Abstract
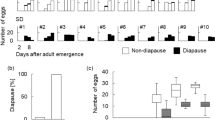
This study examines the effect of juvenile hormone (JH) or a similarly acting juvenoid on the expression of maternal egg guarding and its life history alternative, egg dumping, in the lace bug, Gargaphia solani Heidemann. JH manipulations were indirect: methoprene, a synthetic JH analog, and precocene II, an allatocidal phytochemical commonly used to reduce JH synthesis, were applied exogenously to test the hypothesis that high JH titers promote egg production and egg dumping behavior, while low titers terminate egg production and initiate maternal care. As predicted, egg dumpers treated with precocene II ignored dumping opportunities and became egg guarders. Similarly, egg guarders that were treated with methoprene became gravid within 2 days and abandoned their eggs to become egg dumpers. These manipulations suggest that hormones can trigger the expression of both egg dumping and egg guarding in G. solani even when environmental conditions are inappropriate.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Albert, A., and Anderson, J. A. (1984). On the existence of maximum likelihood estimates in logistic regression models. Biometricka 71: 1–10.
Bowers, W. S. (1981). How anti-juvenile hormones work. Am. Zool. 21: 737–742.
Bowers, W. S., and Aldrich, J. R. (1980). In vitro inactivation of denervated corpora allata by precocene II in the bug, Oncopeltus fasciatus. Experientia 36: 362–364.
Bowers, W. S., and Martinez-Pardo, R. (1977). Anti-allatotropins: Inhibition of corpus allatum development. Science 197: 1369–1371.
Bowers, W. S., Ohta, T., Cleere, J. S., and Marsella, P. A. (1976). Discovery of insect anti-juvenile hormones in plants. Science 193: 542–547.
Campero, D. M., and Haynes, K. F. (1990). Effects of methoprene on chemical communication, courtship and oviposition in the cabbage looper (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 83: 2263–2268.
Caussamel, C., Baehr, J., Cassier, P., Dray, F., and Procheron, P. (1979). EsCorrélations humorales et ultrastructurales au cours de la vitellogenèse et de la péiode de soins aux uffs chez Labidora riparia (Insecte, Dermaptera). C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) Ser. D 288: 513–516.
Eberhard, W.G. (1985).Possible mutualism between females of the subsocial membracidPolyglypta dispar (Hewmoptera). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 19: 447–453.
Kight, S. L. (1998). Precocene II modifies maternal responsiveness in the burrower bug, Sehirus cinctus (Heteroptera).Physiol. Entomol. 23: 38–42.
Koeppe, J. D., Fuchs, M., Chen, T. T., Hunt, L. M., Kovalick, G. E. and Biers, T. (1985). The role of juvenile hormone reproduction. In Kerkut, G. A., and Gilbert, L. I. (eds.), Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology, Vol.8, Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 165–203.
Martinez, M. I. (1994). Observations on reproductive control in females of two species of Canthun Hoffmannsegg (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae). Elytron 8: 183–193.
Martinez, M.I., and Huerta, C. (1997). Coordinated activity of the ovary, pars intercerebralis and corpus allatum during the prenesting and nesting cycles of Copris incertus Say (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae). Coleopt. Bull. 51: 351–383.
Melksham, J. A. (1984). Colonial oviposition and maternal care in two strains of Leptobyrsa decora Drake (Hemiptera: Tingidae). J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 23: 205–210.
Monaco, E. L., Tallamy, D.W., and Johnson, R. K. (1998). Chemical mediation of egg dumping in the lace bug Gargaphia solani Heidemann (Heteroptera: Tingidae).Anim. Behav. 56: 1491–1495.
Numata, H., and Hidaka, T. (1984). Termination of adult diapause by a juvenile hormone analogue in the bean bug, Riptortus clavans. Zool. Sci. 1: 751–754.
Okuda, T., and Chinzei, Y. (1998). Vitellogenesis in a lady-beetle, Coccinella septempunctata, in relation to the aestivation-diapause.J. Insect Physiol.34: 393–401.
Parr, A. (2001). Proximate factors regulating maternal care in the lace bug, Gargaphia solani Heidemann, (Hemiptera: Tingidae). MS thesis. University of Delaware, Newark, DE.
Parr, A., Tallamy, D. W., Monaco, E. L., and Pesek, J. D. (2002). Proximate factors regulating maternal options in Gargaphia solani (Heteroptera:Tingidae). J. Insect Behav. 15:495–511.
Ramswamy, S. B., Shu, S., Park, Y. I., and Zeng, F. (1997). Dynamics of juvenile hormonemediated gonadotropism in the Lepidoptera. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 35: 539–558.
Rankin, S. M., and Rankin, M. A. (1980). The hormonal control of migratory flight behavior in the convergent ladybird beetle, Hippodamia convergens. Physiol. Entomol. 5: 175–182.
Rankin, M. A., and Riddiford, L. M. (1977). Hormonal control of migratory flight in Oncopeltes fasciatus:The effects of the corpora cardiacum, corpora allatum and starvation on migration and reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol.33: 309–321.
Rankin, S. M., Fox, K. M., and Stotsky, C. E. (1995a). Physiological correlates to courtship, mating, ovarian development and maternal behaviour in the ring-legged earwig. Physiol. Entomol.20: 257–265. Lace Bug Maternal Hormones 475
Rankin, S. M., Palmer, J. O., Yagi, K. J., Scott, G. L., and Tobe, S. S. (1995b). Biosynthesis and release of juvenile hormone during the reproductive cycle of the ring-legged earwig. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 110C: 241–251.
Ringo, J., Werczberger, R., Altaratz, M., and Segal, D. (1981). Female sexual receptivity is defective in juvenile hormone-deficient mutants of the apterous gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Behav. Genet. 21: 453–470.
Robinson, G., and Vargo, E. (1997). Juveinle morhome in adult eusocial Hymenoptera: Gonadotropin and behavioral pacemaker. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 35: 559–583.
Roth, L. M., and Stay, B. (1962). Oocyte development in Blattella germanica and Blattella vaga (Blattaria). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 55: 633–642.
Rotin, D., Feyereisen, R., Koener, J., and Tobe, S. S. (1992). Haemolymph juvenile hormone esterase activity during the reproductive cycle of the vivparious cockroach Diploptera punctuata. Insect Biochem. 12: 283–268.
Schal, C., Holbrook, G., Bachmann, J. A. S., and Sevala, V. L. (1997). Reproductive biology of the German cockroach, Blattella germanica: Juvenile hormone as a pleiotropic master regulator. Arch. Insects Biochem. Physiol. 35: 405–426.
Scott, M. P., Trumbo, S. T., Neese, P. A., Bailey, W. D. and Roe, R. M. (2001). Changes in biosynthesis and degradation of juvenile hormone during breeding by burying beetles: A reproductive or social role? J. Insect Physiol. 47: 295–302.
Shooneveld, H. (1979). Precocene-induced collapse and resorption of corpora allata in nymphs of Locusta migratoria. Experientia 35: 363–364.
Siegel, S., and Castellan, N. J., Jr. (1998). Non-parametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. McGraw Hill, New York.
Socha, R., Sula, J., Kodrik, D., and Gelbic, I. (1991). Hormonal control of vitellogenin synthesis in Pyrrhocoris apteros (L.) (Heteroptera). J. Insect Physiol. 37: 805–816.
Staal, G. B. (1986). Anti-juvenile hormone agents. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 31: 391–429.
Stokes, M. E., Davis, C. S., and Koch, G. G. (2000). Categorical Data Analysis Using SASr Systems, 2nd ed. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC.
Tallamy, D.W. (1985). Egg-dumping in lace bugs (Hemiptera: Tingidae). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 17: 357–362.
Tallamy, D. W. (1986). Age specificity of egg dumping in Gargaphia solani (Hemiptera: Tingidae). Anim. Behav. 34: 599–603.
Tallamy, D. W., and Brown, W. P. (1999). Semelparity and the evolution of maternal care in insects. Anim. Behav. 57: 727–730.
Tallamy, D.W., and Denno, R. F. (1981). Maternal care in Gargaphia solani (Hemiptera: Tingidae). Anim. Behav. 29: 771–778.
Tallamy, D.W., and Denno, R. F. (1992). Life history trade-offs in Gargaphia solani (Hemiptera: Tingidae): The cost of reproduction.Ecology 63: 616–620.
Tallamy, D.W., and Horton, L. A. (1990). Costs and benefits of the egg-dumping alternative in Gargaphia lace bugs (Hemiptera: Tingidae). Anim. Behav. 39: 352–359.
Tobe, S. S., and Stay, B. (1985). Structure and regulation of the corpus allatum. Adv. Insect Physiol. 18: 305–432.
Trabalon, M., Campan, M., Porcheron, P., Clement, J. L., Baehr, J. C., Moriniere, M., and Joulie, C. (1980). Relationships among hormonal changes, cuticular hydrocarbons and attractiveness during the first gonadotropic cycle of the female Calliphora vomitoria (Diptera). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 80: 216–222.
Trumbo, S. T. (1997). Juvenile hormone-mediated reproduction in burying beetles: From behavior to physiology. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 35: 479–490.
Trumbo, S. T. (2002). The hormonal regulation of parental care in insects. In Pfaff, D. (ed.), Hormones, Brain and Behavior Vol 2 Chapter 37. Academic Press.
Vancassel, M., Foraste, M., Strambi, A., and Strambi, C. (1984). Normal and experimentally induced changes in hormonal hemolymph titers during prenatal behavior of the earwig Labidura riparia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 56: 444–456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tallamy, D.W., Monaco, E.L. & Pesek, J.D. Hormonal Control of Egg Dumping and Guarding in the Lace Bug, Gargaphia solani (Hemiptera: Tingidae). Journal of Insect Behavior 15, 467–475 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016325115747
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016325115747