Abstract
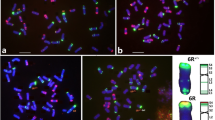
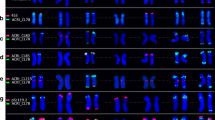
Chromatin originating from wild beets of the genus Beta, section Procumbentes, has been investigated in nematode-resistant hybrid-derived lines of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) by in situ hybridization using satellite, telomeric and ribosomal DNA repeats, a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) and total genomic DNA as probes. The alien chromosome was detected in three monosomic addition lines(2n=18+1) by genomic in situ hybridization. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with a genome-specific satellite repeat and YAC DNA enabled the visualization of Procumbentes chromosomes, and in double-target hybridization it was shown that they do not carry 18S–5.8S–25S rRNA and 5S rRNA genes. The wild beet-specific satellite repeat and the telomere sequence from Arabidopsis thaliana were used to perform a structural analysis of the wild beet chromosome fragments of two resistant fragment addition lines. It was shown that one physical end of the chromosome fragments consists of telomeric repeats. Comparison of fragment sizes indicated that the small chromosome fragments harbouring the resistance gene most likely resulted from the loss of one wild beet chromosome arm and an internal deletion of the remaining arm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albini SM, Schwarzacher T (1992) In situlocalization of two repetitive DNA sequences to surface-spread pachytene chromosomes of rye. Genome 35: 551–559.
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9: 208–218.
Bosemark NO, Bormotov VE (1971) Chromosome morphology in a homozygous line of sugar beet. Hereditas 69: 205–212.
Brandes A, Jung C, Wricke G (1987) Nematode resistance derived from wild beet and its meiotic stability in sugar beet. Plant Breed 99: 56–64.
Butterfass T (1964) Die Chloroplastenzahlen in verschiedenartigen Zellen trisomer Zuckerrüben (Beta vulgarisL.). Z. Bot 52: 46–77.
Cai D, Kleine M, Kifle S, Harloff H et al. (1997) Positional cloning of a gene for nematode resistance in sugar beet. Science 275: 832–834.
Coons GH (1975) Interspecific hybrids between Beta vulgarisL. and the wild species of Beta. Proc Am Soc Sug Beet Techn 8: 281–306.
de Jong JH, Speckmann GJ, De Bock TSM, Van Voorst A (1985) Monosomic additions with resistance to beet cyst nematode obtained from hybrids of Beta vulgarisand wild Betaspecies of the section Patellares. II. Comparative analysis of the alien chromosomes. Z Pflanzenzüchtung 95: 84–94.
Dubcovsky J, Luo M-C, Zhong G-Y, Bransteitter R, Desai A, Kilian A, Kleinhofs A, Dvorak J (1996) Genetic map of diploid wheat, Triticum monococcumL., and its comparison with maps of Hordeum vulgareL.Genetics 143: 983–999.
Fuchs J, Brandes A, Schubert I (1995) Telomere sequence localization and karyotype evolution in higher plants. Plant Syst Evol 196: 227–241.
Gerlach WL, Bedbrook JR (1979) Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acids Res 7: 1869–1885.
Harrison GE, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) Centromeric repetitive DNA sequences in the genus Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 90: 157–165.
Heller R, Schondelmaier J, Steinrü cken G, Jung C (1996) Genetic localization of four genes for nematode (Heterodera schachtiiSch.) resistance in sugar beet (Beta vulgarisL.). Theor Appl Genet 92: 991–997.
Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Nuclear architecture in plants. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2: 913–917.
Jacobsen E, de Jong JH, Kamstra SA, van den Berg PMMM, Ramanna MS (1995) Genomic in situhybridization (GISH) and RFLP analysis for the identification of alien chromosomes in the backcross progeny of potato + tomato fusion hybrids. Heredity 74: 250–257.
Jung C, Herrmann RG (1991) A DNA probe for rapid screening of sugar beet (Beta vulgarisL.) carrying extra chromosomes from wild beets of the Procumbentessection. Plant Breeding 107: 275–279.
Jung C, Wehling P, Löptien H (1986) Electrophoretic investigations on nematode resistant sugar beets. Plant Breeding 97: 39–45.
Jung C, Kleine M, Fischer F, Herrmann RG (1990) Analysis of DNA from a Beta procumbenschromosome fragment in sugar beet carrying a gene for nematode resistance. Theor Appl Genet 79: 663–672.
Jung C, Koch R, Fischer F, Brandes A, Wricke G, Herrmann RG (1992) DNA markers closely linked to nematode resistance genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgarisL.) using chromosome additions and translocations originating from wild beets of the Procumbentesspecies. Mol Gen Genet 232: 271–278.
Jung C, Pillen K, Frese L, Melchinger A (1993) Phylogenetic relationships between cultivated and wild species of the genus Betarevealed by DNA 'fingerprinting'. Theor Appl Genet 86: 449–457.
Jung C, Herrmann RG, Eibl C, Kleine M (1994) Molecular analysis of a translocation in sugar beet carrying a gene for nematode resistance from Beta procumbens. J Sugar Beet Res 31, 1 & 2: 27–42.
Kamm A, Galasso I, Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) Analysis of a repetitive DNA family from Arabidopsis arenosaand relationship between Arabidopsisspecies. Plant Mol Biol 27: 853–862.
Kamm A, Doudrick RL, Heslop-Harrison JS, Schmidt T (1996) The genomic and physical organization Ty1-copia-like sequences as a component of large genomes in Pinus elliottiivar. elliottiiand other gymnosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 2708–2713.
Kleine M, Cai D, Eibl C, Herrmann RG, Jung C (1995) Physical mapping and cloning of a translocation in sugar beet (Beta vulgarisL.) carrying a gene for nematode (Heterodera schachtii) resistance from B. procumbens. Theor Appl Genet 90: 399–406.
Kleine M, Cai D, Klein-Lankhorst R et al. (1997) Breeding for nematode resistance in sugar beet: A molecular approach. In: Fenoll C, Ohl S, Grundler FMW, eds. Cellular and Molecular Basis for Plant-Nematode Interactions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (in press).
Kubis S, Heslop-Harrison JS, Schmidt T (1996) A family of differentially amplified repetitive DNA sequences in the genus Betareveals genetic variation in Beta vulgarissubspecies and cultivars. J Mol Evol 44: 310–320.
Leitch IJ, Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Physical mapping of 18S-5.8S-26S rRNA genes in barley by in situhybridisation. Genome 35: 1013–1018.
Leitch AR, Mosgöller W, Shi M, Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Different patterns of rDNA organization at interphase in nuclei of wheat and rye. J Cell Sci 101: 751–757.
Lö ptien H (1984) Breeding nematode-resistant beets. I. Development of resistant alien additions by crosses between Beta vulgarisL. and wild species of the section Patellares. Z Pflanzenzü chtung 92: 208–220.
Moore G, Devos KM, Wang Z, Gale MD (1995) Grasses, line up and form a circle. Curr Biol 7: 737–739.
Orgaard M, Jacobsen N, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) The hybrid origin of two cultivars of Crocus(Iridaceae) analysed by molecular cytogenetics including genomic southern and in situhybridization. Ann Bot 76: 253–262.
Parokonny AS, Kenton A, Gleba YY, Bennett MD (1992) Genome reorganization in Nicotianaasymmetric somatic hybrids analyzed by in situhybridization. Plant J 2: 863–874.
Parokonny AS, Kenton A, Gleba YY, Bennett MD (1994) The fate of recombinant chromosomes and genome interaction in Nicotianaasymmetric somatic hybrids and their sexual progeny. Theor Appl Genet 89: 488–497.
Pich U, Fuchs J, Schubert I (1996) How do Alliaceae stabilize their chromosome ends in the absence of TTTAGGG sequence. Chrom Res 4: 207–213.
Reamon-Ramos SM, Wricke G (1992) A full set of monosomic addition lines in Beta vulgarisfrom Beta webbiana: morphology and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 84: 411–418.
Ribeiro-Carvalho C, Guedes-Pinto H, Harrison G, Heslop-Harrison JS (1997) Wheat-rye translocation involving small terminal and intercalary rye chromosome segments in the Portuguese landrace Barbela. Heredity (in press) [95].
Richards EJ, Ausubel FM (1988) Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 53: 127–136.
Romagosa I, Hecker RJ, Tsuchiya T, Lasa JM (1986) Primary trisomics in sugar beet. I. Isolation and morphological characterization. Crop Sci 26: 243–249.
Salentijn EMJ, Sandal NN, Lange W, De Bock TSM, Krens FA, Marcker KA, Stiekema WJ (1992) Isolation of DNA markers linked to a beet cyst nematode resistance locus in Beta patellarisand Beta procumbens. Mol Gen Genet 235: 432–440.
Savitsky H (1975) Hybridization between Beta vulgarisand B. procumbensand transmission of nematode (Heterodera schachtii) resistance to sugarbeet. Can J Genet Cytol 17: 197–209.
Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1993) Variability and evolution of highly repeated DNA sequences in the genus Beta. Genome 36: 1074–1079.
Schmidt T, Junghans H, Metzlaff M (1990) Construction of B. procumbens-specific DNA probes and their application for the screening of B. vulgaris × B. procumbens(2n.19) addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 79: 177–181.
Schmidt T, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1994) Physical mapping of rRNA genes by fluorescent in-situ hybridization and structural analysis of 5S rRNA genes and intergenic spacer sequences in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Theor Appl Genet 88: 629–636.
Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1996a) The physical and genomic organization of microsatellites in sugar beet. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 8761–8765.
Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1996b) High resolution mapping of repetitive DNA by in situhybridization-molecular and chromosomal features of prominent dispersed and discretely localized DNA families of the wild beet species Beta procumbens. Plant Mol Biol 30: 1099–1119.
Schondelmaier J, Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS, Jung C (1997) Genetic and chromosomal localization of the 5S rDNA locus in sugar beet (Beta vulgarisL.). Genome (in press).
Schwarzacher T, Anamthawat-Jonsson K, Harrison GE, Islam AKMR, Jia JZ, King IP, Leitch AR, Miller TE, Reader SM, Rogers WJ, Shi M, Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Genomic in situhybridization to identify alien chromosomes and chromosome segments in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84: 778–786.
Speckmann GJ, De Bock TSM (1982) The production of alien monosomic additions in Beta vulgarisas a source for the introgression of resistance to beet root nematode (Heterodera schachtii) from Betaspecies of the section Patellares. Euphytica 31: 313–323.
Telenius H, Carter NP, Bebb CE, Nordenskö ld M, Ponder BAJ, Tunnacliffe A (1992) Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics 13: 718–725.
Toxopeus H, Lubberts H (1979) Breeding for resistance to the sugar beet nematode (Heterodera schachtiiSchm.) in cruciferous crops. Eucarpia Crucif Conf Wageningen 151.
Van Geyt JPC, Oleo M, Lange W, De Bock ThSM (1988) Monosomic additions in beet (Beta vulgaris) carrying extra chromosomes of Beta procumbens. I. Identification of the alien chromosomes with the help of isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 76: 577–586.
Van Geyt JPC, Lange W, Oleo M, De Bock ThSM (1990) Natural variation within the genus Betaand its possible use for breeding sugar beet: a review. Euphytica 49: 57–76.
Wagner H, Gimbel EM, Wricke G (1989) Are Beta procumbensChr. Sm. and Beta webbianaMoq. different species? Plant Breeding 102: 17–21.
Wang S, Lapitan NLV, Tsuchiya T (1992) Characterization of telomeres in Hordeum vulgarechromosomes by in situhybridization. II. Healed broken chromosomes in telotrisomic 4L and acrotrisomic 4L4S lines. Genome 35: 975–980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, T., Jung, C., Heslop-Harrison, J.S. et al. Detection of alien chromatin conferring resistance to the beet cyst nematode (Heterodera schachtii Schm.) in cultivated beet (Beta vulgaris L.) using in situ hybridization. Chromosome Res 5, 186–193 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018447031020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018447031020