–421 (1982).
F. Seil and A. Leiman, “Neural subsystem and learning. Tissue-culture approaches,” in: Neural Mechanisms and Learning, London (1997).
L. Zavalova, S. Lukyanov, I. Bascova, S. Berezhnoy, E. Bogdanova, E. Barsova, and E. Sverdlov, “Genes from the medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis) coding for unusual enzymes that specifically cleave endo e(g)-Glu-Lys isopeptide bonds and help to dissolve blood clots,” Mol. Gen. Genet., 253, 20–25 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chalisova, N.I., Baskova, I.P., Zavalova, L.L. et al. The Neurite-Stimulating Influence of Components of Medicinal Leech Salivary Gland Secretions in Organotypic Culture of Spinal Ganglia. Neurosci Behav Physiol 33, 85–88 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021187500632
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021187500632