Abstract
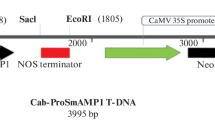
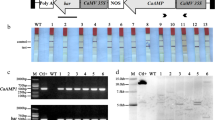
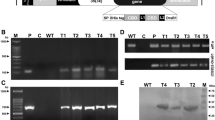
Two hevein-like peptides from the seed of Pharbitis nil, designated Pharbitis nil antimicrobial peptide 1 (Pn-AMP1) and Pn-AMP2, had been purified previously. Both exhibit potent in vitro antifungal activity against a broad spectrum of phytopathogenic fungi. We now report the isolation of two cDNA clones, designated pnAMP-h1 and pnAMP-h2, and the corresponding genomic clones encoding these proteins from mature seeds of P. nil. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence to that of the mature protein suggests that the peptides are produced as a prepropeptide consisting of an N-terminal signal peptide, the mature protein and C-terminal domains. The transcripts of the two genes are accumulated seed-specifically, and the maximum transcripts are observed in the mid-to-late stage of seed development. Constitutive over-expression of the pnAMP-h2 cDNA in transgenic tobacco under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter conferred enhanced resistance against the oomycete Phytophthora parasitica, the causal agent of black shank disease. Thus the Pn-AMPs may play a role in the protection of seeds and may be useful as a novel gene source to engineer plants resistant to fungal pathogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, D., Goodman, R.M., Gut-Rella, M., Glascock, C., Weymann, K., Friedrich, L., Maddox, D., Ahl-Goy, P., Luntz, T., Ward, E. and Ryals, J. 1993. Increased tolerance to two oomycete pathogens in transgenic tobacco expressing pathogenesis-related protein 1a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 7327–7331.
An, G., Ebert, P.R., Mitra, A. and Ha, S.B. 1988. Binary vectors. In: S.B. Gelvin, R.A. Schilperoort and D.P.S. Verma (Eds) Plant Molecular Biology Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. A3/1–A3/19.
Broekaert, W., Lee, H.I., Kush, A., Chua, N.H. and Raikhel, N. 1990. Wound-induced accumulation of mRNA containing a hevein sequence in laticifers of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 7633–7637.
Broekaert, W.F., Marien, W., Terras, F.R.G., De Bolle, M.F., Proost, P., Van Damme, J., Dillen, L., Claeys, M., Rees, S.B., Vanderleyden, J. and Cammue, B.P.A. 1992. Antimicrobial peptides from Amaranthus caudatus seeds with sequence homology to the cysteine/glycine-rich domain of chitin-binding proteins. Biochemistry 31: 4308–4314.
Broekaert, W.F., Terras, F.R.G., Cammue, B.P.A., and Osborn, R.W. 1995. Plant defensins; novel antimicrobial peptides as components of the host defense system.Plant Physiol. 108: 1353–1358.
Cammue, B.P.A., De Bolle, M.F., Terras, F.R., Proost, P., Van Damme, J., Rees, S.B., Vanderleyden, J. and Broekaert, W.F. 1992. Isolation and characterization of a novel class of plant antimicrobial peptides form Mirabilis jalapa L. seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 2228–2233.
Cammue, B.P.A., Thevissen, K., Hendriks, M., Eggermont, K., Goderis, I.J., Proost, P., Van Damme, J., Osborn, R.W., Guerbette, F., Kader, J.C. and Broekaert, W.F. 1995. A potent antimicrobial protein from onion seeds showing sequence homology to plant lipid transfer proteins. Plant Physiol. 109: 445–455.
De Bolle, M.F., Osborn, R.W., Goderis, I.J., Noe, L., Acland, D., Hart, C.A., Torrekens, S., Van Leuven, F. and Broekaert, W.F. 1966. Antimicrobial peptides from Mirabilis jalapa and Amaranthus caudatus: expression, processing, localization and biological activity in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 31: 993–1008.
Duvick, J.P., Rood, T., Rao, A.G. and Marshak, D.R. 1992. Purification and characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from maize (Zea mays L.) kernels. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 18814–18820.
Epple, P., Apel, K. and Bohlmann, H. 1997. Overexpression of an endogenous thionin enhances resistance of Arabidopsis against Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell 9: 509–520.
Fernandez de Caleya, R., Gonzalez-Pascual, B., Garcia-Olmedo, F. and Carbonero, P. 1972. Susceptibility of phytopathogenic bacteria to wheat purothionins in vitro. Appl. Microbiol. 23: 998–1000.
Flyg, C., Dalhammar, G., Rasmuson, B. and Boman, H. 1987. Insect immunity: inducible antibacterial activity in Drosophila. Insect Biochem. 17: 153–160.
Gao, A.G., Hakim, S.M., Mittanck, C.A., Wu, Y., Waerner, B.M., Stank, D.M., Shah, D.M., Liang, J. and Rommrns, C.M.T. 2000. Fungal pathogen protection in potato by expression of a plant defensin peptide. Nature Biotechnol. 18: 1307–1310.
Hong, J.C., Nagao, R.T. and Key, J.L. 1987. Characterization and sequence analysis of a developmentally regulated putative cell wall protein gene isolated from soybean. J. Biol. Chem. 262: 8367–8376.
Horsch, R.B., Fry, J.E., Hoffmann, N.L., Eichholfz, D., Rogers, S.G. and Fraley, R.T. 1985. A simple and general method for transfering genes into plants. Science 227: 1229–1231.
Koo, J.C., Lee, S.Y., Chun, H.J., Cheong, Y.H., Choi, J.S., Kawabata, S., Miyagi, M., Tsunasawa, S., Ha, K.S., Bae, D.W., Han, C.D., Lee, B.L. and Cho, M.J. 1998. Two hevein homologs isolated from the seed of Pharbitis nil L. exhibit potent antifungal activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1382: 80–90.
Koo, J.C., Bendahmane, M., Lettieri, G.A., Paoletti, A.D., Lane, T.E., Fitchen, J.H., Buchmeier, M.J. and Beachy, R.N. 1999. Protective immunity against murine hepatitis virus (MHV) induced by intranasal or subcutaneous administration of hybrids of tobacco mosaic virus that carries an MHV epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 7774–7779.
Molina, A., Segura, A. and Garcia-Olmedo, F. 1993. Lipid transfer proteins (nsLTPs) from barley and maize leaves are potent inhibitors of bacterial and fungal plant pathogens. FEBS Lett. 316: 119–122.
Murashige, T. and Skoog, F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497.
Nielsen, K.K., Nielsen, J.E., Madrid, S.M. and Mikkelsen, J.D. 1997. Characterization of a new antifungal chitin-binding peptide from sugar beet leaves. Plant Physiol. 113: 83–91.
Penninckx, I.A., Eggermont, K., Terras, F.R., Thomma, B.P., De Samblanx, G.W., Buchala, A., Metraux, J.P., Manners, J.M. and Broekaert, W.F. 1996. Pathogen-induced systemic activation of a plant defensin gene in Arabidopsis follows a salicylic acid-independent pathway. Plant Cell 8: 2309–2323.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A.R. 1977. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467.
Segura, A., Moreno, M., Madueno, F., Molina, A. and Garcia-Olmedo, F. 1999. Snakin-1, a peptide from potato that is active against plant pathogens. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 12: 16–23.
Shao, F., Hu, Z., Xiong, Y.M., Huang, Q.Z., Wang, C.G., Zhu, R.H. and Wang, D.C. 1999. A new antifungal peptide from the seeds of Phytolacca americana: characterization, amino acid sequence and cDNA cloning. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1430: 262–268.
Shure, M., Wessler, S. and Fedoroff, N. 1983. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell 35: 225–233.
Tailor, R.H., Acland, D.P., Attenborough, S., Cammue, B.P., Evans, I.J., Osborn, R.W., Ray, J.A., Rees, S.B. and Broekaert, W.F. 1997. A novel family of small cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides from seed of Impatiens balsamina is derived from a single precursor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 24480–24487.
Terras, F.R., Schoofs, H.M., De Bolle, M.F., Van Leuven, F., Rhee, S.G., Vanderleyden, J., Cammue, B.P.A. and Broekaert, W.F. 1992. Analysis of two novel classes of antifungal proteins from radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 15301–15309.
Terras, F.R., Eggermont, K., Kovaleva, V., Raikhel, N.V., Osborn, R.W., Kester, A., Rees, S.B., Torrekens, S., Van Leuven, F., Vanderleyden, J. and Cammue, B.P.A. 1995. Small cysteine-rich antifungal proteins from radish: their role in host defense. Plant Cell 7: 573–588.
Thevissen, K., Osborn, R.W., Acland, D.P. and Broekaert, W.F. 2000. Specific binding sites for an antifungal plant defensin from dahlia (Dahlia merckii) on fungal cells are required for antifungal activity. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 13: 54–61.
Van Damme, E.J., Charels, D., Roy, S., Tierens, K., Barre, A., Martins, J.C., Rouge, P., Van Leuven, F., Does, M. and Peumans, W.J. 1999. A gene encoding a hevein-like protein from elderberry fruits is homologous to PR-4 and class V chitinase genes. Plant Physiol. 119: 1547–1556.
von Heijne, G. 1988. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 974: 307–333.
Waljuno, K., Scholma, R.A., Beintema, J., Mariono, A. and Hahn, A.M. 1975. Amino acid sequence of hevein. In: Proceedings of the International Rubber Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Vol. 2, Rubber Research Institute of Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, pp. 518–531.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choon Koo, J., Jin Chun, H., Cheol Park, H. et al. Over-expression of a seed specific hevein-like antimicrobial peptide from Pharbitis nil enhances resistance to a fungal pathogen in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 50, 441–452 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019864222515
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019864222515