Abstract
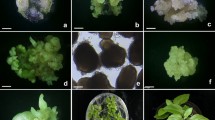
Explants of germinating zygotic embryos of Eleutherococcus sessiliflorus,an important medicinal plant, produced somatic embryos directly on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 4.5 μM 2,4-D. In addition, embryogenic callus formed at a low frequency (less than 7%) from hypocotyl segments after prolonged culture. High frequency somatic embryogenesis was obtained through cell suspension culture after the cells were transferred to medium lacking 2,4-D. Maturation and germination of embryos was influenced by the sucrose concentration of the medium. At a low concentration of sucrose (1%), maturation and germination of embryos occurred readily. At over 6% sucrose, somatic embryos did not germinate although this could be overcome by GA3 treatment. Cold treatment during acclimatization after transfer to soil enhanced survival. Surviving plantlets produced new sprouts after overwintering in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SD & Choi EO (1993) Study of the propagation of Acanthopanax plants. 1. Effect of growth regulators on rooting in stem cuttings. Korean J. Ginseng Sci. 16: 138–145
Brekhman II & Dardymov IV (1969) New substances of plant origin which increase nonspecific resistance. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 9: 415
Choi YE, Kim JW & Yoon ES (1999a) High frequency of plant production via somatic embryogenesis from callus or cell suspension cultures in Eleutherococcus senticosus. Ann. Bot. 83: 309–314
Choi YE, Yang DC & Yoon ES (1999b) Rapid propagation of Eleutherococcus senticosus via direct somatic embryogenesis from explants of germinating zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 58: 93–97
Choi YE, Yang DC, Yoon ES & Choi KT (1999c) High-efficiency plant production via direct somatic single embryogenesis from preplasmolysed cotyledons of Panax ginseng and possible dormancy of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 493–499
Gui Y, Guo Z, Ke S & Skirvin RH (1991) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Acanthopanax senticosus. Plant Cell Rep. 9: 514–516
Isoda S & Shoji J (1994) Studies on the cultivation of Eleutherococus senticosus Maxim. II On the germination and raising of seedling. Nat. Med. 48: 75–81
Lee WT (1979) Distribution of Acanthopanax plants in Korea. Korean J. Pharmocology 10: 103–107
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Shoyama Y, Kamura K & Nishioka I (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and clonal multiplication of Panax ginseng. Planta Med. 54: 155–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Y., Ko, S., Lee, K. et al. Production of plantlets of Eleutherococcus sessiliflorus via somatic embryogenesis and successful transfer to soil. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 69, 201–204 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015290718273
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015290718273