Abstract
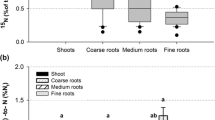
Recycling of plant waste materials from household, gardening and municipal origin to soils is usually done after an intermediate composting step. In this study, as an alternative to composting, direct application of plant wastes has been evaluated in an on-farm experiment by quantifying the contribution to the nitrogen nutrition of winter oilseed rape and assessing the risk of nitrogen immobilisation in soil. Within experimental field plots receiving non-labeled green material, one-square metre subplots received 7.4 Mg ha−1 of 15N-labelled fresh-shredded green material corresponding to 60 kg Nt ha−1. After application and incorporation into the soil in autumn, 0.50% of the total green material nitrogen was recovered in oilseed rape plants at harvest. Mulch application in spring resulted in a recovery of 1.62% of the green material nitrogen applied. Determination of the glutamine content in oilseed rape leaves, sampled at flowering, and CaCl2 extraction of the soil indicated that on the Black Earth Soil there was no temporal nitrogen deficiency of the fertilised crop or nitrogen immobilisation in soil. As a comparison to 15N uptake, 0.0125 M CaCl2 extraction of fresh-shredded green material was assessed as an estimation of the nitrogen contribution from green material to the following crop. This estimate was unsatisfactory for spring application, but was acceptable for autumn application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asche E & Steffens D (1995) Influence of various N fractions on the N supply of biowaste composts. Mitteilgn Dtsch Bodenkundl Gesellsch 76: 725–728
Babel U & Hemmann C (1995) Transport of organic substances in black earths – micro-morphological and other investigations. Mitteilgn Dtsch Bodenkundl Gesellsch 76: 565–568
Biowaste Ordinance (1998) Ordinance on the utilisation of biowaste on soils under agricultural, silvicultural and horticultural use. German Bundestag Decision, August 24, 1998. Draft
Brückner U (1995) Nährstoffgehalte von Komposten: Anwendungsmengen und Verfügbarkeit von Nährstoffen. Kolloquium über die Verwertung von Komposten im Pflanzenbau, HLRL/HLVA, Kassel
Dittert K, Goerges T, Lin S & Sattelmacher B (1998) Nitrogen turnover in soil after application of animal manure and slurry as studied by the stable isotope 15N: a review. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 161: 453–463
Ebertseder T, Gutser R & Claassen N (1994) Parameters for the assessment of the effect of biowaste composts on plant growth. VDLUFA Publ 38: 325–328
Ebertseder T, Popp L & Gutser R (1996) Prediction of the shortterm effect of composts by combined chemical and biological parameters. 108th VDLUFA Conference, Trier, Germany EU Council Directive 1999/31/EC (1999) Directive on the landfill of waste, 16/04/1999 Official Journal L 182, 16/07/1999: 1–19
Fischer P (1992) Kompostierung und Kompostverwendung zur Bodenverbesserung und Düngung im Produktionsgartenbau und Garten-und Landschaftsbau. In: Symposium Proceedings 'Perspektiven der biologischen Abfallbehandlung'. Saarbrücken: German Ministry of Environment, Nature Protection and Nuclear Energy Security
Fricke K & Vogtmann H (1994) Compost quality: physical characteristics, nutrient content, heavy metals and organic chemicals. Toxicol Env Chem 43: 95–114
Fritter A, Atkinson D, Read D & Usher M (1985) Ecological interactions in soil, plants, microbes and animals. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific
Gerendás J & Sattelmacher B (1997) Significance of Ni supply for growth, urease activity and the concentrations of urea, amino acids and mineral nutrients of urea-grown plants. Plant Soil 190: 153–162
German Classification Agency for Compost [Bundesgütegemeinschaft Kompost e.V.] (1994) Methodenbuch zur Analyse von Kompost. Abfall Now e.V. Verlag, Stuttgart
Goerges T & Dittert K (1998) Improved diffusion technique for 15N:14N analysis of ammonium and nitrate from aqueous samples by stable isotope spectrometry. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29: 361–368
Harada T, Takaki H & Yamada Y (1968) Effect of nitrogen sources on the chemical components of young plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 14: 47–55.
Helm M (1995) Prozeßführung bei der Kompostierung von organischen Reststoffen aus Haushalten. KTBL Publ No 371, Darmstadt: KTBL
Houba VJD, Novozamsky I, Lexmond TM & Lee JJ (1990) Applicability of 0.01 M CaCl2 as a single extraction solution for the assessment of the nutrient status of soils and other diagnostic purposes. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 21: 2281–2290
Hüseyin S (1993) Einfluß einer langjährigen Anwendung von Müllkompost auf die chemischen und physikalischen Bodeneigenschaften sowie den Ertrag einer ackerbaulich genutzten Fläche. Dissertation, Gießen University
Iglesias-Jimenez E & Perez-Garcia V (1989) Evaluation of city refuse compost maturity. A review. Biol Wastes 27: 35–62
Jenkinson DS, Fox RH & Rayner JH (1985) Interactions between fertilizer nitrogen and soil nitrogen – the so-called 'priming' effect. J Soil Sci 36: 425–444
Kehres B (1991) Zur Qualität von Kompost aus unterschiedlichen Ausgangsstoffen. Dissertation Gesamthochschule Kassel-Witzenhausen
Müller-Westermeier G (1996) Climatic data of Germany – 1961– 1990. Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach
Novozamsky J, Houba VJG & van Eck R (1983) A novel digestion technique for multielement plant analysis. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 14: 239–249
Poletschny H (1992) Kompostverwertung aus Sicht des Verbandes Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs-und Forschungsanstalten (VDLUFA). In: Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit (ed.) Perspektiven der biologischen Abfallbehandlung. Bonn: BMU
Raven JA & Smith FA (1976) Nitrogen assimilation and transport in the vascular land plants in relation to intracellular pH regulation. New Phytol 76: 415–431
Scherer H, Werner W & Neumann A (1996) N mobilization and N immobilization of composts from different resources, differing in degree of decomposition and C/N ratio. Agribiol Res 49: 120–129
Schjørring JK, Bock JGH, Gammelvind L, Jensen CR & Mogensen VO (1995) Nitrogen incorporation and remobilization in different shoot components of field-grown winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) as affected by rate of nitrogen application and irrigation. Plant Soil 177: 255–264
Siebert S, Leifeld J & Kögel-Knabner I (1998) Nitrogen mineralization of biowaste compost with different maturity after application on arable and recultivated soils. Z Kulturtech Landentw 39: 69–74
VDLUFA (1991) Manual of methods I. Darmstadt: Verband Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs-und Forschungsanstalten
Velthof GL, van Beusichem M, Raijmakers WMF & Janssen BH (1998) Relationship between availability indices and plant uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus from organic products. Plant Soil 200: 215–226
Walker CD, Graham RD, Madison JT, Cary EE & Welch RM (1985) Effects of nickel deficiency on some nitrogen metabolites in cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata L.Welp). Plant Physiol 79: 474–479
Wintzer D, Leible L, Roesch C, Braeutigam R, Fuerniss B & Sardemann G (1996) Wege zur umweltverträglichen Verwertung organischer Abfälle. Abfallwirtschaft in Forschung und Praxis 97: 127–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coester, M., Dittert, K. & Sattelmacher, B. Contribution of fresh-shredded green material to the nitrogen nutrition of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) on a Black Earth Soil (Stagnic Phaeozem). Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 59, 259–267 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014497923599
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014497923599