Abstract
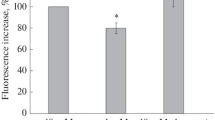
Although the well-known neurotoxic agent bilirubin can induce alterations in neuronal signaling, direct effects on neurotransmitter release have been difficult to demonstrate. In the present study we have used permeabilized nerve terminals (synaptosomes) from rat brain prelabeled with [3H]norepinephrine to examine the effects of bilirubin on transmitter release. Rat cerebrocortical synaptosomes were permeabilized with streptolysin-O (2 U/ml) in the absence or presence of bilirubin (10 μM–320 μM) and Ca2+ (100 μM), and the amount of radiolabeled transmitter released during 5 min to the medium was analysed. Low levels of bilirubin decreased Ca2+-evoked release in a dose-dependent manner, with half-maximal effect at approx 25 μM bilirubin. Higher levels of bilirubin (100–320 μM) increased [3H]norepinephrine efflux in the absence of Ca2+, suggesting that high bilirubin levels induced leakage of transmitter from vesicles. The nontoxic precursor biliverdin had no effect on Ca2+-dependent exocytosis. Our data indicate that bilirubin directly inhibits both exocytotic release and vesicular storage of brain catecholamines.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hansen, T. W. R. and Bratlid, D. 1986. Bilirubin and brain toxicity. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 75:513–522.
Perlman, M., Fainmesser, P., Sohmer, H., Tamari, H., Wax, Y., and Pevsmer, B. 1983. Auditory nerve-brainstem evoked responses in hyperbilirubinemic neonates. Pediatrics 72:658–664.
Karplus, M., Lee, C., Cashore, W. J., and Oh, W. 1988. The effects of brain bilirubin deposition on auditory brain stem evoked responses in rats. Early Hum. Dev. 16:185–194.
Hansen, T. W. R., Cashore, W. J., and Oh, W. 1992. Changes in piglet auditory brainstem response amplitudes without increases in serum or cerebrospinal fluid neuron-specific enolase. Pediatr. Res. 32:524–529.
Hansen, T. W. R., Paulsen, O., Gjerstad, L., and Bratlid, D. 1988. Short-term exposure to bilirubin reduces synaptic activation in rat transverse hippocampal slices. Pediatr. Res. 23:453–456.
Hansen, T. W. R., Bratlid, D., and Walaas, S. I. 1988. Bilirubin decreases phosphorylation of synapsin I, a synaptic vesicle-associated neuronal phosphoprotein, in intact synaptosomes from rat cerebral cortex. Pediatr. Res. 23:219–223.
Ochoa, E. L. M., Wennberg, R. P., An, Y., Tandon, T., Takashima, T., Nguyen, T., and Chui, T. 1993. Interactions of bilirubin with isolated presynaptic nerve terminals: functional effects on the uptake and release of neurotransmitters. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 13:69–86.
Cashore, W. J. and Kilguss, N. V. 1989. Inhibition of synaptosomal tyrosine uptake by bilirubin. Pediatr. Res. 25:209A.
Schweizer, F. E., Betz, H., and Augustine, G. J. 1995. From vesicle docking to endocytosis: intermediate reactions of exocytosis. Neuron 14:689–696.
Sudhof, T. C. 1995. The synaptic vesicle cycle: a cascade of protein-protein interactions. Nature 375:645–653.
Neher E. 1998. Vesicle pools and Ca2+ microdomains: New tools for understanding their roles in neurotransmitter release. Neuron 20:389–399.
Day, R. L. 1954. Inhibition of brain respiration in vitro by bilirubin: Reversal of inhibition by various means. Am. J. Dis. Child. 88:504–506.
Zetterström, R. and Ernster, L. 1956. Bilirubin, an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in isolated mitochondria. Nature (London) 178:1335–1337.
Ernster, L., Herlin, L., and Zetterström, R. 1957. Experimental studies on the pathogenesis of kernicterus. Pediatrics 20:647–652.
Ives, N. K., Bolas, B. M., and Gardiner, R. M. 1989. The effects of bilirubin on brain energy metabolism during hyperosmolar opening of the blood-brain barrier: an in vivo study using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr. Res. 26:356–361.
Kashiwamata, S., Goto, S., Semba R. K., and Suzuki, F. N. 1979. Inhibition by bilirubin of (Na+/K+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase and K+-activated p-nitrophenylphosphatase activities of Nal-treated microsomes from young rat cerebrum. J. Biol. Chem. 254:4577–4588.
Cowger, M. L. 1971. Mechanism of bilirubin toxicity on tissue culture cells: Factors that affect toxicity, reversibility by albumin, and comparison with other respiratory poisons and surfactants. Biochem. Med. 5:1–16.
O'Callaghan, A. and Duggan, P. F. 1984. Possible biochemical basis for bilirubin neurotoxicity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 12:483.
Mayor, F. J., Diez-Guerra, J., Valdivieso, F., and Mayor, F. 1986. Effect of bilirubin on the membrane potential of rat brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 47:363–369.
Roseth, S., Hansen, T. W. R., Fonnum, F., and Walaas, S. I. 1998. Bilirubin inhibits transport of neurotransmitters in synaptic vesicles. Pediatric Res. 44: 312–316.
Dekker, L. V., DeGraan, P. N., Oestreicher, A. B., Versteeg, D. H., and Gispen, W. H. 1989. Inhibition of noradrenaline release by antibodies to B-50 (GAP-43). Nature 342:74–76.
Hens, J. J., Ghijsen, W. E., Dimjati, W., Wiegant, V. M., Oestreicher, A. B., Gispen, W. H., and DeGraan, P. N. 1993. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C substrate B-50 (GAP-43) in Ca2+-induced neuropeptide cholecystokinin-8 release from permeated synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 61:602–609.
Stecher, B., Hens, J. J., Weller, U., Gratzl, M., Gispen, W. H., and De Graan P.N. 1992. Noradrenaline release from permeabilized synaptosomes is inhibited by the light chain of tetanus toxin. FEBS Lett. 312:192–194.
Tandon, A., Bannykh, S., Kowalchyk, J. A., Banerjee, A., Martin, T. F. J., and Balch, W. E. 1998. Differential regulation of exocytosis by calcium and CAPS in semi-intact synaptosomes. Neuron 21:147–154.
Floor, E., Leventhal, P. S., Wang, Y., Meng, L., and Chen, W. 1995. Dynamic storage of dopamine in rat brain synaptic vesicles in vitro. J. Neurochem. 64:689–699.
Hansen, T. W. R., Mathiesen, S. B. W., Sefland, I., and Walaas, S.I. 1996. Bilirubin inhibits Ca++-dependent release of norepinephrine from permeabilized nerve terminals. Pediatr. Res. 39:60A.
Hansen, T. W. R., Mathiesen, S. B. W., Sefland, I., and Walaas, S. I. 1996. Bilirubin increases leakage of 3H-norepinephrine from presynaptic vesicles in the absence of Ca++ Pediatr. Res. 39:60A.
Wang, J. K., Walaas, S. I., and Greengard, P. 1988. Protein phosphorylation in nerve terminals: comparison of calcium/calmodulin-dependent and calcium/diacyl-glycerol-dependent systems. J. Neurosci. 8:281–288.
Helmerhorst, E., Stokes, G. B. 1978. Microcentrifuge desalting: A rapid, quantitative method for desalting small amounts of protein. Anal. Biochem. 104:130–135.
Dekker, L. V., DeGraan, P. N., Pijnappel, P., Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H. 1991. Noradrenaline release from streptolysin O-permeated rat cortical synaptosomes: effects of calcium, phorbol esters, protein kinase inhibitors, and antibodies to the neuron-specific protein kinase C substrate B-50 (GAP-43). J. Neurochem. 56:1146–1153.
Johnson, M. K. 1960. The intracellular distribution of glycolytic and other enzymes in rat-brain homogenates and mitochondrial preparations. Biochem. J. 77:610–618.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein determination with the Folin Phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–279.
Hansen, T. W. R., Mathiesen, S. B. W., and Walaas, S. I. 1996. Bilirubin has widespread inhibitory effects on protein phosphorylation. Pediatr. Res. 39:1072–1077.
Churn, S. B., DeLorenzo, R. J., and Shapiro, S. M. 1996. Bilirubin induces a calcium-dependent inhibition of multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II activity in vitro. Pediatr. Res. 38:949–954.
Li, L., Chin, L. S., Shupliakov, O., Brodin, L., Sihra, T. S., Hvalby, Ø., Jensen, V., Zheng, D., McNamara, J. O., Greengard, P. et al. 1995. Impairment of synaptic vesicle clustering and of synaptic transmission, and increased seizure propensity, in synapsin I-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:9235–9239.
Nakanishi, N., Onozawa, S., Matsumoto, R., Hasegawa, H., and Yamada, S. 1995. Cyclic AMP-dependent modulation of vesicular monoamine transport in pheochromocytoma cells. J. Neurochem. 64:600–607.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansen, T.W.R., Mathiesen, S.B., Sefland, I. et al. Bilirubin Inhibits Ca2+-Dependent Release of Norepinephrine from Permeabilized Nerve Terminals. Neurochem Res 24, 733–738 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020775312214
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020775312214