Abstract
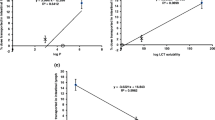
To study the lymphatic delivery of exogenous macromolecules via the enteral route in renal insufficiency, we determined the transfer selectivity to the systemic blood and lymph of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled dextrans of different average molecular weight (10, 18, 39, and 69kD). The compounds were administered into the large intestinal lumen of rats with occluded renal circulation, with the aid of lipid-surfactant mixed micelles as an absorption prometer. Whereas concentrations of the smaller dextrans (molecular weight under 18 kD) in the lymph of the thoracic duct and in the peripheral plasma were similar, levels of dextrans over 39 kD were significantly higher in the lymph than in the plasma. Further, dextran plasma concentrations decreased in inverse proportion to increasing molecular weight. The molecular weight threshold for a high lymph-to-blood level ratio (18-39 kD) was higher than that previously found in rats with normal renal function (10-18 kD). This difference was accounted for by reduced renal clearance of the low molecular weight dextrans in renal failure. These results are useful in the design of lymphotropic drug delivery in disease states.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshikawa, H., Takada, K. & Muranishi, S. Molecular Weight-Dependent Lymphatic Transfer of Exogenous Macromolecules from Large Intestine of Renal Insufficiency Rats. Pharm Res 9, 1195–1198 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015812124219
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015812124219