Abstract
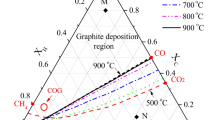
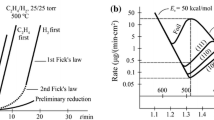
The thermodynamics and kinetics of pyrolytic carbon deposition via hydrogen reduction of CCl4 were studied. Thermodynamic analysis of the C–Cl–H system was used to determine the compositions of the gas and condensed phases at CCl4 : H2 = 1 : 4 to 1 : 90, temperatures from 700 to 1400 K, and a pressure of 105 Pa. The reactions leading to the formation of solid carbon in the H2–CCl4 system were considered, and the deposition parameters were optimized in terms of carbon yield.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Haase, R., Thermodynamik der irreversiblen Prozesse, Darmstadt, 1963. Translated under the title Termodinamika neobratimykh protsessov, Moscow: Mir, 1967.
Vatolin, N.A., Moiseev, G.K., and Trusov, B.G., Termodinamicheskoe modelirovanie v vysokotemperaturnykh neorganicheskikh sistemakh (Thermodynamic Modeling in High-Temperature Inorganic Systems), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1994.
Ostrovskii, A.A., Iskusstvennyi grafit (Artificial Graphite), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elyutin, A.V., Vorob'eva, M.V. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Carbon Deposition from Mixtures of Hydrogen and Carbon Tetrachloride. Inorganic Materials 38, 468–470 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015466920985
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015466920985