Abstract
A series of studies was conducted to determine the optimum manganese and niobium contents in steels alloyed with the system C–Mn–Nb. Researchers also wanted to find the starting and finishing temperatures for rolling on a 2800 mill that would be best in order to obtain the necessary mechanical properties when the metal is deformed in the austenite range with small reductions.
The studies established the following:
– a greater improvement in strength properties is obtained from an increase in the mass content of manganese if the carbon content is reduced (0.09–0.10%) rather than increased (0.12–0.13%);
– other conditions being equal, an increase in the niobium content of the steel from 0.02–0.03% to 0.04–0.06% leads to a substantial increase in strength and toughness properties and a decrease in ductility;
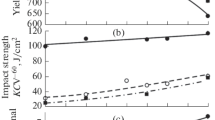
– it was established that in terms of its effect on the yield point, microalloying steel with 0.01% niobium is equivalent to alloying with 0.30–0.40% manganese;
– the percentage of the tough B component in the fracture of IPG specimens of low-alloy steel with a niobium content of 0.02–0.03 mass % can be increased from 30 to 100% by decreasing the temperature of the slab after the second pass through the two-high stand from 1020 to 980°C. For steels with a higher niobium content (0.05–0.06%), the temperature of the metal when it enters the roughing stand can be increased to 1010–1040°C without adversely affecting the standard characteristic B (%);
– a decrease in the finishing temperature is accompanied by an increase in the strength and toughness properties of the metal and a decrease in ductility. Reducing the finishing temperature to below 760°C makes it possible to increase strength properties but does not change impact toughness.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. K. Shafigin, A. M. Stepashin, and S. V. Aleksandrov, “Mastering the production of skelp made of naturally alloyed steels for durable gas and oil line pipe,” Metallurg, No. 9, 39-42 (2000).
E. K. Shafigin, A. M. Stepashin, S. V. Aleksandrov, and A. V. Gavrilov, “Mastering the production of rolled plates of strength class K52 for welded gas and oil line pipe made of dispersion-hardened steels,” Metallurg, No. 2, 23-25 (2000).
M. I. Gol'dshtein, A. A. Emel'yanov, and I. Yu. Pyshmintsev, “Strengthening low-carbon steels,” Stal', No. 6, 53-58 (1996).
V. K. Potemkin and V. A. Peshkov, “Controlled rolling. Thermomechanical treatment of plates,” Itogi Nauk. Tekh. Prokatnoe i Volochil'noe Proizv., 14, 3-55 (1986).
A. N. Sorokin, “Study of the effect of micro-additions of titanium, niobium, and vanadium on the properties of low-pearlite steels after controlled rolling,” Author's Abstract of Engineering Sciences Candidate Dissertation, Moscow (1981).
Yu. I. Matrosov, V. N. Filimonov, M. M. Borodkina, et al., Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Metall., No. 5, 99-104 (1980).
F. Khaisterkamp, K. Khulka, Yu. D. Morozov, et al. Niobium-Bearing Low-Alloy Steels [in Russian]. “Intermet Engineering,” Moscow, St. Petersburg (1999), pp. 37-40.
L. Tom, Carbides and Nitrides of Transition Metals [Russian translation], Nauka, Moscow (1974).
Kahn (ed.), Physical Metallurgy [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1968).
M. I. Gol'dshtein and V. M. Farber, Dispersion-Hardening of Steel, Metallurgiya, Moscow (1985).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morozov, Y.D., Stepashin, A.M. & Aleksandrov, S.V. Effect of Manganese and Niobium and Rolling Conditions on the Properties of Low-Alloy Steel. Metallurgist 46, 152–156 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020428702409
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020428702409