Abstract
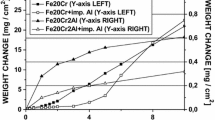
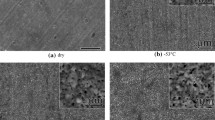
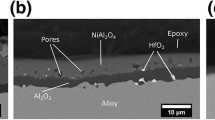
A study has been undertaken of the effects oflanthanum on the oxidation of thin foils of Fe-20Cr-5Alin air at 1150°C. The addition of lanthanum causesthe time to breakaway to increase from about 24 hr for Fe-20Cr-5Al to over 400 hr. Oxidationof the lanthanum-containing alloy occurs in threestages. During the first stage, anα-Al2O3 layer is establishedand thickens with time until the aluminum in the foil is depleted sufficiently for alayer of Cr2O3 to become stableand develop at the scale-alloy interface. This continuesto thicken at a relatively slow rate until breakawayoccurs. The main emphasis in the present paper has been anexamination and analysis of the scale established on thelanthanum-containing alloy in cross section in theanalytical transmission electron microscope (TEM), after an exposure period that coincides with thesecond stage of oxidation, prior to breakaway. The scaleat that time consists of three layers. The outer layeris composed of equiaxed Al2O3grains. The intermediate and inner layers consist of columnarAl2O3 grains and equiaxedCr2O3 grains, respectively.Numerous voids are observed in the oxide grainboundaries and at the intermediate-inner layerinterface. Lanthanum segregates in the oxide grain boundaries andits concentration increases toward the outermost surfaceof the scales. These results are consistent with the“dynamic segregation model” to account for the effects of reactive elements on thegrowth of Al2O3 scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Ishii and T. Kawasaki, J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 56, 854 (1992).
N. Hiramatsu and Y. Uematsu, Tetsu to Hagane 81, 59 (1996).
B. A. Pint, Oxid. Met. 48, 303 (1997).
J. Stringer, I. M. Allan, and D. P. Whittle, Thin Solid Films 59, 377 (1979).
G. C. Wood and F. H. Stott, in High Temperature Corrosion, Proc. Intern. Conf., San Diego, Californiam, NACE-6, R. A. Rapp, ed. (National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, 1981), p. 227.
B. A. Pint and L. W. Hobbs, Oxid. Met. 41, 203 (1994).
H. M. Tawancy, Oxid. Met. 45, 323 (1996).
T. A. Ramanarayanan, M. Raghavan, and R. Petkovic-Luton, Oxid. Met. 22, 83 (1984).
B. Pieraggi and R. A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 2844 (1993).
B. A. Pint, Oxid. Met. 45, 1 (1996).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiramatsu, N., Stott, F.H. The Effect of Lanthanum on the Scales Developed on Thin Foils of Fe-20Cr-5Al at Very High Temperatures. Oxidation of Metals 51, 479–494 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018891211160
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018891211160