Abstract
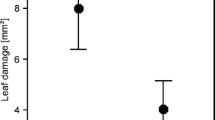
We investigated the effects of plant architecture on predator–prey interactions by quantifying the behavior of green lacewing larvae on perennial grasses with divergent leaf architectures. Crested wheatgrass produces flat, broad leaves similar to those of wheat, whereas Indian ricegrass bears linear leaves that are tightly rolled inward. In the absence of prey, lacewing time budgets and residence times were similar on the two grasses, although predators tended to search longer on crested wheatgrass. On plants infested with the Russian wheat aphid, lacewing larvae dislodged, contacted, and captured significantly more aphids on Indian ricegrass than on crested wheatgrass. Comparisons between aphid-free and aphid-infested plants suggest that differences in plant architecture modified prey accessibility rather than predator movement. Aphids on seedlings and mature plants of crested wheatgrass frequently occurred in concealed locations, such as in the rolls of immature leaves or in the blade–sheath junctions of mature leaves; aphids on Indian ricegrass were more likely to feed in exposed locations. Our focal-animal observations were consistent with results from population-level experiments and suggest that short-term, behavioral studies may help predict the effectiveness of predators at larger spatial and temporal scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aebischer, N. J., Robertson, P. A., and Kenward, R. E. (1993). Compositional analysis of habitat use from animal radio-tracking data. Ecology 74: 1313–1325.
Aitchison, J. (1986). The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data, Chapman and Hall, London.
Alonso, C., and Herrara, C. M. (1996). Variation in herbivory within and among plants of Daphne laureola (Thymelaeaceae): Correlation with plant size and architecture. J. Ecol. 84: 495–502.
Bell, W. J. (1990). Searching behavior patterns in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 353: 447–467.
Bishop, Y. M. M., Fienberg, S. E., and Holland, P. W. (1975). Discrete Multivariate Analysis: Theory and Practice, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Bond, A. B. (1980). Optimal foraging in a uniform habitat: The search mechanism of the green lacewing. Anim. Behav. 28: 10–19.
Carter, M. C., Sutherland, D., and Dixon, A. F. G. (1984). Plant structure and the searching efficiency of coccinellid larvae. Oecologia 63: 394–397.
Elsey, K. D. (1974). Influence of plant host on searching speed of two predators. Entomophaga 19: 3–6.
Elston, D. A., Illius, A. W., and Gordon, I. J. (1996). Assessment of preference among a range of options using log ratio analysis. Ecology 77: 2538–2548.
Ferran, A., and Deconchat, M. (1992). Exploration of wheat leaves by Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) larvae. J. Insect Behav. 5: 147–159.
Frazer, B. D., and McGregor, R. R. (1994). Searching behaviour of adult female Coccinellidae (Coleoptera) on stem and leaf models. Can. Entomol. 126: 389–399.
Freese, G. (1995). Structural refuges in two stem boring weevils on Rumex crispus. Ecol. Entomol. 20: 351–358.
Gardner, S. M., and Dixon, A. F. G. (1985). Plant structure and the success of Aphidius rhopalosiphi (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Ecol. Entomol. 10: 171–179.
Geitzenauer, H. L., and Bernays, E. A. (1996). Plant effects on prey choice by a vespid wasp, Polistes arizonensis. Ecol. Entomol. 21: 227–234.
Greany, P. D., and Hagen, K. S. (1981). Prey selection. In Nordlund, D. A., Jones, R. L., and Lewis, W. J. (eds.), Semiochemicals: Their Role in Pest Control, Wiley, New York, pp. 121–135.
Grevstad, F. S., and Klepetka, B. W. (1992). The influence of plant architecture on the foraging efficiencies of a suite of ladybird beetles feeding on aphids. Oecologia 92: 399–404.
Gross, P. (1991). Influence of target pest feeding niche on success rates in classical biological control. Environ. Entomol. 20: 1217–1227.
Hawkins, B. A., Thomas, M. B., and Hochberg, M. E. (1993). Refuge theory and biological control. Science 262: 1429–1432.
Henry, C. S., Wells, M. M., and Pupedis, R. J. (1993). Hidden taxonomic diversity within Chrysoperla plorabunda (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae): Two new species based on courtship songs. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 86: 1–13.
Jeffries, M. J., and Lawton, J. H. (1984). Enemy-free space and the structure of ecological communities. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 23: 269–286.
Kareiva, P., and Perry, R. (1989). Leaf overlap and the ability of ladybird beetles to search among plants. Ecol. Entomol. 14: 127–129.
Kareiva, P., and Sahakian, R. (1990). Tritrophic effects of a simple architectural mutation in pea plants. Nature 345: 433–434.
Kauffman, W. C., and LaRoche, S. L. (1994). Searching activities by coccinellids on rolled wheat leaves infested by the Russian wheat aphid. Biol. Control 4: 290–297.
Kindler, S. D., and Springer, T. L. (1989). Alternate hosts of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 82: 1358–1362.
Marquis, R. J., and Whelan, C. (1996). Plant morphology and recruitment of the third trophic level: subtle and little-recognized defenses? Oikos 75: 330–334.
Messina, F. J., and Dickinson, J. A. (1993). Egg-laying behavior in divergent strains of the cowpea weevil (Coleoptera: Bruchidae): Time budgets and transition matrices. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 86: 207–214.
Messina, F. J., Jones, T. A., and Nielson, D. C. (1993). Seasonal variation in performance of the Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on alternate hosts. Environ. Entomol. 22: 1022–1030.
Messina, F. J., Jones, T. A., and Nielson, D. C. (1995). Host plant affects the interaction between the Russian wheat aphid and a generalist predator, Chrysoperla carnea. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 68: 313–319.
Messina, F. J., Jones, T. A., and Nielson, D. C. (1997). Host-plant effects on the efficacy of two predators attacking Russian wheat aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 26: 1398–1404.
Milliken, G. A., and Johnson, D. E. (1984). Analysis of Messy Data, Lifetime Learning, Belmont, CA.
Obrycki, J. J. (1986). The influence of foliar pubescence on entomophagous species. In Boethel, D. J., and Eikenbarry, R. D. (eds.), Interactions of Plant Resistance and Parasitoids and Predators of Insects, Wiley, New York, pp. 61–83.
Parr, M. J., Tran, B. M. D., Simmonds, M. S. J., and Credland, P. F. (1996). Oviposition behaviour of the cowpea seed beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus. Physiol. Entomol. 21: 107–117.
Pimentel, D. (1961). An evaluation of insect resistance in broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, collards, and kale. J. Econ. Entomol. 54: 156–158.
Price, P. W. (1986). Ecological aspects of host plant resistance and biological control: Interactions among three trophic levels. In Boethel, D. J., and Eikenbarry, R. D. (eds.), Interactions of Plant Resistance and Parasitoids and Predators of Insects, Wiley, New York, pp. 11–30.
SAS Institute (1990). SAS/STAT User's Guide: Statistics, Version 6, SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
Stadler, B., and Völkl, W. (1991). Foraging patterns of two aphid parasitoids, Lysiphlebus testaceipes and Aphidius colemani on banana. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 58: 221–229.
Stubbendieck, J. L., Hatch, S. L., and Butterfield, C. H. (1992). North American Range Plants, 4th ed., University of Nebraska, Lincoln.
Tauber, C. A., and Tauber, M. J. (1987). Inheritance of seasonal cycles in Chrysoperla (Insecta: Neuroptera). Genet. Res. 49: 215–223.
Vet, L. E. M., and Dicke, M. (1992). Ecology of infochemical use by natural enemies in a tritrophic context. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 37: 141–172.
Völkl, W. (1994). Searching at different spatial scales: The foraging behavior of the aphid parasitoid Aphidius rosae in rose bushes. Oecologia 100: 177–183.
Wickens, T. D. (1989). Multiway Contingency Tables Analysis for the Social Sciences, Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ.
Wilkinson, L., Blank, G., and Gruber, C. (1996). Desktop Data Analysis with SYSTAT, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, T.L., Messina, F.J. Foraging Behavior of Lacewing Larvae (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) on Plants with Divergent Architectures. Journal of Insect Behavior 11, 303–317 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020979112407
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020979112407