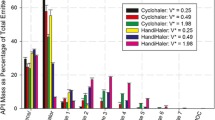
Abstract
Purpose. The purpose of this study is to investigate the albuterol loading effect on particle size measurements by studying the effect of the amount of albuterol delivered, the number of puffs used, and the sampling techniques used in particle size measurement.
Methods. Particle size distribution profiles for different albuterol loadings were evaluated using an 8-stage cascade impactor and a sensitive HPLC electrochemical assay method. A commercial albuterol MDI (ProventilR) and other specially prepared albuterol MDIs were used in the study.
Results. As the amount of albuterol was increased, either by increasing the number of puffs or the amount delivered per puff, the measured MMAD increased. This increase was more prominent in some formulations (ProventilR) than others. Further, albuterol particles previously deposited on the valve and/or actuator didn't play a role in the observed multi-puff/loading effect.
Conclusions. The collection of the least amount of aerosol in a cascade impactor provides a better estimate of MMAD, as it minimizes modifications of the collection surfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
W. P. Adams, G. Poochikian, A. S. Taylor, R. M. Patel, G. P. Burke, and R. L. Williams. Regulatory aspects of modifications to innovator bronchodilator metered dose inhalers and development of generic substitutes. J. Aerosol Med. Deposition Clear. Eff. Lung. 7:119–134 (1994).
T. D. Cyr, S. J. Graham, K. Y. Robert Li, and E. G. Lovering. Low first-spray drug content in albuterol metered-dose inhalers. Pharm Res. 8:658–660 (1991).
S. J. Graham, Eric D. Ormsby, and E. G. Lovering. Single spray drug content in a metered-dose aerosol formulation and a collection scheme for content uniformity. Pharm. Forum 18:4400–4403 (1992).
P. R. Byron. Dosing reproducibility from experimental albuterol suspension metered-dose inhalers. Pharm. Res. 11:580–584 (1994).
United States Pharmacopeia, 23rd Rev., United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., Rockville, MD, 1995, pp. 1762–1767.
M. M. Nasr. Single-puff particle-size analysis of albuterol metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) by high-pressure liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (HPLC-EC). Pharm. Res. 10:1381–1384 (1993).
N. C. Miller and R. K. Schultz. Size analysis of single shots of metered dose inhaler (MDI) sprays by cascade impactor. Pharm. Res. 9:S-142 (1992).
The MDIs were manufactured by Armstrong Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Norwood, Massachusetts, under a contract with Johns Hopkins University. Manufactured albuterol MDIs were used in the joint FDA/Johns Hopkins clinical study.
M. M. Nasr. Liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (LC-EC): Recent applications in pharmaceutical analysis. Challenges in pharmaceutical analysis symposium. AOAC International, Midwest Meeting, Columbia, Missouri (June, 1994).
Y. Q. Wu, R. Shi, R. L. Williams, and E. T. Lin. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay for basic amine drugs in human plasma with a silica gel column and an aqueous mobile phase. IV. Albuterol. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 14:253–264 (1991).
C. G. Thiel. A pitfall in the use of the log-probability curve for particle size calculations and a solution to the problem. Pharm. Res. 11:S-39 (1994).
M. Van Oort, R. O. Gollmar, and R. J. Bohinski. Effects of sampling chamber volume and geometry on aerodynamic size distribution of metered-dose inhalation aerosols measured with the Andersen cascade impactor. Pharm. Res. 11:604–607 (1994).
K. Fults, T. D. Cyr, and A. J. Hickey. The influence of sampling chamber dimensions on aerosol particle size measurement by cascade impactor and twin impinger. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 43:726–728 (1991).
C. S. Kim, D. Trujillo, and M. A. Sackner. Size aspects of metered-dose inhaler aerosol. Am. Rev. resp. Dis. 132:137–142 (1985).
A. H. Hickey. Factors influencing aerosol deposition in inertial impactors and their effect on particle size characterization. Pharm. Technol. 14:118–130 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasr, M.M., Allgire, J.F. Loading Effect on Particle Size Measurements by Inertial Sampling of Albuterol Metered Dose Inhalers. Pharm Res 12, 1677–1681 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016253303206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016253303206