Abstract
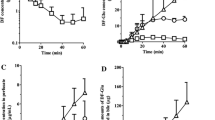
Methods for continuous in vivo sampling in the bile, blood, and liver extracellular fluid are described. These methods are based on microdialysis sampling in anesthetized rats. A new flow-through microdialysis probe is described for sampling bile while maintaining normal bile flow. All three sites are simultaneously and continuously sampled to provide concentration–time profiles at multiple sites in a single experimental animal. This technique is demonstrated by studying the hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion of phenol in rats. Following an i.v. infusion of phenol, the major hepatic metabolite was found to be phenyl-glucuronide. Hydroquinone and 2-glutathionyl–hydroquinone were also detected but at lower concentrations. A similar pattern of metabolites was found in the bile and blood. For all of the metabolites, bile concentrations are higher than liver concentrations, indicating that the metabolites are actively excreted into the bile.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. D. Blakely, S. A. Wages, J. B. Justice, Jr., J. G. Herndon, and D. B. Neill. Neuroleptics increase striatal catecholamine metabolites but not ascorbic acid in dialyzed perfusate. Brain Res. 308:1–8 (1984).
T. Zetterstrom and U. Ungerstedt. Effects of apomorphine on the in vivo release of dopamine and its metabolites, studied by brain dialysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 97:29–36 (1984).
T. E. Robinson and J. B. Justice, Jr. Microdialysis in the Neurosciences, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1991.
D. O. Scott, K. L. Steele, L. R. Sorensen, and C. E. Lunte. In vivo microdialysis sampling for pharmacokinetic investigations. Pharm. Res. 8:389–392 (1991).
D. O. Scott, L. R. Sorensen, and C. E. Lunte. In vivo microdialysis sampling coupled to liquid chromatography for the study of acetaminophen metabolism. J. Chromatogr. 506:461–469 (1990).
K. L. Steele, D. O. Scott, and C. E. Lunte. Pharmacokinetic studies of aspirin in rats using in vivo microdialysis sampling. Anal. Chim. Acta 246:181–186 (1991).
M. Telting-Diaz, D. O. Scott, and C. E. Lunte. Intravenous microdialysis sampling in awake, freely-moving rats. Anal. Chem. 64:806–810 (1992).
D. O. Scott, M. A. Bell, and C. E. Lunte. Microdialysis perfusion sampling for the investigation of phenol metabolism. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 7:1249–1259 (1989).
P. Lönnroth, P.-A. Jannson, and U. Smith. A microdialysis method allowing characterization of intercellular water space in humans. Am. Physiol. Soc. 253:E228–E231 (1987).
P. Arner, E. Kriegholm, and P. Engfeldt. In situ studies of catecholamine-induced lipolysis in human adipose tissue using microdialysis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 254:284–288 (1990).
J. Ben-Nun, D. A. Joyce, R. L. Cooper, S. J. Cringle, and I. J. Constable. Pharmacokinetics of intravitreal injection. Invest. Ophthamol. Vis. Sci. 30:1055–1061 (1989).
A. Lehmann. Effects of microdialysis-perfusion with anisosmotic media on extracellular amino acids in rat hippocampus and skeletal muscle. J. Neurochem. 51:525–535 (1989).
C. E. Lunte, D. O. Scott, and P. T. Kissinger. Sampling living systems using microdialysis probes. Anal. Chem. 63:773A–780A (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, D.O., Lunte, C.E. In Vivo Microdialysis Sampling in the Bile, Blood, and Liver of Rats to Study the Disposition of Phenol. Pharm Res 10, 335–342 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018971818689
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018971818689