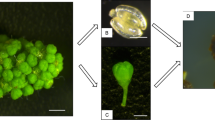
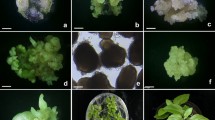
Abstract
Petioles from in vitro grown plants of interspecific grapevine hybrids cvs `Bianca', `Podarok Magaracha' and `Intervitis Magaracha' were cultured on solid NN medium supplemented with 2,4-D and BA at various concentrations. The callus developed was cultured in liquid NN medium supplemented with 0.5 mg l−1 BA to induce formation of somatic embryos. Somatic embryos of globular and heart-stage developed in suspensions of `Podarok Magaracha' and `Intervitis Magaracha'. In contrast, `Bianca' did not undergo embryogenesis beyond globular stage. This made it necessary to perform subculture of the suspensions to HTE liquid medium supplemented with 0.2 mg l−1 BA for the development of globular embryos into heart stage. Heart-stage embryos developed into torpedo-stage after subculturing suspensions of all three cultivars to liquid HTE medium supplemented with 0.1 mg l−1 IAA and 30 mg l−1 sodium hummate. Torpedo-stage embryo suspensions were subcultured in liquid HTE medium supplemented with 0.5 mg l−1 BA, 0.5 mg l−1 GA3 and 0.5 mg l−1 GA3 + 0.2 mg l−1 BA. After 12 days of incubation, plantlets were cultured on solid M2MS medium: without growth regulators and with 0.5 mg l−1 BA. Plantlets that developed in liquid HTE media with 0.5 mg l−1 GA3 or 0.5 mg l−1 GA3 + 0.2 mg l−1 BA produced 82–90% shoots on solid M2MS medium with 0.5 mg l−1 BA after 50 days of culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bomhoff B-A & Harst M (2000) Establishment of embryo suspension cultures of grapevine (Vitis L.). Vitis 39: 27–29
Franks T, He DG & Thomas M (1998) Regeneration of transgenic Vitis vinifera L. Sultana plants: Genotypic and phenotypic analysis. Molecular Breeding 4: 321–333
Gray D & Mortensen J (1987) Initiation and maintenance of long term somatic embryogenesis from anthers and ovaries of Vitis longii ‘Microsperma'. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 9: 73–80
Harst M, Bornhoff B-A, Zyprian E & Töpfer R (2000) Influence of culture technique and genotype on the efficiency of Agrobacterium - mediated transformation of somatic embryos (Vitis vinifera) and their conversion to transgenic plants. Vitis 39: 99–102
Jayasankar S, Gray DJ & Litz RE (1999) High-efficiency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of grapevine. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 533–537
Kikkert JR, Hébert-Soulé D, Wallace PG, Striem MJ & Reisch BI (1996) Transgenic plantlets of ‘Chancellor’ grapevine (Vitis sp.).from biolistic transformation of embryogenic cell suspensions. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 311–316
Krul WR & Narragansett RI (1987) In vitro propagation of grape. US Patent No. 4, 714, 679
Lebrun L, Rajasekaran K & Mullins MG (1985) Selection in vitro for NaCl-tolerance in Vitis rupestris Scheele. Ann. Bot. 56: 733–739
Mozsár J, Viczián O & Süle S (1998) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of an interspecific grapevine. Vitis 37: 127–130
Mozsár J & Süle S (1994) A rapid method for somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cultured anthers of Vitis riparia. Vitis 33: 245–246
Mullins MG & Srinivasan C (1976) Somatic embryos and plantlets from an ancient clone of the grapevine (cv. Cabernet Sauvignon) by apomixis in vitro. J. Exp. Bot. 27: 1022–1030
Murashige T & Skoog FA (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Nakajima I, Kobayashi S & Nakamura Y (2000) Embryogenic callus induction and plant regeneration from unfertilized ovule of Kyoho grape. J. Jap. Soc. Hort. Sci. 69(2): 186–188
Nitsch JP & Nitsch C (1969) Haploid plants from pollen grains. Science 163: 85–87
Perl A, Lotan O, Abu-Abied M & Holland D (1996) Establishment of an Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system for grape (Vitis Vinifera L.): The role of antioxidants during grape-Agrobacterium interactions. Nat. Biotechnol. 14: 624–628
Pryce RJ (1973) Decomposition of aqueous solutions of gibberellic acid on autoclaving. Phytochemistry 12: 507–514
Rajasekaran K & Mullins MG (1979) Embryos and plantlets from cultured anthers of hybrid grapevines. J. Exp. Bot. 30: 399–407
Rajasekaran K & Mullins MG (1983) Influence of genotype and sex-expression on formation of plantlets by cultured anthers of grapevines. Agronomie 3: 233–238
Salunkhe CK, Rao PS & Mhatre M (1997) Induction of somatic embryogenesis and plantlets in tendrils of Vitis vinifera L. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 65–67
Salunkhe CK, Rao PS & Mhatre M (1999) Plantlet regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in anther callus of Vitis latifolia L. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 670–673
Slenko WA, Troschin LP & Kotikow IV (2001) Der Einfluss der Nährmedienzusammensetzung bei der in vitro - Vermehrung verschiedener Rebgenotypen. Mitteilungen Klosterneuburg 51: 15–26
Takeno K, Koshioka M, Pharis RP, Rajasekaran K & Mullins MG (1983) Endogenous gibberellin-like substances in somatic embryos of grape (Vitis vinifera × Vitis rupestris) in relation to embryogenesis and the chilling requirement for subsequent development of mature embryos. Plant Physiol. 73: 803–808
Torregrosa L (1998) A simple and efficient method to obtain stable embryogenic cultures from anthers of Vitis vinifera L. Vitis 37: 91–92
Yamamoto T, Iketani H, Leki H, Nishizawa Y, Notsuka K, Hibi T, Hayashi T & Matsuta N (2000) Transgenic grapevine plants expressing a rice chitinase with enhanced resistance to fungal pathogens. Plant Cell Rep. 19: 639–646
Yu X, Li P, Lu B, Wang M, Zheng X & Liu T (1999) Plant regeneration from protoplasts of wine grapes. J. Fruit Sci. 16(2): 115–118
Zlenko VA & Trochine LP (1994) Sélection clonale de la vigne. 74 e Assemblée Générale OIV, 6-10 Juin, 1994, Paris. Viticulture 1: 1–14
Zlenko VA & Troshin LP (1993) Somatic embryogenesis of grapevine from cell suspensions (in Russian). Cytology and Genetics 27(3): 53–63
Zlenko VA, Troshin LP & Levenko BA (1990) Methodological recommendations pertaining to somatic embryogenesis of grapevine in liquid medium with subsequent plant regeneration (in Russian). VASHNIL, Moscow
Zlenko VA, Troshin LP & Kotikov IV (1995) An optimized medium for clonal micropropagation of grapevine. Vitis 34: 125–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zlenko, V.A., Kotikov, I.V. & Troshin, L.P. Efficient GA3-assisted plant regeneration from cell suspensions of three grape genotypes via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 70, 295–299 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016593227463
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016593227463