Abstract
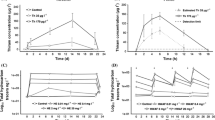
The effect of the surfactant dodecyl alkyl sulphate (C12AS) on the structure and function of lotic protistan assemblages was examined using the Experimental Stream Facility (ESF) operated by the Procter and Gamble Company. Population- and community-level responses to C12AS were monitored on introduced substrates placed in the channels 28 days prior to dosing (mature communities) as well as those placed in the channels on day 0 of dosing (immature communities), to allow for a broad assessment of the effect of the chemical on processes contributing both to community development and maintenance. C12AS appeared to elicit a subsidy response from the native protistan assemblage which may have resulted from both positive and negative responses at trophic levels above and below the assemblage. Protistan responses to the surfactant tended to occur more rapidly and be more sensitive than those documented for invertebrates and fish. C12AS elicited a modest response (i.e. a 20% change) from several reliable parameters including community respiration (reduced dissolved oxygen at 289 μg per L), protozoan species richness (increased at 63 μg per L) and protozoan community composition (increased dissimilarity at 1254 μg per L). Responses to C12AS exceeded expected exposures in the real world by a factor of six or greater thereby indicating that the hazard of exposure to C12AS to stream communities is low. The results of this study support the use of mesocosms as decisive tools for evaluating the hazard posed by consumer product chemicals to natural communities and ecosystems
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, O.R. (1988) Comparative protozoology: ecology, physiology, life history. New York: Springer-Verlag, USA.
Beaver, J.R. and Crisman, T.L. (1989) The role of ciliated protozoa in pelagic freshwater ecosystems. Microbial Ecol. 17, 111–36.
Belanger, S.E. (1992) Use of mesocosms in predicting ecosystem risk from cationic surfactant exposure. In J. Cairns, Jr., B.R. Neiderlehner and D.B. Orvos, (eds), Predicting Ecosystem Risk pp. 263–287. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
Belanger, S.E., Barnum, J.B., Woltering, D.M., Bowling, J.W., Ventullo, R.M., Schermerhorn, S. and Lowe, R.L. (1994) Structural and functional responses of periphytic communities to a cationic surfactant exposure. In R.L. Graney, J.R. Rodgers and J. Kennedy (eds), Use of Simulated Field Studies in Risk Assessment pp. 535–568. Chelsea, Michigan: Lewis Publishers, Inc.
Belanger, S.E. (1994) Review of experimental microcosm, mesocosm, and field tests used to evaluate the potential hazard of surfactants to aquatic life and the relation to single species data. In I.R. Hill, F. Heimbach, P. Leeuwangh and P. Matthiessen (eds), Freshwater Field Tests for Hazard Assessment of Chemicals pp. 299–326. Chelsea, Michigan: Lewis Publishers.
Belanger, S.E., Meiers, E.M. and Bausch, R.G. (1995a) Direct and indirect ecotoxicological effects of alkyl sulfate and alkyl ethoxysulfate on macroinvertebrates in stream mesocosms. Aquatic Toxicol. 33, 65–87.
Belanger, S.E., Rupe, K.L. and Bausch, R.G. (1995b) Responses of selected aquatic invertebrates and fish to alkyl sulfate and alkyl ethoxylate sulfate anionic surfactants during chronic exposure. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 55, 751–8.
Bott, T.L. and Kaplan, L.A. (1990) Potential for protozoan grazing of bacteria in streambed substrates. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 9, 336–45.
Cairns, J., Jr. (1983) Are single species tests alone adequate for estimating hazard? Hydrobiologia 137, 271–8.
Cairns, J., Jr. and Henebry, M.S. (1982) Interactive and noninteractive protozoan colonization processes. In J. Cairns, Jr. (ed), Artificial substrates pp. 23–70. Ann Arbor, MI: Ann Arbor Scientific.
Cairns, J., Jr., Kuhn, D.L. and Plafkin, J.L. (1979) Protozoan colonization of artificial substrates. In R.L. Weitzel (ed), Methods and measurements of periphyton communities: a review. pp. 34–57. Philadelphia, PA: American Society for Testing and Materials.
Cairns, J., Jr. and Niederlehner, B.R. (1987) Problems associated with selecting the most sensitive species for toxicity testing. Hydrobiologia 153, 89–94.
Cairns, J., Jr. and Pratt, J.R. (1986) Ecological consequence assessment: effects of bioengineered organisms. Water Resour. Bull 22, 171–82
Carlough, L.A. and Meyer, J.L. (1989) Protozoans in two southeastern blackwater rivers and their importance to trophic transfer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34, 163–77.
Curds, C.R. (1973) The role of protozoa in the activated sludge process. Am. Zool. 13, 161–9.
Dillon, W.R. and Goldstein, M. (1984) Multivariate analysis: Methods and application. John Wiley & Sons: New York.
Engelberg, J. and Boyarsky, L.L. (1979) The noncybernetic nature of ecosystems. Am. Nat. 114, 317–24.
Fendinger, N.J., Begley, W.M., McAvoy, D.C. and Eckhoff, W.S. (1992) Determination of alkyl sulfate surfactants in natural waters. Environm. Sci. Technol. 26, 2493–8.
Fendinger, N.J., Versteeg, D.J., Weeg, E., Dyer, S. and Rapaport, R.A. (1994) Environmental behavior and Fate of anionic surfactants. In L.A. Baker (ed), Environmental Chemistry of lakes and Reservoirs pp. 528–557. ACS Advances in Chemistry Series No. 237. American Chemical Society.
Guckert, J.B. (in press) Toxicity assessment by community analysis. J. Microbiological Methods.
Guckert, J.B., Walker, D.D. and Belanger, S.E. (1996) Environmental chemistry for a surfactant ecotoxicology study supports rapid degradation of C12-alkyl sulfate in a continuous flow stream mesocosm. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 262–9.
Kimball, K.D. and Levin, S.A. (1985) Limitations of laboratory bioassays: the need for ecosystem level testing. Bioscience 35, 165–71.
Kleinbaum, D.G. and Kupper, L.L. (1978) Applied regression analysis and other multivariable methods. Buxbury Press: Boston, MA.
Lewis, M.A. (1990) Chronic toxicities of surfactants and detergent builders to algae: a review and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 20, 123–40.
Lowe, R.L., Guckert, J.B., Belanger, S.E., Davidson, D.H. and Johnson, D.W. An evaluation of periphyton community structure and function on tile and cobble substrata in experimental stream mesocosms. Hydrobiologia. In press.
Mayer, F.L., Jr. and Ellersieck, M.R. (1986) Manual of acute toxicity: Interpretation and datebase for 410 chemicals and 66 species of freshwater animals. United States Department of the Interior, Washington, D.C.
McAvoy, D.C., Eckhoff, W.S. and Rapaport, R.A. (1993) Fate of linear alkyl benzene sulfonate in the environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 977–87.
McAvoy, D.C., Lawrence, D.L., Begley, W.M., Eckhoff, W.S., Fendinger, N.J. and Dyer, S.D. Fate of alcohol ethoxylates, alkyl ethoxylate sulfates, and linear alkyl benzene sulfonate in wastewater treatment and receiving systems. In review.
McCormick, P.V. (1991) Lotic protistan herbivore selectivity and its potential impact on benthic algal assemblages. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 10, 238–50.
McCormick, P.V. and Cairns, J., Jr. (1991) Effects of micrometazoa on on the protistan assemblage of a littoral food web. Freshwater Biol. 26, 111–9.
McCormick, P.V., Cairns, J., Jr., Belanger, S.E. and Smith, E.P. (1992) Response of protistan assemblages to a model toxicant, the surfactant C12-TMAC (dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride), in laboratory streams. Aquatic Toxicol. 21, 41–70.
McCormick, P.V. and Stevenson, R.J. (1992) Mechanisms of benthic algal succession in lotic environments. Ecology 72, 1835–48.
National Research Council (1981) Testing for effects of chemicals on ecosystems. National Academy Press: Washington, D.C.
Niederlehner, B.R., Pratt, J.R., Buikema, A.L., Jr. and Cairns, J., Jr. (1986) Comparison of estimates of hazard derived at different levels of biological organization. In J. Cairns, Jr. (ed), Community toxicity testing pp. 30–48. Philadelphia, PA: American Society of Testing and Materials.
Odum, E.P., Finn, J.T. and Franz, H. (1979) Perturbation theory and the subsidy-stress gradient. Bioscience 29, 349–52.
Odum, E.P. (1984) The mesocosm. Bioscience 34, 558–62.
O'Neill, R.V. and Waide, J.B. (1981) Ecosystem theory and the unexpected: implications for environmental toxicology. In B.W. Cornday, (ed), Management of toxic substances in our ecosystems pp. 43–73. Ann Arbor, MI: Ann Arbor Science.
Patrick, R., Cairns, J., Jr. and Scheier, A. (1968) The relative sensitivity of diatoms, snails, and fish to twenty common constituents of industrial wastes. Prog. Fish. Cult. 30, 137–40.
Pielou, E.C. (1984) The interpretation of ecological data: A primer on classification and ordination. John Wiley & Sons;, New York.
Pratt, J.R. and Cairns, J., Jr. (1985) Functional groups in the protozoa: roles in differing ecosystems. J. Protozool. 32, 409–17.
Stevenson, R.J. and Stoermer, E.F. (1981) Quantitative differences between benthic algal communities along a depth gradient in Lake Michigan. J. Phycol. 17, 29–36.
Welch, E.B. (1980) Ecological effects of waste water. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Woodwell, G.M. (ed) (1990) The Earth in transition: Patterns and processes of biotic impoverishment. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mccormick, P.V., Belanger, S.E. & Cairns, J. Evaluating the hazard of dodecyl alkyl sulphate to natural ecosystems using indigenous protistan communities. Ecotoxicology 6, 67–85 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018606206549
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018606206549