Abstract
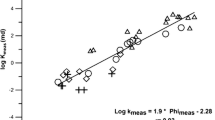
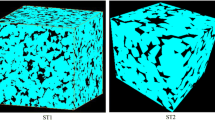
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is an increasingly popular well-logging tool in petroleum industry because it is the only tool that attempts to estimate formation permeability. In this paper, spatially correlated porous media are generated. Permeabilities of these media are computed by the lattice Boltzmann method. NMR relaxation responses are simulated by a random walk technique and formation factors are computed by solving a Laplacian equation. The testing of commonly used NMR permeability correlations shows that three conditions should be met for the validity of these correlations. The surface relaxivity should not vary significantly. The formation factor should depend only on porosity. And the characteristic pore body radius should be proportional to the characteristic throat radius. The correlations are improved by including surface relaxivity and formation factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, P. M., Jacquin, C. G. and Thovert, J. F.: 1992, The formation factor of a recontructed porous media, Water Resour. Res. 28(6), 1571–1576.
Adler, P. M. and Thovert, J. F.: 1996, Real porous media; local geometry and macrocopic properties, Appl. Mech. Rev. 51(9), 537–585.
Adrover, A. and Giona, M.: 1996, A predictive model for permeability of correlated porous media, Chem. Eng. J. 64(1), 7–19.
Bergmann, D. J., Dunn, K. J., Schwartz, L. M. and Mitra, P. P.: 1995, Self-diffusion in a periodic porous medium, Phys. Rev. E 51(4), 3393–3400.
Bloch, F.: 1946, Nuclear introduction, Phys. Rev. 70(7), 460–474.
Carman, P. C.: 1956, Flow of Gases through Porous Media, Academic, New York.
Chen, S. and Doolen, G. D.: 1998, Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 329–364.
Coates, G. R., Peveraro, R. C. A., Hardwick, A. and Robert, D.: 1991, The magnetic resonance imaging log characterized by comparison with petrophysical properties and laboratory core data, SPE 22723.
Davis, M. E.: 1984, Numerical Methods and Modeling for Chemical Engineers, Wiley, New York.
Dullien, F. A. L.: 1979, Porous Media – Fluid Transport and Pore Structure, Academic, New York.
Dunn, K. J., LaTorraca, G. A. and Bergman, D. J.: 1999, Permeability relation with other petro-physical parameters for periodic porous media, Geophysical 64(2), 470–478.
Fordham, E. J., Sezginer, A. and Hall, L. D.: 1995, Imaging multiexponential relaxation in the (y,loge T1) plane, with application to clay filtration in rock cores, J. Magn. Reson. A 113(2), 139–150.
Fukushima, E. and Roeder, S. B. W.: 1981, Experimental Pulse NMR – A Nuts and Bolts Approach, Addison-Wesley, Masschusets.
Gerald, F. C. and Wheatley, P. O.: 1989, Applied Numerical Analysis, Addison-Wesley, Masschusets.
He, X. and Luo, L.: 1997, Theory of lattice Boltzmann method: from the Boltzmann equation to the lattice Boltzmann equation, Phys. Rev. E 56(6), 6811–6817.
Huang, C. C.: 1997, Estimation of Rock Properties by NMR Relaxation Methods, MSc Thesis, Rice University, U.S.A.
Isichenko, M. B.: 1992, Percolation, statistical topography, and tranport in random media, Rev. Mod. Phys. 64(4), 961–1043.
Katz, A. J. and Thompson, A. H.: 1986, Quantitative prediction of permeability in porous rock, Phys. Rev. B 34(11), 8179–8181.
Kenyon, W. E., Day, P. I., Straley C. and Willemsen, J. F.: 1988, A three-part study of NMR longitudinal relaxation propeties of water-saturated sandstones, SPE Form. Eval. 3(3), 622–636.
Kenyon, W. E.: 1997, Petrophysical principles of applictions of NMR logging, Log Anal. 38(2),21–43.
Kubica, P.: 1995, Statistical test of permeability estimates based on NMR measurements, Trans. SPWLA 36, paper VVV.
LaTorraca, G. A., Dunn, K. J. and Brown, R. J. S.: 1993, Predicting permeability from nuclear mag-netic resonance and electrical properties measurement, Soc. Core Anal. SCA-9312, September 1993.
Lee, S. B., Kim, I. C., Miller, C. A. and Torquato, S.: 1989, Random-walk simulation of diffusion controlled processes among static traps, Phys. Rev. B 39(16), 11833–11839.
Maier, R. S., Bernard, R. S. and Grunau, D. W.: 1996, Boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann method, Phys. Fluids 8(7), 1788–1801.
Qian, Y. H., d'Humieres, D. and Lallemand, P.: 1992, Lattice BGK models for the Navier–Stokes equation, Europhys. Lett. 17(6), 479–484.
Ramakrishnan, T. S., Schwartz, L. M., Fordham, E. J., Kenyon, W. E. and Wilkinson, D. J.: 1998, Forward models for nuclear magnetic resonance in carbonate rocks, Trans. SPWLA 39, paper SS.
Sahimi, M.: 1993, Flow phenomena in rocks: from continuum models to fractals, percolation, cellular automata and simulated annealing, Rev. Mod. Phys. 65(4), 1393–1534.
Seevers, D. O.: 1966, A nuclear magnetic method for determining the permeability of sandstones, Trans. SPWLA 6, paper L.
Singh, M. and Mohanty, K. K.: 2000, Permeability of spatially-correlated porous media, Chem. Engng Sci. 55(22), 5393–5403.
Skordos, P. A.: 1993, Initial and boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann method, Phys. Rev. E. 48(16), 4823–4842.
Straley, C., Rossini, D., Vinegar, H., Tutunjian, P. N. and Morris, P.: 1995, Core analysis by low-field NMR, Soc. Core Anal., SCA-9494.
Timur, A.: 1968, An investigation of permeability, porosity and residual water saturation relationship, Trans. SPWLA 9, paper K.
Timur, A.: 1969(a), Producible porosity and permeability of sandstones investigated through nuclear magnetic resonance principles, Log. Anal. 10(1), 3–11.
Timur, A.: 1969(b), Pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance studies of porosity, movable fluid, permeab-ility of sandsotnes, J. Petr. Tech. 21 (June), 775–786.
Torquato, S., and Kim, I. C.: 1989, Efficient simulation technique to compute effective properties of heterogeneous media, Appl. Phys. Lett. 55(18), 1847–1849.
Zheng, L. H. and Chiew, Y. C.: 1988, Computer simulation of diffusion controlled reactions in dispersions of spherical sinks, J. Chem. Phys. 90(1), 322–327.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidajat, I., Singh, M., Cooper, J. et al. Permeability of Porous Media from Simulated NMR Response. Transport in Porous Media 48, 225–247 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015682602625
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015682602625