Abstract
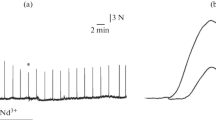
A hyperpolarizing effect of noradrenaline (NA) on muscle cells of the earthworm caused by activation of the membrane ion pumps is eliminated in a Ca-free medium, in the case of replacement of Na+ by Mn2+, or when verapamil or chlorpromazine have been added to the bath solution. A decrease or an increase in the Ca2+ concentration in the solution, as well as caffeine application, do not influence the resting membrane potential (RMP) of muscle cells. It is supposed that signal transmission from the membrane adrenoreceptors to the ion pump of earthworm muscle cells by NA is provided via entry of extracellular Ca2+ ions into the cell with subsequent involving of Ca2+ acceptor proteins similar to calmodulin in vertebrate animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. M. Volkov, L. P. Nurullin, and E. E. Nikolsky, “Influence of ion composition on the resting membrane potential of filaments of longitudinal somatic muscle cells of the earthworm,” Ross. Zh. Fiziol., 86,No. 3, 329–334 (2000).
E. M. Volkov, L. P. Nurullin, and E. E. Nikolsky, “Influence of the sodium pump and co-transport of Na+-K+-Cl− on the resting membrane potential of cells of somatic muscle cells of earthworm Lumbricus terrestris,” Ross. Zh. Fiziol., 87,No. 9, 1153–1160 (2001).
E. M. Volkov, L. P. Nurullin, E. E. Nikolsky, and G. I. Blokhina, “Influence of noradrenaline and adrenaline on the resting membrane potential of cells of the muscle wall of earthworm Lumbricus terrestris,” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 132,No. 9, 244–246 (2001).
C. P. Drewes and R. A. Pax, “Neuromuscular physiology of the longitudinal muscle of the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris. I. Effects of different physiological salines,” J. Exp. Biol., 60, 445–462 (1974).
E. M. Volkov, “Influence of verapamil and Mg ions on the sensitivity to acetylcholine of membrane innervate and denervate frog muscle fibers,” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 94,No. 7, 25–27 (1982).
I. M. Gotgilph and L. G. Magazanik, “Influence of blockers of calcium channels (verapamil, D-600 and Mg ions) on mediator release from the motor terminals of frog muscles,” Ross. Zh. Neirofiziol., 9,No. 3, 415–421 (1977).
A. Weber and R. Hertz, “The regulation between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum,” J. Gen. Physiol., 52,No. 3, 750–759 (1968).
P. V. Sergeev, N. L. Shymanovsky, and V. I. Petrov, Receptors [in Russian], Moscow, Volgograd (1999).
E. M. Volkov, I. V. Kudryavseva, G. A. Nasledov, and N. N. Nikolsky, “Supplement of cyclic nucleotides in frog muscle in vitro,” Ukr. Zh. Biokhim., 60,No. 5, 40–45 (1988).
M. P. Walsh, “Calmodulin and its roles in skeletal muscle function,” Can. Anaesth. Soc. J., 30,No. 4, 390–398 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkov, E.M., Nurullin, L.P. A Calcium Aspect of the Effect of Noradrenaline on the Resting Membrane Potential in Somatic Muscle Cells of the Earthworm. Neurophysiology 34, 255–257 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020752727791
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020752727791