Abstract
The WKB method has been used to develop an approximate solutionof the semi-geostrophic Ekman boundary layer with height-dependenteddy viscosity and a baroclinic pressure field. The approximate solutionretains the same simple form as the classical Ekman solution. Behavioursof the approximate solution are discussed for different eddy viscosityand the pressure systems. These features show that wind structure inthe semi-geostrophic Ekman boundary layer depends on the interactionbetween the inertial acceleration, variable eddy viscosity and baroclinicpressure gradient. Anticyclonic shear has an acceleration effect on theair motion in the boundary layer, while cyclonic shear has a decelerationeffect. Decreasing pressure gradient with height results in a super-geostrophicpeak in the wind speed profile, however the increasing pressure gradient withheight may remove the peak. Anticyclonic shear and decreasing the variableeddy viscosity with height has an enhanced effect on the peak.
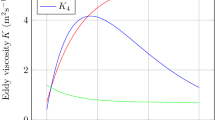
Variable eddy viscosity and inertial acceleration has an important role in thedivergence and vorticity in the boundary layer and the vertical motion at the top of the boundary layer that is called Ekman pumping. Compared to the constanteddy viscosity case, the variable eddy diffusivity reduces the absolute value ofEkman pumping, especially in the case of eddy viscosity initially increasing with height. The difference in the Ekman pumping produced by different eddy diffusivity assumptions is intensified in anticyclonic flow and reduced in cyclonic flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannon, P. R.andSalfm, T. L.: 1995,' Aspects of Baroclinic Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 52, 574-596.
Bender, C. M.andOrszag. S. A.: 1970, Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers, McGraw-Hill, New York, 593 pp.
Berger, B. W.andGrisogono, B.: 1998,' The Baroclinic, Variable Eddy Viscosity Ekman Layer: An Approximate Analytical Solution', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 87, 363-380.
Blumen, W.andWu, R.: 1983,' Baroclinic Instability and Frontogenesis with Ekman Boundary Layer Dynamics Incorporating the Geostrophic Momentum Approximation', J. Atmos. Sci. 40, 2630-2637.
Grisogono, B.: 1995,' A Generalized Ekman Layer Profile with Gradually Varying Eddy Diffusivities', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, 445-453.
Holton, J. R.: 1992, An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Academic Press, San Diego, 570 pp.
Hoskins, B. J.: 1975,' The Geostrophic Momentum Approximation and the Semi-geostrophic Equations', J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 233-242.
Levy, G.: 1989,' Surface Dynamics of Observed Maritime Fronts', J. Atmos. Sci. 46, 1219-1232.
Miles, J.: 1994,' Analytical Solutions for the Ekman Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 1-10.
O'Brien, J. J.: 1970,' A Note on the Vertical Structure of the Eddy Exchange Coefficient in the Planetary Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 27, 1213-1215.
Panchev, S.: 1985, Dynamic Meteorology, D. Reidel, Dordrecht, 360 pp.
Panchev, S.andSpassova, T. S.: 1987,' A BarotropicModel of the Ekman Planetary Boundary Based on the Geostrophic Momentum Approximation', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 40, 339-347.
Snyder, C.,Skamaroch, W. C.,andRotunno, R.: 1993,' Frontal Dynamics Near and Following Frontal Collapse', J. Atmos. Sci. 50, 3194-3211.
Tan, Z.-M.andFarahani, M. M.: 1998,' An Analytical Study of the Diurnal Variations of Wind in a Semi-Geostrophic Ekman Boundary Layer Model', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 86, 313-332.
Wu, R.andBlumen W.: 1982,' An Analysis of Ekman Boundary Layer Dynamics Incorporating the Geostrophic Momentum Approximation', J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 1774-1782.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, ZM. An Approximate Analytical Solution For The Baroclinic And Variable Eddy Diffusivity Semi-Geostrophic Ekman Boundary Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 98, 361–385 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018708726112
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018708726112