Abstract
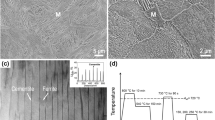
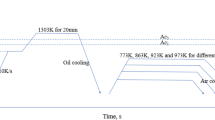
A new interpretation of temper embrittlement dynamics is proposed, which is based on the diffusion of phosphor atoms to grain boundaries by the complex of phosphor atom-vacancy. The dynamics of temper embrittlement in a medium-carbon Cr steel during 538°C tempering was carefully examined. The results show that the dependence of 50% fracture appearance transition temperature (FATT) on tempering time has a maximum, which can be satisfactorily elucidated by diffusion of the complex of phosphor atom-vacancy. However, the dependence of hardness on tempering duration decreases all the time. The fracture morphology was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the variation of intergranular fracture ratio also has a maximum during tempering treatment at 538°C, which is at the near same time as the one in the dynamic of temper embrittlement. The concentration of phosphor on grain boundary was measured by Auger electron microscopy (AES).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. J. Mcmahon Jr, Materials Science Forum 46 (1989) 61.
J. J. Hickey and J. H. Bulloch, Int. J. Pre, Ves. & Pinping 49 (1992) 339.
D. Mclean “Grain Boundaries in Metals” (Oxford University Press, Amen House, London, 1957) p.118, 131.
M. P. Seah, Acta Metall. 25 (1977) 345.
R. A. Moulford, C. J. Mcmahon, D. P. Pope and H. C. Feng, Met. Trans. 7A (1976) 1183.
P. Sevc, J. J. Anovex, M. Lucas and H. J. Grabke, Steel Res. 66 (1995) 537.
V. Vorlicek and P. E. J. J. Flewitt, Acta Metall. Mater. 42 (1994) 3309.
K. T. Aust, S. J. Armijo, E. F. Koch and J. A. Westbrook, Trans. Am. Soc. Metals 60 (1976) 360.
T. R. Anthony, Acta Metall. 17 (1969) 603.
Williams, A. M. Stonham and D. R. Harries, Met. Sci. 10 (1976) 14.
X. L. He, Y. Y. Chu and J. J. Jones, Acta Metall. 37 (1989) 147.
Xu Tingdong, Song Shenhua, Shi Huazhong, Yuan Zhexi and W. Gust, Acta Metall. Mater. 39 (1991) 3119.
Xu Tingdong, J. Mater. Sci. 22 (1987) 337.
Viswannthan, Met. Trans. 2 (1971) 809.
H. Ohtani, H. C. Feng and C. J. Mcmahon. Jr, Met. Trans. 7A (1976) 87.
Idem., ibid. 7A (1976) 1123.
R. G. Faulkner, J. Mater. Sci. 16 (1981) 337.
Idem., Mater. Sci. Tech 1 (1985) 442.
G. Siebel, Mem. Sci. Rev. Met. 61 (1964) 413.
M. A. V. Chapman and R. G. Faulkner, Acta Metall. 31 (1983) 677.
F. S. Buffington, K. Hirano and M. Cohen, ibid. 9 (1961) 434.
Song Shenhua, Xu Tingdong and Yuan Zhexi, ibid. 37 (1989) 319.
Xu Tingdong, J. Mater. Sci. 34 (1999) 3177.
Idem., Materials Sci. Tech. 15 (1999) 659.
A. E. Powers, Trans. ASM 48 (1956) 149.
S. H. Bush and S. A. Siebert, Trans AIME 200 (1954) 1269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaoli, Z., Tingdong, X., Qingying, L. et al. A new interpretation of temper embrittlement dynamics by non-equilibrium segregation of phosphor in steels. Journal of Materials Science 36, 2055–2059 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017543201741
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017543201741