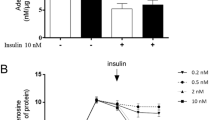
Abstract
The activity of adenosine kinase is significantly impaired in tissues of diabetic rat. Changes in the activity of adenosine kinase were accompanied by alterations in its mRNA and protein level. These changes depended on insulin level and were not related to glucose level. During the first 7 h after insulin treatment the level of adenosine kinase mRNA, protein and enzymatic activity in kidneys, liver and heart returned to normal values. The observed relation between insulin and adenosine kinase expression level may suggest that insulin increases the rate of adenosine kinase gene transcription. Decreased activity of adenosine kinase was associated with elevated level of adenosine in diabetic tissues. On the 10th day after the STZ treatment there was a 3.5 and 2-fold increase in adenosine content in heart and liver, respectively. On the other hand, in diabetic kidney adenosine level was elevated only by 20%. Administration of insulin to diabetic rats resulted in a drop of adenosine to the level seen in normal heart and liver whereas, in kidneys the adenosine content was 50% lower than that observed under normal conditions. The time-dependent coarse of changes in adenosine level was different from that observed for adenosine kinase activity, what may suggest that other factors, possibly nucleoside transporters are also important for controlling adenosine level in the cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krolewski AS, Canessa M, Warram JH, Laffel LM, Christlieb AR, Knowler WC, Rand LI: Predisposition to hypertension and susceptibility to renal disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 318: 140–145, 1988
Thomas PK: Clinical features and investigation of diabetic somatic peripheral neuropathy. Clin Neurosci 4: 341–345, 1997
Epstein M, Sowers JR: Diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Hypertension 19: 403–418, 1992
Fein FS, Komstein LB, Strobeck JE, Capasso JM, Sonnenblick EH: Altered myocardial mechanics in diabetic rats. Circ Res 47: 922–933, 1980
Dilman WH: Diabetes mellitus induces changes in cardiac myosin in the rat. Diabetes 29: 579–582, 1980
Aageneas O, Moe H: Light and electron microscopy study of akin capillaries of diabetes. Diabetes 10: 253–259, 1961
Andersen AR, Sandahl-Christiansen J, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T: Diabetic nephropathy in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes: An epidemiological study. Diabetologia 25: 496–501, 1983
Viberti GC: Early functional and morphological changes in diabetic nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 12: 47–53, 1979
O'Donnell MP, Kasiske BL, Keane WF: Glomerular hemodynamic and structural alterations in experimental diabetes mellitus. FASEB J 2: 2339–2347, 1988
Yasuda H, Dyck PJ: Abnormalities of endoneurial microvessels and sural nerve pathology in diabetic neuropathy. Neurology 37: 20–28, 1987
Sima AAF, Sugimoto K: Experimental diabetic neuropathy: An update. Diabetologia 42: 773–788, 1999
Leighton B, Budohoski L, Lozeman FJ, Challiss RAJ, Newsholme EA: The effect of prostoglandins E1, E2 and F2 and indomethacin on the sensitivity of glycolysis and glycogen synthesis to insulin in stripped soleus muscles of the rat. Biochem J 227: 337–340, 1985
Newsholme EA: Recent developments in metabolism that impinge on research into the nature and treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 15: 1716–1720, 1992
Schwabe U, Schonhofer PS, Ebert R: Facilitation by adenosine of the action of insulin on the accumulation of adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate, lipolysis, and glucose oxidation in isolated fat cells. Eur J Biochem 46: 537–545, 1974
Budohoski L, Challiss RAJ, McManus B, Newsholme EA: Effect of analogues of adenosine and methyl xanthines on insulin sensitivity in soleus muscle of the rat. FEBS Lett 167:1–4, 1984
Wong EHA, Smith JA, Jarett L: Adenosine effects on glucose oxidation of adipocytes isolated from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Biochem J 232: 301–304, 1985
Han DH, Hansen PA, Nolte LA, Holloszy JO: Removal of adenosine decreases the responsiveness of muscle glucose transport to insulin and contraction. Diabetes 47: 1671–1675, 1998
Cheng JT, Liu IM, Chi TC, Shinozuka K, Lu FH, Chang CJ: Role of adenosine in insulin-stimulated release of leptin from isolated while adipocytes of Wistar rats. Diabetes 49: 20–24, 2000
McLane MP, Black PR, Law WR, Raymond RM: Adenosine reversal of in vivo hepatic responsiveness to insulin. Diabetes 39: 62–69, 1990
Lloyd HG, Deussen A, Wuppermann H, Schrader J: The transmethylation pathway as a source for adenosine in the isolated guinea-pig heart. Biochem J 252: 489–494, 1988
Bontemps F, Vincent MF, Van den Berghe G: Mechanism of elevation of adenosine levels in anoxic hepatocytes. Biochem J 290: 671–677, 1993
Headrick JP, Emerson CS, Berr SS, Berne RM, Matherne GP: Interstitial adenosine and cellular metabolism during beta-adrenergic stimulation of the in situ rabbit heart. Cardiovasc Res 31: 699–710, 1996
Spielman WS, Arend LJ: Adenosine receptors and signaling in the kidney. Hypertension 17: 117–130, 1991
Lowenstein JM, Yu M-K, Narto Y: Regulation of adenosine metabolism by 5′-nucleotidase. In: R.M. Berne, T.W. Rall, R. Rubio (eds). Regulatory Function of Adenosine. Martinus Nijhoff Publishing, Boston, 1983, pp 117–131
Stiles GL: Adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem 267: 6451–6454, 1992
Zhou Q-Y, Li C, Olah ME, Johnson RA, Stiles GL, Civelli O: Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel adenosine receptor: The A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89: 7432–7436, 1992
Gur S, Ari N, Ozturk Y: Increased responses to adenosine in isolated left atria from streptozotocin-diabetic rats: Evidence for the involvement of hypothyroidism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 29: 174–179, 1997
Gasser JA, Cooper MB, Tan K, Saggerson ED, Betteridge DJ: Altered cellular signalling and decreased platelet sensitivity to adenosine in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with proliferative retinopathy. Cell Signal 5: 145–153, 1993
Morrison PD, Mackinnon MW, Bartrup JT, Skett PG, Stone TW: Changes in adenosine sensitivity in the hippocampus of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 105: 1004–1008, 1992
Pflueger AC, Schenk F, Osswald H: Increased sensitivity of the renal vasculature to adenosine in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rats. Am J Physiol 269: F529–F535, 1995
Pflueger AC, Osswald H, Knox FG: Adenosine-induced renal vasoconstriction in diabetes mellitus rats: Role of nitric oxide. Am J Physiol 276: F340–F346, 1999
Gur S, Ozturk B: Altered relaxant responses to adenosine and adenosine 5′ triphosphate in the corpus cavernosum from men and rats with diabetes. Pharmacology 60: 105–112, 2000
Angielski S, Jakubowski Z, Pawelczyk T, Piec G, Redlak M: Renal handling and metabolism of adenosine in diabetic rats. Contrib Nephorl 73: 52–58, 1989
Pawelczyk T, Sakowicz M, Szczepanska-Konkel M, Angielski S: Decreased expression of adenosine kinase in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rats. Arch Biochem Biophys 375: 1–6, 2000
Pawelczyk T, Bizon D, Angielski S: The distribution of enzymes involved in purine metabolism in rat kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta 1116: 309–314, 1992
Negrini M, Monaco C, Vorechovsky I, Ohta M, Druck T, Baffa R, Huebner K, Croce CM: The FHIT gene at 3p14.2 is abnormal in breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 56: 3173–3179, 1996
Sakowicz M, Grden M, Pawelczyk T: Expression level of adenosine kinase in rat tissues. Lack of phosphate effect on the enzyme activity. Acta Biochim Pol 48: 745–754, 2000
McNally T, Helfrich RJ, Cowart M, Dorwin SA, Meuth JL, Idler KB, Klute KA, Simmer RL, Kowaluk EA, Halbert DN: Cloning and expression of the adenosine kinase gene from rat and human tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 231: 645–650, 1997
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685, 1970
Kather H, Wieland E, Waas W: Chemiluminescent determination of adenosine, inosine and hypoxanthine/xanthine. Anal Biochem 163: 45–51, 1987
White MF: The insulin signaling system and the IRS proteins. Diabetologia 40: S2–S17, 1997
Osawa H, Sutherland C, Robey RB, Printz RL, Granner DK: Analysis of the signaling pathway involved in the regulation of hexokinase II gene transcription by insulin. J Biol Chem 271: 16690–16694, 1996
Vaulont S, Vasseur-Cognet M, Kahn A: Glucose regulation of gene transcription. J Biol Chem 275: 31555–31558, 2000
Popp DA, Kiechle FL, Kotagal N, Jarett L: Insulin stimulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in isolated plasma membrane-mitochondrial mixture occurs by activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase. J Biol Chem 255: 7540–7543, 1980
Dent P, Lavoinne A, Nakielny S, Caudwell FB, Watt P, Cohen P: The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature 348: 302–308, 1990
Arai K, Maguchi S, Fuji S, Ishibashi H, Oikawa K, Taniguchi N: Glycation and inactivation of human Cu-Zn-superoxide dismutase. Identification of the in vitro glycated sites. J Biol Chem 262: 6969–16972, 1987
Hoshi A, Takahashi M, Fujii J, Myint T, Kaneto H, Suzuki K, Yamasaki Y, Kamada T, Taniguchi N: Glycation and inactivation of sorbitol dehydrogenase in normal and diabetic rats. Biochem J 318: 119–123, 1996
Jenkins RL, McDaniel HG, Digerness S, Parrish SW, Ong RL: Adenine nucleotide metabolism in hearts of diabetic rats. Comparison to diaphragm, liver, and kidney. Diabetes 37: 629–636, 1988
Ely SW, Matherne GP, Coleman SD, Berne RM: Inhibition of adenosine metabolism increases myocardial interstitial adenosine concentration and coronary flow. J Mol Cell Cardiol 24: 1321–1332, 1992
Kroll K, Decking UKM, Dreikorn K, Schrader J: Rapid turnover of the AMP-adenosine metabolic cycle in the guinea pig heart. Circ Res 73: 846–856, 1993
Bontemps F, Vincent MF, Van den Berghe G: Mechanism of elevation of adenosine levels in anoxic hepatocytes. Biochem J 290: 671–677, 1993
Pak MA, Hass HL, Decking UKM, Schrader J: Inhibition of adenosine kinase increases endogenous adenosine and depresses neuronal activity in hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology 33: 1049–1053, 1994
Griffith DA, Jarvis SM: Nucleoside and nucleobase transport systems of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1286: 153–181, 1996
Baldwin SA, Mackey JR, Cass CE, Young JD: Nucleoside transporters: Molecular biology and implications for therapeutic development. Mol Med Today 5: 216–224, 1999
Sobrevia L, Jarvis SM, Yudilevich DL: Adenosine transport in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells is reduced in diabetes. Am J Physiol 267: C39–C47, 1994
Cassar M, Jones MG, Szostakowski M: Reduced adenosine uptake accelerates ischemic block of population spikes in hippocampal slices from streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Eur J Neurosci 10: 239–245, 1998
Lefkowitz RJ: G protein-coupled receptors. III. New roles for receptor kinases and β-arrestins in receptor signaling and desensitization. J Biol Chem 273: 18677–18680
Olah ME, Stiles GL: The role of receptor structure in determining adenosine receptor activity. Pharmacol Ther 85: 55–75, 2000
Liang BT, Donowan LA: Differential desensitization of A1 adenosine receptor-mediated inhibition of cardiac myocyte contractility and adenylate cyclase activity. Relation to the regulation of receptor affinity and density. Circ Res 67: 406–414, 1990
Palmer TM, Benovic JL, Stiles GL: Molecular basis for subtype-specific desensitization of inhibitory adenosine receptors. Analysis of himeric A1–A3 adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem 271: 15272–152728, 1996
Abbracchio MP, Fogliatto G, Paoletti AM, Rovati GE, Cattabeni F: Prolonged in vitro exposure of rat brain slices to adenosine analogues: Selective desensitization of adenosine A1 but not A2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 227: 317–324, 1992
Conti A, Lozza G, Monopoli A: Prolonged exposure to 5′-N ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) does not affect the adenosine A2A mediated vasodilatation in porcine coronary arteries. Pharmacol Res 35: 123–128, 1997
Romano FD, Kopp JT, Smith CA: The antiadrenergic effect of cyclopentyladenosine on myocardial contractility is reduced in vivo in diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 72: 1245–1251, 1994
Laurent F, Hillaire-Buys D, Chapal J, Dietz S, Portet K, Cros G, Petit C, Michel A: Contrasting effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the in vitro relaxant properties of adenosine in rat pancreatic vascular bed and thoracic aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 360: 309–316, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakowicz, M., Pawelczyk, T. Insulin restores expression of adenosine kinase in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rats. Mol Cell Biochem 236, 163–171 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016163517896
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016163517896