Abstract
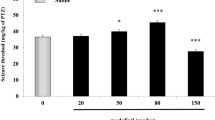
The effect of chronic perfusion of ammonia on the seizure threshold against pentylenetetrazol was studied. Ammonia plus sodium bicarbonate and saline (0.9%) was continuously administered to two groups of rats respectively. All animals were tested three times for seizure threshold, and were then decapitated and the brains removed for analysis of the amino acids. The results showed that the infusion of ammonia increased the seizure threshold, and this protective effect was accompanied by selective changes in brain glutamate and glutamine. Thus, continuous infusion of ammonia may cause an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory systems in favor of inhibitory systems. These findings may provide insights into the basic mechanisms of seizures observed in hepatic failure, in other hyperammonemic states, and in epilepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Plum F., Cooper A.J.L. (1987). Biochemistry and Physiology of brain ammonia: Physiological Review, 76,2, 440–519.
Wise T. (1987). Gastroenterology, in: Principles of Medical Psychiatry, Stoudemire A., Fogel B.S. (eds.), Grune and Stratton Inc., Orlando, FL, 571–582.
Butterworth R.F. (1998). Effects of hyperammonaemia on brain function. J. Inherit Metab. Dis., 21(Suppl. 1), 6–20.
Stryer L: (1988). Biosynthesis of aminoacids and heme. pp. 575–600, Biochemistry, 3rd edition, W. H. Freeman and Company, New York.
Lacoste L., Bartolucci S., Lapointe J., (1988). Pentylenetetrazole inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase and aspartate aminotransferase, and stimulates GABA aminotransferase in homogenates from rat cerebral cortex. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 66:9, 1135–8.
Kanamori, K., Parivar, F., Ross, B.D., (1993). “15N NMR Study of In Vivo Cerebral Glutamine Synthesis in Hyperammoniemic Rats”, N.M.R-Biomed, 6,1: 21–26, 1993.
Hebel, R., and Stromberg, M.W., (1976). Anatomy of the Laboratory Rat. Baltimore, The Williams & Wilkins Co., 119–144.
Sejima, H., Ito, M., Kishi, K., Tsuda, H., Shiraishi, H. (1997). Regional excitatory and inhibitory amino acid concentrations in pentylenetetrazol kindling and kindled rat brain. Brain Dev, 19:3, 171–5.
Raabe, W., (1987). The H-reflex in the encephalopathy due to ammonia intoxication. Exp Neurol, 96:3, 601–11.
Szerb, J.C., Butterworth, R.F. (1992). Effect of ammonium ions on synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol, 39:2, 135–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arikan, K., Coskun, T., Guvener, B. et al. Effects of Ammonia on Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizure Threshold. Metab Brain Dis 14, 223–230 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020780908096
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020780908096