Abstract
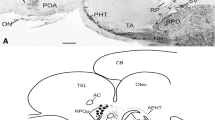
The distribution of the neurosecretory hormones vasotocin, isotocin and melanin-concentrating hormone and the hypophysio-tropic hormone corticotropin-releasing factor was studied in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system of the white seabream (Diplodus sargus) using immunocytochemical techniques. Magnocellular and parvocellular perikarya immunoreactive for arginine-vasotocin and isotocin were present in the nucleus preopticus. Perikarya immunoreactive for arginine-vasotocin extended more caudally with respect to isotocin-immunoreactive perikarya. Parvocellular perikarya were located at rostroventral levels and magnocellular perikarya in the dorsocaudal portion of the nucleus. Arginine-vasotocin and isotocin did not coexist in the same neuron. Fibres immunoreactive for arginine-vasotocin and isotocin innervated all areas of neurohypophysis and terminate close to corticotropic and melanotropic cells. Perikarya immunoreactive for melanin-concentrating hormone and corticotropin-releasing factor were observed in the nucleus lateralis tuberis, with a few neurons in the nucleus periventricularis posterior. In addition, melanin-concentrating hormone immunoreactive perikarya were detected in the nucleus recessus lateralis. The preoptic nucleus did not show immunoreactivity for these antisera. Fibres showing melanin-concentrating hormone and corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity ended close to the melanotropic and somatolactotrophic cells of the pars intermedia, and close to the corticotrophic cells of the rostral pars distalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando H, Hasegawa M, Ando J, Urano A (1999) Expression of salmon corticotropin-releasing hormone precursor gene in the preoptic nucleus in stressed rainbow trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol 113: 87–95.
Anglade I, Zandbergen T, Kah O (1993) Origin of the pituitary innervation in the goldfish. Cell Tissue Res 273: 345–355.
Arai M, Assil IQ, Abou-Samra AB (2001) Characterization of three corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in catfish: A novel third receptor is predominantly expressed in pituitary and urophysis. Endocrinology 142: 446–454.
Baker BI (1991) Melanin-concentrating hormone: a general vertebrate neuropeptide. Int Rev Cytology 126: 1–47.
Balm PH, Groneveld D (1998) The melanin-concentrating hormone system in fish. Ann NY Acad Sci 839: 205–209.
Balment RJ, Warne JM, Tierney M, Hazon N (1993) Arginine vasotocin and fish osmoregulation. Fish Physiol Biochem 11(1–6): 189–194.
Batten TFC (1986) Ultrastructural characterization of neurosecretory fibres immunoreactive for vasotocin, isotocin, somatostatin, LHRH and CRF in the pituitary of a teleost fish, Poecilia latipinna. Cell Tissue Res 244: 661–672.
Batten TFC, Baker BI (1988) Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) immunoreactive hypophysial neurosecretory system in the teleost Poecilia latipinna: Light and electron microscopic study. Gen Comp Endocrinol 70: 193–205.
Batten TFC, Cambre ML, Moons L, Vandesande F (1990) Comparative distribution of neuropeptide-immunoreactive systems in the brain of the green molly, Poecilia latipinna. J Comp Neurol 302: 893–919.
Batten TFC, Moons L, Vandesande F (1999) Innervation and control of the adenohypophysis by hypothalamic peptidergic neurons in teleost fishes: EM immunohistochemical evidence. Microsc Res Tech 44: 19–35.
Bernier NJ, Lin X, Peter RE (1999) Differential expression of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and urotensin I precursor genes, and evidence of CRF gene expression regulated by cortisol in goldfish brain. Gen Comp Endocrinol 116: 461–477.
Billard R, Peter RE (1982) A stereotaxic atlas and techniques for nuclei of the diencephalon of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Reprod Nutr Dev 22: 893–919.
Cerdá-Reverter JM, Zanuy S, Muñoz-Cueto JA(2001) Cytoarchitectonic study of the brain of a perciform species, the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). II. The diencephalon. J Morphol 247: 229–251.
Cumming R, Reaves TA, Hayward JN (1982) Ultrastructural immunocytochemical characterization of isotocin, vasotocin and neurophysin neurons in the magnocellular preoptic nucleus of the goldfish. Cell Tissue Res 223: 685–694.
Divanach P, Kentouri M, Paris J (1982) Etapes du développement ambryonnaire et larvaire du sar, Diplodus sargus L., en elevage. Aquaculture 27: 339–353.
Foran CM, Bass AH (1998) Preoptic AVT immunoreactive neurons of a teleost fish with alternative reproductive tactics. Gen Comp Endocrinol 111: 271–282.
Foran CM, Bass AH (1999) Preoptic GnRH and AVT: Axes for sexual plasticity in teleost fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 116: 141–152.
Francis K, Suzuki M, Baker BI (1997) Responses of melaninconcentrating hormone mRNA to salt water challenge in the rainbow trout. Neuroendocrinology 66: 195–202.
Fryer JN, Lederis K (1986) Control of corticotropin secretion in teleost fishes. Am Zool 26: 1017–1026.
Gilchriest BJ, Tipping DR, Hake L, Levy A, Baker BI (2000) The effects of acute chronic stresses on vasotocin gene transcripts in the brain of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Neuroendocrinol 12: 795–801.
Godwin J, Sawby R Warner RR, Crews D, Grober MS (2000) Hypothalamic arginin vasotocin mRNA abundance variation across sexes and with sex change in a coral reef fish. Brain Behav Evol 55: 77–84.
Goosens N, Dietrickx K, Vandesande F (1977) Immunocytochemical localization of vasotocin and isotocin in the preopticohypophysial neurosecretory system of teleosts. Gen Comp Endocrinol 32: 371–375.
Groneveld D, Eckhardt ERM, Coenen AJM, Martens GJM, Balm PHM, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1995) Expression of tilapia prepro-melaninconcentrating hormonemRNAin hypothalamic and neurohypophysial cells. J Endocrinol 14: 199–207.
Holmqvist BI, Ekström P (1995) Hypophysiotrophic systems in the brain of the Atlantic salmon. Neuronal innervation of the pituitary and the origin of pituitary dopamine and nonapeptides identified by means combined carbocyanine tract tracing and immunocytochemistry. J Chemical Neuroanat 8: 125–145.
Kawazoe I, Kawauchi H, Hirano T, Naito N (1987) Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone in teleost hypothalamus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 65: 423–431.
Lovejoy DA, Balment RJ (1999) Evolution and physiology of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family of neuropeptides in vertebrates. Gen Comp Endocrinol 115: 1–22.
Mahlmann S, Meyerhof W, Hausmann H, Heierhost J, Schönrock C, Zwiers H, Lederis K, Richter D (1994) Structure, function, and phylogeny of (Arg8)vasotocin receptors from teleost fish and toad. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 9: 1342–1345.
Mancera JM, Fernández-Llebrez P (1995a) Localization of corticotropinreleasing factor immunoreactivity in the brain of the teleost Sparus aurata. Cell Tissue Res 281: 569–572.
Mancera JM, Fernández-Llebrez TP (1995b) Development of melaninconcentrating hormone-immunoreactive elements in the brain of gilthead seabream (Sparus auratus). Cell Tissue Res 282: 523–526.
Mancera JM, LopezAvalos MD, Pérez-Fígares JM, Fernández-Llebrez P (1991) The distribution of corticotropic-releasing factor-immunoreactive neurons and nerve fibres in the brain of the snake, Natrix maura.Cell Tissue Res 264: 539–548.
Meurling P, Rodríguez EM, Peña P, Mateos Grondona J, Pérez J (1996) Hypophysial and extrahypophysial projections of the neurosecretory system of cartilaginous fishes: An immunocytochemical study using a polyclonal antibody against dogfish neurophysin. J Comp Neurol 373: 400–421.
Moons L, Camber M, Batten TFC, Vandesande F (1989a) Auto radiographic localization of binding sites for vasotocin in the brain and pituitary of the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Neurosci Lett 100: 11–16.
Moons L, Cambré M, Ollevier F, Vandesande (1989b) Immunocytochemical demonstration of close relationship between neuropeptidergic nerve fibres and hormone-producing cell types in the adenohypophysis of the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Gen Comp Endocrinol 73: 270–283.
Mordenti O, Roncarati A, Melotti P, Gennari L, Dees A (1996) Breeding and feeding of juveniles of the white seabream (Diplodus sargus L.). Biol Mar Mediterr 1: 425–426.
Naito N, Nakai Y, Kawauchi H, Hayashi Y (1985) Immunocytochemical identification of melanin-concentrating hormone in the brain and pituitary gland of the teleost fishes Oncorhynchus keta and Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tissue Res 242: 41–48.
Olivereau M, Olivereau J (1988) Localization of CRF-like immunoreactivity in the brain and pituitary of teleost fish. Peptides 9: 13–21.
Olivereau M, Olivereau JM (1990) Corticotropin-like immunoreactivity in the brain and pituitary of three teleost species (goldfish, trout and eel). Cell Tissue Res 262: 115–123.
Olivereau M, Moons J, Olivereau J, Vandesande F (1988) Coexistence of corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity and vasotocin in perikarya of the preoptic nucleus in the eel. Gen Comp Endocrinol 70: 41–48.
Perrin MH, Vale WW(1999) Corticotropin releasing factor receptors and their ligand family. Ann NY Acad Sci 885: 312–328.
Peter RE, Macey MJ, Gill VE(1975)Astereotaxic atlas and technique for forebrain nuclei of the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. J Comp Neurol 159: 103–128.
Peter RE, Yu KL, Marchant TA, Rosenblum PM (1990) Direct neural regulation of the adenohypophysis. J Exp Zool 4: 84–89.
Rivier CL, Plotsky PM(1986) Mediation by corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) of adenohypophysial hormone secretion. Ann Rev Physiol 48: 475–494.
Saito Y, Nothacker HP, Wang Z, Lin SH, Leslie F, Civelli O(1999) Molecular characterization of melanin-concentrating-hormone receptor. Nature 400: 265–269.
Sawchenko PE, Imaki T, Potter E, Kovacs K, Imaki J, Vale W (1993) The functional neuroanatomy of corticotropin-releasing factor. Ciba Found Symp 172: 5–21.
Schreibman MP, Halpern LR (1980) The demonstration of neurophysin and arginine vasotocin by immunocytochemical methods in the brain and pituitary gland of the platyfish, Xiphophorus maculatus. GenComp Endocrinol 40: 1–7.
Segura-Noguera, MM, Laíz-Carriön R, Martn del Río MP, Mancera JM (2000) An immunocytochemical study of the pituitary gland of the white seabream (Diplodus sargus). Histochem J 32: 733–742.
Sone M, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Totsune K, Arihara Z, Satoh F, Sasano H, Ito H, Mouri T (2000) Binding sites for melanin-concentrating hormone in the human brain. Peptides 21: 245–250.
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1968) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: Preparation and properties of soluble antigen–antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase–antiperoxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18: 315–333.
Suzuki M, Narnaware YK, Baker BI, Levy A (1995) Influence of environmental colour and diurnal phase on MCH gene expression in the trout. J Neuroendocrinol 7: 319–328.
Vallarino M, Andersen AC, Delbende C, Ottonello I, Eberle AN, Vaudry H(1989a) Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) immunoreactivity in the brain and pituitary of the dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. Colocalization with alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) in hypothalamic neurons. Peptides 10: 375–382.
Vallarino M, Fasolo A, Ottonello I, Perroteau I, Tonon MC, Vandesande F, Vaudry H (1989b) Localization of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRF)-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the elasmobranch fish, Scyliorhinus canicula. Cell Tissue Res 258: 541–546.
Vallarino M, Viglietti-Panzica C, Panzica JC (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of vasotocin-like immunoreactivity in the brain of the cartilaginous fish, Scyliorhinus caniculus. Cell Tissue Res 262: 507–513.
van den Dungen HM, Buijs RM, Pool CW, Terlou M (1982) The distribution of vasotocin and isotocin in the brain of the rainbow trout. J Comp Neurol 212: 146–157.
van Enckevort FH, Pepels PP, Leunissen JA, Martens GJ, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Balm PH (2000) Oreochromis mossambicus (tilapia) corticotropin-releasing hormone: cDNA sequence and bioactivity. J Neuroendocrinol 12: 177–186.
van Zoest ID, Heijmen PS, Cruijsen PMJM, Jenks BG (1989) Dynamics of background adaptation in Xenopus laevis: Role of catecholamines and melanophore stimulating hormone. Gen Comp Endocrinol 76: 19–28.
Warne JM, Balment RJ (1997) Vascular variations of neurohypophysial peptides in the flounder. Fish Physiol Biochem 17: 313–318.
Warne JM, Hyodo S, Harding K, Balment RJ (2000) Cloning of provasotocin and pro-isotocincDNAs from the flounder Platichthys flesus; levels of hypothalamicmRNAfollowing acute osmotic challenge. Gen Comp Endocrinol 119: 77–84.
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77: 591–625.
Yulis CR, Lederis K (1987) Co-localization of the arginine vasotocin in the brain and pituitary system of the teleost Catostomus commersoni. Cell Tissue Res 247: 267–273.
Yulis CR, Lederis K, Wong KL, Fisher AWF (1986) Localization of urotensin I-and corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of Catostomus commersoni. Peptides 7: 79–86.
Zupanc GKH, Horschke I, Lovejoy DA (1999) Corticotropin releasing factor in the brain of the gymnotiform fish, Apteronotus leptorhynchus: Immunohistochemical studies combined with neuronal tract tracing. Gen Comp Endocrinol 114: 349–364.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, G., Segura-Noguera, M., Martín del Río, M. et al. The Hypothalamo-hypophyseal System of the White Seabream Diplodus Sargus: Immunocytochemical Identification of Arginine-vasotocin, Isotocin, Melanin-concentrating Hormone and Corticotropin-releasing Factor. Histochem J 33, 569–578 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014912110318
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014912110318