Abstract
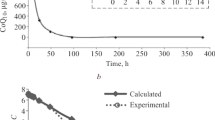
A pharmacokinetic study of cyanamide, an inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC1.2.1.3) used as an adjuvant in the aversive therapy of chronic alcoholism, has been carried out in healthy male volunteers following intravenous and oral administration. Cyanamide plasma levels were determined by a sensitive HPLC assay, specific for cyanamide. After intravenous administration cyanamide displayed a disposition profile according to a two-compartmental open model. Elimination half-life and total plasma clearance values ranged from 42.2 to 61.3 min and from 0.0123 to 0.0190 L · kg −1 · min−1, respectively. After oral administration of 0.3, 1.0, and 1.5 mg/kg \(x -\) ± SEM values of Cmax, tmax (median) and AUC were 0.18 ± 0.03, 0.91 ± 0.11, and 1.65 ± 0.27 μg · ml −1 ; 13.5, 13.5, and 12 min; and 8.59 ± 1.32, 45.39 ± 1.62, and 77.86 ± 17.49 μg · ml −1 · min, respectively. Absorption was not complete and the oral bioavailability, 45.55 ± 9.22, 70.12 ± 4.73, and 80.78 ± 8.19% for the 0.3, 1.0, and 1.5 mg/kg doses, respectively, increased with the dose administered. The models that consider a first-order absorption process alone (whether with a fixed or variable bioavailability value as a function of dose) or with loss of drug due to presystemic metabolism (with zero-order or Michaelis–Menten kinetics) were simultaneously fitted to plasma level data obtained following 1 mg/kg iv and 0.3, 1.0, and 1.5 mg/kg oral administrations. The model that best fit the data was that with a first-order absorption process plus a loss by presystemic metabolism with Michaelis–Menten kinetics, suggesting the presence of a saturable first-pass effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. W. Loomis and J. F. Brien. Specificity of hepatic aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition by calcium carbimide (calcium cyanamide) in the rat. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 61:431–435 (1983).
C. W. Loomis and J. F. Brien. Inhibition of hepatic aldehyde dehydrogenase in the rat by calcium carbimide (calcium cyanamide). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 61:1025–1034 (1983).
I. Cederbaum and E. Dicker. Inhibition of peroxidatic activity of catalase toward alcohols by the aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor cyanamide. Toxicol. Lett. 29:107–114 (1985).
J. F. Brien, J. E. Peachey, C. W. Loomis, and B. J. Rogers. A study of the calcium carbimide ethanol interaction in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 25:454–463 (1979).
J. F. Brien, J. E. Peachey, B. J. Rogers, and C. W. Loomis. A study of the calcium carbimide ethanol interaction in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 14:133–141 (1978).
E. G. DeMaster, E. Kaplan, F. N. Shirota, and H. T. Nagasawa. Metabolic activation of cyanamide by liver mitochondria, a requirement for the inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes. Biochem. Biophys. Pharmacol. 28:2551–2556 (1979)
J. Pruñonosa, M. L. Sagristá, and J. Bozal. Inactivation of low-K m rat liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase by cyanamide in vitro. A catalase-mediated reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 38:2099–2105 (1989).
J. Pruñonosa, M. L. Sagristá, and J. Bozal. Inactivation mechanism of low-K m rat liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase by cyanamide in vitro. Drug Metab. Dispos. 19:787–792 (1991).
R. A. Deitrich, P. A. Troxell, W. Worth, and G. V. Erwin. Inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase in brain and liver by cyanamide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 25:2733–2737 (1976).
R. Obach, C. Valentí, J. Vallés, J. M. Vallés, and J. Domenech. Bioavailability of cyanamide in fasted and unfasted rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 7:273–280 (1986).
R. Obach, J. Moreno, J. Domenech, and J. M. Pla-Delfina. Etude pharmacocinetique de la cyanamide chez le lapin. In Actas del 1er Congreso Europeo de Biofarmacia y Farmacocinética, Vol. 2, Clermont-Ferrand, 1981, pp. 367–375.
R. Obach, H. Colom, J. Arso, C. Peraire, and J. Pruñnosa. Pharmacokinetics of cyanamide in dog and rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 41:624–627 (1989).
J. Pruñonosa, R. Obach, and J. M. Vallés. Determination of cyanamide in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatog. 377:253–260 (1986).
B. Mertschenk, W. Bornemann, J. G. Filser, L. Von Meyer et al. Urinary excretion of acetylcyanamide in rat and human after oral and dermal application of hydrogen cyanamide (H2NCN). Arch. Toxicol. 65:268–272 (1991).
R. Obach, J. Torrent, H. Colom, J. Pruñonosa, C. Peraire, and J. Domenech. Pharmacokinetic and oral bioavailability of carbimide in man. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 12:425–434 (1991).
F. N. Shirota, H. T. Nagasawa, C. H. Kwon, and E. G. DeMaster. N-acetylcyanamide, the major urinary metabolite of cyanamide in rat, rabbit, dog and man. Drug Metab. Dispos. 12:337–344 (1984).
R. C. Shumaker, PKCALC: A basic interactive computer program for statistical and pharmacokinetic analysis of data. Drug. Metab. Rev. 17:341–348 (1986).
D. Perrier and M. J. Mayersohn. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution for any mode of administration. J. Pharm. Sci. 71:372–373 (1982).
R. Gomeni. SIPHAR's Manual Ver 4.0 SIMED, Creteil, France (1991).
K. Yamaoka, T. Nakagawoa, and T. Uno. Application of Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:165–175 (1978).
J. C. K. Loo and S. Riegelman. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 57:918–928 (1968).
WINNONLIN Version 1.1. Scientific Consulting Inc., 1995.
USP-NF XXIII. suppl. 5.
SOLO Statistical System Version 4.0. BMDP Statistical Software, Los Angeles, CA.
W. J. Dixon and F. J. Massey, Jr. Introduction to Statistical Analysis, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1969.
J. T. Doluisio, N. F. Billups, L. W. Dittert, E. T. Sugita, J. V. Swintosky, G. H. Tan, and L. Diamond. Drug Absorption I: An in situ rat gut technique yielding realistic absorption rates. Drug absorption II: Effect of fasting on intestinal drug absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 58:1196–1202 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colom, H., Pruñonosa, J., Peraire, C. et al. Absolute Bioavailability and Absorption Profile of Cyanamide in Man. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 27, 421–436 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020969106163
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020969106163