Abstract
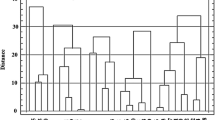
Comparative analyses of genetic variability of aluminium tolerance response were made in a range of triticale genotypes of two sets, one consisting of six Australian cultivars (or lines), the other consisting of eight South African lines and an Australian check, by following solution culture and screening under controlled growth cabinet conditions. Results showed that Tahara, Tahara ‘S’ and Abacus were the most Al-tolerant triticales among the Australian genotypes in terms of root regrowth characteristics at 10 μg.g-1 Al. The 19th ITSN 70-4, along with the standard cultivar Tahara was superior to all other South African genotypes; the eight South African genotypes spanned the range from Al-tolerant, moderately Al-tolerant to Al-sensitive. Regrown root length and percentage of seedlings with root regrowth were the two key indicators for screening and evaluating Al tolerance response. Considerable genetic variability of tolerance to Al stress among the two sets of tested genotypes was revealed by the estimates of genetic parameters. High heritability values were recorded for those two indicators, with associated high levels of relative genetic advance (RGA). Further improvement of varietal tolerance to Al stress in triticale could be anticipated through selection and breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniol, A., 1983. Aluminium uptake by roots of two winter wheat varieties of different tolerance to aluminium. Biochem Physiol Pflanzen 178: 11–20.
Aniol, A., 1991. Genetics of acid tolerant plant. In: R.J. Wright, V.C. Baligar & R.P. Murrmann (Eds). Plant-Soil Interactions at Low pH, pp. 1007–1017. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Camargo, C.E.O., J.C. Felicio & A.W.P. Ferrcira Pilho, 1990. Abiotic stresses: mineral toxicities, low nutrient availability, drought and heat. Proc. 2nd Intern Triticale Symp, 1–5 October 1990, Passo Fundo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. pp. 164–170.
Cosci, T., M. Poljak, M. Custic & Z. Rengel, 1994. Aluminium tolerance of durum wheat germplasm. Euphytica 78: 239–243.
Foy, C.D., 1988. Plant adaptation to acid, Al-toxic soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19: 959–987.
Jessop, R.S., 1996. Stress tolerance in newer triticales compared to other cereals. In: H. Guedes-Pinto, N. Darvey & V.P. Carnide (Eds), Triticale: Today and Tomorrow, pp. 419–427. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Jessop, R.S., R.A. McCallum, R.L. Wright & T. Wright, 1990. Selecting for improved low pH/aluminium tolerance in Australian triticale varieties. Proc 2nd Intern Triticale Symp. 1–5 October 1990, Passo Fundo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. pp. 196–199.
Jessop, R.S. & R.L. Wright, 1991. Triticale. In: New Crops; Agronomy and Potential of Alternative Crop Species, pp. 175–182. Inkata Press, Melbourne, Sydney
Josephides, C.M., 1993. Analysis of adaptation of barley, triticale, durum and bread wheat under Mediterranean conditions. Euphylica 65: 1–8.
Ma, Y.H., 1982. Fundamentals of Quantitative Genetics in Plant Breeding. Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, P.R. China (in Chinese). 470 p.
Malcolm, B., P. Sale & A. Egan, 1996. Agriculture in Australia: An Introduction. Oxford University Press. 472 p.
Pfeiffer, W., 1993. Estimation of triticale area in countries growing 1,000 hectares or more in 1986, 1991–92. Triticale Topics 11: 1.
Taylor, G.J., 1991. Current views of the aluminium stress response: The physiological basis of tolerance. Curr Top Plant Biochem Physiol 10: 57–93.
Von Uexküll, H.R. & E. Mutert, 1995. Global extent, development and economic impact of acid soils. Plant and Soil 171: 1–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Jessop, R.S. Analysis of genetic variability of aluminium tolerance response in triticale. Euphytica 102, 177–182 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018311426393
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018311426393