Abstract
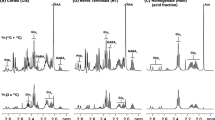
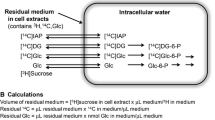
Metabolism of glutamine was determined under a variety of conditions to study compartmentation in cortical synaptosomes. The combined intracellular and extracellular amounts of [U-13C]GABA, [U-13C]glutamate and [U-13C]glutamine were the same in synaptosomes incubated with [U-13C]glutamine in the presence and absence of glucose. However, the concentration of these amino acids was decreased in the latter group, demonstrating the requirement for glucose to maintain the size of neurotransmitter pools. In hypoglycemic synaptosomes more [U-13C]glutamine was converted to [U-13C]aspartate, and less glutamate was re-synthesized from the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, suggesting use of the partial TCA cycle from α-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate for energy. Compartmentation was studied in synaptosomes incubated with glucose plus labeled and unlabeled glutamine and glutamate. Incubation with [U-13C]glutamine plus unlabeled glutamate gave rise to [U-13C]GABA but not labeled aspartate; however, incubation with [U-13C]glutamate plus unlabeled glutamine gave rise to [U-13C]aspartate, but not labeled GABA. Thus the endogenous glutamate formed via glutaminase in synaptic terminals is preferentially used for GABA synthesis, and is metabolized differently than glutamate taken up from the extracellular milieu.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Battaglioli, G. and Martin, D. L. 1996. Glutamine stimulates gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in synaptosomes but other putative astrocyte-to-neuron shuttle substrates do not. Neurosci. Lett. 209:129–133.
Westergaard, N., Sonnewald, U., Petersen, S. B., and Schousboe, A. 1995. Glutamate and glutamine metabolism in cultured GABAergic neurons studied by 13C NMR spectroscopy may indicate compartmentation and mitochondrial heterogeneity. Neurosci. Lett. 185:24–28.
McKenna, M. C., Tildon, J. T., Stevenson, J. H., Jr., Boatright, R., and Huang, S. 1993. Regulation of energy metabolism in synaptic terminals and cultured rat brain astrocytes: Differences revealed using aminooxyacetate. Develop. Neurosci. 15:320–329.
Johnson, J. L. and Roberts, E. 1984. Proline, glutamate and glutamine metabolism in mouse brain synaptosomes. Brain Res. 323:247–256.
Erecinska, M., Zaleska, M. M., Nissim, I., Nelson, D., Dagani, F., and Yudkoff, M. 1988. Glucose and synaptosomal glutamate metabolism: studies with [15N]glutamate. J. Neurochem. 51:892–902.
Yudkoff, M., Zaleska, M. M., Nissim, I., Nelson, D., and Erecinska, M. 1989. Neuronal glutamine utilization: pathways of nitrogen transfer studied with [15N]glutamine. J. Neurochem. 53:632–640.
Yudkoff, M., Nelson, D., Daikhin, Y., and Erecinska, M. 1994. Tricarboxylic acid cycle in rat brain synaptosomes. Fluxes and interactions with aspartate aminotransferase and malate/aspartate shuttle. J. Biol. Chem. 269:27414–27420.
Fitzpatrick, S. M., Hetherington, H. P., Behar, K. L., and Shulman, R. G. 1990. The flux from glucose to glutamate in the rat brain in vivo as determined by 1H-observed, 13C-edited NMR spectroscopy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 10:170–179.
Gruetter, R., Seaquist, E. R., Kim, S., and Ugurbil, K. 1998. Localized in vivo 13C-NMR of glutamate metabolism in the human brain: initial results at 4 tesla. Dev. Neurosci. 20:380–388.
McKenna, M. C., Tildon, J. T., Stevenson, J. H., and Hopkins, I. B. 1994. Energy metabolism in cortical synaptic terminals from weanling and mature rat brain: Evidence for multiple compartments of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle activity. Develop. Neurosci. 16:291–300.
Shurr, A., West, C. A., and Rigor, B. M. 1988. Lactate supported synaptic function in rat hippocampal slice preparation. Science 240:1326–1328.
Waagepetersen, H. S., Bakken, I. J., Larsson, O. M., Sonnewald, U., and Schousboe, A. 1998. Comparison of lactate and glucose metabolism in cultured neocortical neurons and astrocytes using 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Dev. Neurosci. 20:310–320.
Ransom, B. R. and Fern, R. 1997. Does astrocytic glycogen benefit axon function and survival in CNS white matter during glucose deprivation? Glia 21:134–141.
Gundersen, V., Fonnum, F., Ottersen, O. P., and Storm-Mathisen, J. 2001. Redistribution of neuroactive amino acids in hippocampus and striatum during hypoglycemia: a quantitative immunogold study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21:41–51.
Kauppinen, R. A. and Nicholls, D. G. 1986. Synaptosomal bioenergetics. The role of glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and responses to hypoglycaemia. Eur. J. Biochem. 158:159–165.
Petroff, O. A., Burlina, A. P., Black, J., and Prichard, J. W. 1991. Metabolism of [1–13C]glucose in a synaptosomally enriched fraction of rat cerebrum studied by 1H/13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurochem. Res. 16:1245–1251.
Lai, J. C. and Clark, J. B. 1976. Preparation and properties of mitochondria derived from synaptosomes. Biochem. J. 154:423–432.
Smith, P. K., Khron, R. I., Hermanson, G. T., Mallia, A. K., Artner, F. H., Provenzano, M. D., Fujimoto, E. K., Goeke, N. M., Olson, B. J., and Klenck, D. C. 1985. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 150:76–85.
Geddes, J. W. and Wood, J. D. 1984. Changes in the amino acid content of nerve endings (synaptosomes) induced by drugs that alter the metabolism of glutamate and 4–aminobutyric acid. J. Neurochem. 42:16–24.
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W. G. 1967. Statistical Methods, 6th edit., Iowa State University Press, Ames.
Kvamme, E., Torgner, I. A., and Svenneby, G. 1985. Glutaminase from mammalian tissues. Methods Enzymol. 113:241–256.
McKenna, M. C., Stevenson, J. H., Huang, X., Tildon, J. T., Zielke, C. L., and Hopkins, I. B. 2000. Mitochondrial malic enzyme activity is much higher in mitochondria from cortical synaptic terminals compared with mitochondria from primary cultures of cortical neurons or cerebellar granule cells. Neurochem. Int. 36:451–459.
Engelsen, B. and Fonnum, F. 1983. Effects of hypoglycemia on the transmitter pool and the metabolic pool of glutamate in rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 42:317–322.
Akasu, T., Tsurusaki, M., and Shoji, S. 1996. Depletion of glucose causes presynaptic inhibition of neuronal transmission in the rat dorsolateral septal nucleus. Synapse 24:125–134.
McKenna, M. C., Tildon, J. T., Stevenson, J. H., Hopkins, I. B., Huang, X., and Couto, R. 1998. Lactate transport by cortical synaptosomes from adult rat brain: Characterization of kinetics and inhibitor specificity. Develop. Neurosci. 20:300–309.
Wender, R., Brown, A. M., Fern, R., Swanson, R. A., Farrell, K., and Ransom, B. R. 2000. Astrocytic glycogen influences axon function and survival during glucose deprivation in central white matter. J. Neurosci. 20:6804–6810.
Hertz, L., Peng, L., Westergaard, N., Yudkoff, M., and Schousboe, A. 1991. Neuronal-astrocytic interactions in metabolism of transmitter amino acids of the glutamate family. Pages 30–48, in Schousboe, A., Diemer, N. H., and Kofod, H. (eds.), Drug research related to neuroactive amino acids. Munksgaard, Copenhagen, DK.
Bakken, I. J., White, L. R., Unsgard, G., Aasly, J., and Sonnewald, U. 1998. [U-13C]glutamate metabolism in astrocytes during hypoglycemia and hypoxia. J. Neurosci. Res. 51:636–645.
McKenna, M. C., Stevenson, J. H., Huang, X., and Hopkins, I. B. 2000. Differential distribution of the enzymes glutamate dehydrogenase and aspartate aminotransferase in cortical synaptic mitochondria contributes to metabolic compartmentation in cortical synaptic terminals. Neurochem. Int. 37:229–241.
Palaiologos, G., Hertz, L., and Schousboe, A. 1989. Role of aspartate aminotransferase and mitochondrial dicarboxylate transport for release of endogenously and exogenously supplied neurotransmitter in glutamatergic neurons. Neurochem. Res. 14:359–366.
Madl, J. E. and Royer, S. M. 1999. Glutamate in synaptic terminals is reduced by lack of glucose but not hypoxia in rat hippocampal slices. Neuroscience 94:417–430.
Waagepetersen, H. S., Sonnewald, U., Larsson, O. M., and Schousboe, A. 2000. A possible role of alanine for ammonia transfer between astrocytes and glutamatergic neurons. J. Neurochem. 75:471–479.
Zwingmann, C., Richter-Landsberg, C., Brand, A., and Leibfritz, D. 2000. NMR spectroscopic study on the metabolic fate of [3–13C]alanine in astrocytes, neurons, and cultures: implications for glia-neuron interactions in neurotransmitter metabolism. Glia 32:286–303.
Berl, S. and Clarke, D. D. 1969. Metabolic compartmentalization of glutamate in the CNS. Vol 1, pages 447–472, in Lajtha, A. (editor), Handbook of Neurochemistry, Plenum Press, New York.
Norenberg, M. D. and Martinez-Hernandez, A. 1979. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 161:303–310.
Sonnewald, U., Westergaard, N., Petersen, S. B., Unsgård, G., and Schousboe, A. 1993. Metabolism of [U-13C]glutamate in astrocytes studied by 13C NMR spectroscopy: Incorporation of more label into lactate than into glutamine demonstrates the importance of the TCA cycle. J. Neurochem. 61:1179–1182.
Sonnewald, U., Hertz, L., and Schousboe, A. 1998. Mitochondrial heterogeneity in the brain at the cellular level. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18:231–237.
Qu, H., Færø, E., Jørgensen, P., Dale, O., Gisvold, S. E., Unsgård, G., and Sonnewald, U. 1999. Decreased glutamate metabolism in cultured astrocytes in the presence of thiopental. Biochem. Pharmacol. 58:1075–1080.
Choi, I. Y., Tkac, I., Ugurbil, K., and Gruetter, R. 1999. Noninvasive measurements of [1–13C]glycogen concentrations and metabolism in rat brain in vivo. J. Neurochem. 73:1300–1308.
Brand, M. D. and Chappell, J. B. 1974. Glutamate and aspartate transport in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem. J. 140:205–210.
Martin, D. L. and Rimvall, K. 1993. Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J. Neurochem. 60:395–407.
Waagepetersen, H. S., Sonnewald, U., Gegelashvili, G., Larsson, O. M., and Schousboe, A. 2001. Metabolic distinction between vesicular and cytosolic GABA in cultured GABAergic neurons using 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Neurosci. Res. 63:347–355.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonnewald, U., McKenna, M. Metabolic Compartmentation in Cortical Synaptosomes: Influence of Glucose and Preferential Incorporation of Endogenous Glutamate into GABA. Neurochem Res 27, 43–50 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014846404492
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014846404492